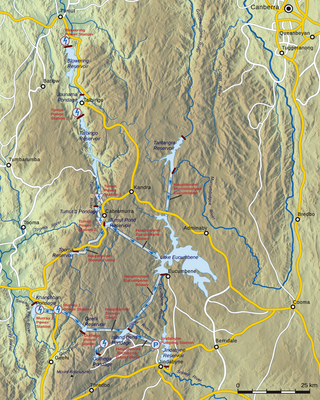
The Snowy Mountains Scheme, also known as the Snowy Hydro or the Snowy scheme, is a hydroelectricity and irrigation complex in south-east Australia. Near the border of New South Wales and Victoria, the scheme consists of sixteen major dams; nine power stations; two pumping stations; and 225 kilometres (140 mi) of tunnels, pipelines and aqueducts that were constructed between 1949 and 1974. The Scheme was completed under the supervision of Chief Engineer, Sir William Hudson. It is the largest engineering project undertaken in Australia.

The Elan Valley Reservoirs are a chain of man-made lakes created from damming the Elan and Claerwen rivers within the Elan Valley in Mid Wales. The reservoirs, which were built by the Birmingham Corporation Water Department, provide clean drinking water for Birmingham in the West Midlands of England. The five lakes are known as the Claerwen, Craig-goch, Pen-y-garreg, Garreg-ddu, and Caban-coch.

Warragamba Dam is a heritage-listed dam in the outer South Western Sydney suburb of Warragamba, Wollondilly Shire in New South Wales, Australia. It is a concrete gravity dam, which creates Lake Burragorang, the primary reservoir for water supply for the city of Sydney. The dam wall is located approximately 65 kilometres (40 mi) W of Sydney central business district, 4½ km SW of the town of Wallacia, and 1 km NW of the village of Warragamba.

Kielder Water is a large man-made reservoir in Northumberland in North East England. It is the largest artificial lake in the United Kingdom by capacity of water and it is surrounded by Kielder Forest, one of the biggest man-made woodlands in Europe. The scheme was planned in the late 1960s to satisfy an expected rise in demand for water to support a booming UK industrial economy.

Rhayader is a market town and community in Powys, Wales, within the historic county of Radnorshire. The town is 20 miles (32 km) from the source of the River Wye on Plynlimon, the highest point of the Cambrian Mountains, and is located at the junction of the A470 road and the A44 road 13 miles (21 km) north of Builth Wells and 30 miles (48 km) east of Aberystwyth.

A reservoir is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, usually built to store fresh water, or it may be a natural formation.

The Upper Nepean Scheme is a series of dams and weirs in the catchments of the Cataract, Cordeaux, Avon and Nepean rivers of New South Wales, Australia. The scheme includes four dams and two weirs, and a gravity-fed canal system that feeds into a large storage reservoir to provide water to the Macarthur and Illawarra regions, the Wollondilly Shire, and metropolitan Sydney. The four dams and associated infrastructure are individually listed on the New South Wales State Heritage Register.
The Shoalhaven Scheme is a dual-purpose water supply and Pumped-storage Hydroelectricity scheme located on the South Coast region of New South Wales, Australia.

The Tumut Hydroelectric Power Stations is a series of three hydroelectric power stations on the Tumut River in New South Wales, Australia, that are part of the Snowy Mountains Scheme.

Chichester Dam is a minor concrete gravity dam across the Chichester and Wangat rivers, upstream of Dungog, in the Hunter Region of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's main purpose is water supply for the Lower Hunter region. A mini hydro-electric power station operates at times of peak flow and is connected to the national grid. The impounded reservoir is Lake Chichester.
The Elan Valley Railway (EVR) was a Welsh industrial railway built to assist in the construction of the Elan Valley Reservoirs in mid Wales. It was in operation from 1896 to about 1912/1916.

The Birmingham Corporation Water Department was responsible for the supply of water to Birmingham, England, from 1876 to 1974. It was also known as Birmingham Corporation Waterworks Department.

Elan Village is a small purpose-built community in Powys, Wales. It was designed by architect Herbert Tudor Buckland as part of Birmingham Corporation's scheme to construct a series of water supply reservoirs in the Elan Valley between 1892 and 1904. It housed workers and their families responsible for maintaining the scheme's dams and the filtration systems. Elan Village is the only purpose-built Arts and Crafts "Model Village" in Wales.
The Grand Contour Canal in England and Wales was intended to enhance and upgrade the British canal system, but was never built. This canal was proposed in 1943, and again ten years later, by J F Pownall. Pownall observed that there was a natural 'contour' down the spine of England, around the 300 ft level that connected several of the most populated areas. He put forward the idea that this contour could be used to define the course of a large European sized canal which contained no locks except at its entry and exit points. It would also serve as a water grid capable of distributing domestic water supply around England as need arises.

Elenydd is an upland area of Mid Wales, extending across parts of northern and eastern Ceredigion and Powys between Aberystwyth and Rhayader. Elenydd is also a name given to the medieval commote of Cwmwd Deuddwr which covered approximately the same area.

The Afon Elan is a tributary of the River Wye which runs through the wide expanse of upland moors, traditionally known as Elenydd, in central Wales. Its valley is the Elan Valley. The name probably arises from elain meaning 'hind' or 'fawn' in reference perhaps to the rushing, bounding nature of its course.

Geehi Dam is a major ungated rockfill embankment dam across the Geehi River in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales, Australia. The reservoir impounded by the dam is known as Geehi Reservoir.

Guthega Dam is concrete gravity dam with an uncontrolled spillway across the Snowy River in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's main purpose is for the storage of water used in the generation of hydro-power. It is the first to be completed of the sixteen major dams of the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro.
There are a large number of reservoirs in Wales reflecting the need for the supply of water for both industry and for consumption, both within the country itself and in neighbouring England. A number also provide hydroelectricity and many old reservoirs also provided motive power for industries, especially for the processing of minerals such as metal ores and slate.


















