
A DNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that transfects a specific antigen-coding DNA sequence into the cells of an organism as a mechanism to induce an immune response.

Peptide nucleic acid (PNA) is an artificially synthesized polymer similar to DNA or RNA.
Oligonucleotides are short DNA or RNA molecules, oligomers, that have a wide range of applications in genetic testing, research, and forensics. Commonly made in the laboratory by solid-phase chemical synthesis, these small fragments of nucleic acids can be manufactured as single-stranded molecules with any user-specified sequence, and so are vital for artificial gene synthesis, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), DNA sequencing, molecular cloning and as molecular probes. In nature, oligonucleotides are usually found as small RNA molecules that function in the regulation of gene expression, or are degradation intermediates derived from the breakdown of larger nucleic acid molecules.
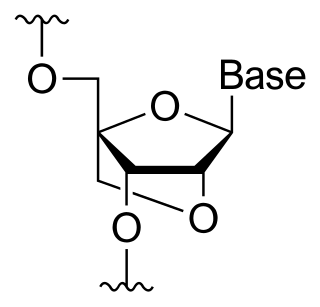
A locked nucleic acid (LNA), also known as bridged nucleic acid (BNA), and often referred to as inaccessible RNA, is a modified RNA nucleotide in which the ribose moiety is modified with an extra bridge connecting the 2' oxygen and 4' carbon. The bridge "locks" the ribose in the 3'-endo (North) conformation, which is often found in the A-form duplexes. This structure provides for increased stability against enzymatic degradation. LNA also offers improved specificity and affinity in base-pairing as a monomer or a constituent of an oligonucleotide. LNA nucleotides can be mixed with DNA or RNA residues in a oligonucleotide.
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are small molecular motifs conserved within a class of microbes, but not present in the host. They are recognized by toll-like receptors (TLRs) and other pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) in both plants and animals. This allows the innate immune system to recognize pathogens and thus, protect the host from infection.

Methylation specific oligonucleotide microarray, also known as MSO microarray, was developed as a technique to map epigenetic methylation changes in DNA of cancer cells.
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) are a rare type of immune cell that are known to secrete large quantities of type 1 interferon (IFNs) in response to a viral infection. They circulate in the blood and are found in peripheral lymphoid organs. They develop from bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells and constitute < 0.4% of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). Other than conducting antiviral mechanisms, pDCs are considered to be key in linking the innate and adaptive immune systems. However, pDCs are also responsible for participating in and exacerbating certain autoimmune diseases like lupus. pDCs that undergo malignant transformation cause a rare hematologic disorder, blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm.
In immunology, an adjuvant is a substance that increases or modulates the immune response to a vaccine. The word "adjuvant" comes from the Latin word adiuvare, meaning to help or aid. "An immunologic adjuvant is defined as any substance that acts to accelerate, prolong, or enhance antigen-specific immune responses when used in combination with specific vaccine antigens."
Oligonucleotide synthesis is the chemical synthesis of relatively short fragments of nucleic acids with defined chemical structure (sequence). The technique is extremely useful in current laboratory practice because it provides a rapid and inexpensive access to custom-made oligonucleotides of the desired sequence. Whereas enzymes synthesize DNA and RNA only in a 5' to 3' direction, chemical oligonucleotide synthesis does not have this limitation, although it is most often carried out in the opposite, 3' to 5' direction. Currently, the process is implemented as solid-phase synthesis using phosphoramidite method and phosphoramidite building blocks derived from protected 2'-deoxynucleosides, ribonucleosides, or chemically modified nucleosides, e.g. LNA or BNA.

Transcription factor 4 (TCF-4) also known as immunoglobulin transcription factor 2 (ITF-2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TCF4 gene located on chromosome 18q21.2.

Toll-like receptor 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TLR9 gene. TLR9 has also been designated as CD289. It is a member of the toll-like receptor (TLR) family. TLR9 is an important receptor expressed in immune system cells including dendritic cells, macrophages, natural killer cells, and other antigen presenting cells. TLR9 is expressed on endosomes internalized from the plasma membrane, binds DNA, and triggers signaling cascades that lead to a pro-inflammatory cytokine response. Cancer, infection, and tissue damage can all modulate TLR9 expression and activation. TLR9 is also an important factor in autoimmune diseases, and there is active research into synthetic TLR9 agonists and antagonists that help regulate autoimmune inflammation.

Lymphocyte-activation gene 3, also known as LAG-3, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the LAG3 gene. LAG3, which was discovered in 1990 and was designated CD223 after the Seventh Human Leucocyte Differentiation Antigen Workshop in 2000, is a cell surface molecule with diverse biological effects on T cell function but overall has an immune inhibitory effect. It is an immune checkpoint receptor and as such is the target of various drug development programs by pharmaceutical companies seeking to develop new treatments for cancer and autoimmune disorders. In soluble form it is also being developed as a cancer drug in its own right.

A computational gene is a molecular automaton consisting of a structural part and a functional part; and its design is such that it might work in a cellular environment.

Gunther Hartmann is a German immunologist and clinical pharmacologist. Since 2007 he has been the Director of the Institute of Clinical Chemistry and Clinical Pharmacology at the University Hospital of the University of Bonn.

Afovirsen is an oligonucleotide capable of antisense interactions with mRNA of human papillomavirus. It has been investigated as a tool for diagnostics and therapeutics.
A hybridization assay comprises any form of quantifiable hybridization i.e. the quantitative annealing of two complementary strands of nucleic acids, known as nucleic acid hybridization.
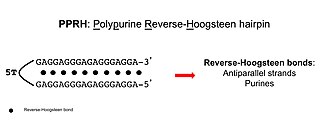
Polypurine reverse-Hoogsteen hairpins (PPRHs) are non-modified oligonucleotides containing two polypurine domains, in a mirror repeat fashion, linked by a pentathymidine stretch forming double-stranded DNA stem-loop molecules. The two polypurine domains interact by intramolecular reverse-Hoogsteen bonds allowing the formation of this specific hairpin structure.
i-motif DNA, short for intercalated-motif DNA, are cytosine-rich four-stranded quadruplex DNA structures, similar to the G-quadruplex structures that are formed in guanine-rich regions of DNA.

Dipyaman Ganguly is an Indian physician-scientist immunologist and cell biologist, currently a Principal Scientist and Swarnajayanthi Fellow at the CSIR-Indian Institute of Chemical Biology (IICB). He heads the Dendritic Cell Laboratory of IICB, popularly known as the Ganguly Lab, where he hosts several researchers involved in research on regulation of innate Immunity and pathogenesis of inflammatory disorders. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for his contributions to Medical Sciences in 2022.
Gapmers are short DNA antisense oligonucleotide structures with RNA-like segments on both sides of the sequence. These linear pieces of genetic information are designed to hybridize to a target piece of RNA and silence the gene through the induction of RNase H cleavage. Binding of the gapmer to the target has a higher affinity due to the modified RNA flanking regions, as well as resistance to degradation by nucleases. Gapmers are currently being developed as therapeutics for a variety of cancers, viruses, and other chronic genetic disorders.












