Related Research Articles

Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble carbonate rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by features like poljes above and drainage systems with sinkholes and caves underground. More weathering-resistant rocks, such as quartzite, can also occur, given the right conditions.

The Pennyroyal Plateau or Pennyroyal Region, often spelled Pennyrile, is a large physiographic region of Kentucky that features rolling hills, caves, and karst topography in general. It is named for Hedeoma pulegioides, a wild mint that grows in the area. It is also called the "Mississippian Plateau," for the Mississippian geologic age in which it was formed.

A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are also known as shakeholes, and to openings where surface water enters into underground passages known as ponor, swallow hole or swallet. A cenote is a type of sinkhole that exposes groundwater underneath. Sink and stream sink are more general terms for sites that drain surface water, possibly by infiltration into sediment or crumbled rock.
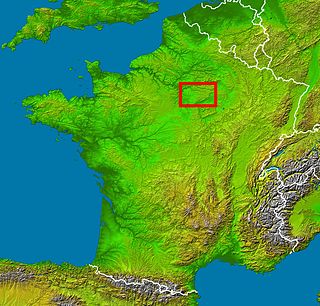
Brie is a historic region of northern France notable in modern times for Brie cheese. It was once divided into three sections ruled by different feudal lords: the western Brie française, corresponding roughly to the modern department of Seine-et-Marne in the Île-de-France region; the eastern Brie champenoise, forming a portion of the modern department of Marne in the historic region of Champagne ; and the northern Brie pouilleuse, forming part of the modern department of Aisne in Picardy.

The Burren is a karst/glaciokarst landscape centred in County Clare, on the west coast of Ireland. It measures around 530 square kilometres (200 sq mi), within the circle made by the villages of Lisdoonvarna, Corofin, Gort and Kinvara. The area includes such natural features as Mullaghmore hill and Ailladie cliffs, and historic monuments such as Poulnabrone dolmen and Caherconnell Stone Fort. The Burren National Park covers a small part of the Burren and is the smallest of the six National Parks in Ireland, while the adjacent territory, including the Cliffs of Moher, is included in the Burren and Cliffs of Moher Geopark.
The Highland Rim is a geographic term for the area in Tennessee, North Alabama, and Kentucky which surrounds the Central Basin. Geologically, the Central Basin is a dome. The Highland Rim is a cuesta surrounding the basin, and the border where the difference in elevation is sharply pronounced is an escarpment.

The Tradewater River is a tributary of the Ohio River, approximately 136 miles (219 km) long, in western Kentucky in the United States. It drains an area of 932 square miles (2,410 km2) in the limestone hills south of Evansville, Indiana, between the basins of the Cumberland River on the west and the Green River on the east.

The Shawnee Hills is a region of southern Illinois that rests mainly in an east-west arc roughly following the outline of the southern end of the Illinois Basin. Whereas Mississippian and Pennsylvania Age rock layers are deep beneath the soil surface in central Illinois, these strata pierce the surface in southern Illinois. The Shawnee Hills are surface expressions of the more weather-resistant limestone and sandstone layers. This formation is due in part to the last glaciation of the Ice Age not reaching this far south.

Bluespring Caverns is a cave system located in Lawrence County, Indiana, approximately 80 miles (128 km) south of Indianapolis. The cave system is a karst and river type cave formation and drains a 15 miles² (38.8 km²) sinkhole plain. The cave contains 21 miles (34 km) of surveyed passages and is most notable for having the longest known subterranean river in the United States with approximately 3 miles (4.8 km) of navigable river.
The Indiana Uplands or the Hoosier Uplands are a geographical region in south-central Indiana. On a topographical map the Indiana Uplands begin slightly north of the city of Martinsville, Indiana and continue south to the Ohio River. The description of the region inspired the name of Upland Brewing Company. The region's approximate boundaries are Interstate 65 to the east and U.S. Route 231 to the west. The Uplands are characterized by terrain varying from rolling hills to cliffs, sharp rugged hills and valleys. Nearly all of these hills are composed of sandstone, limestone, and siltstone from West to east. The siltstone hills are the most rugged followed by the sandstone while the limestone are the smoothest. This is contrast to the Tipton Till Plain immediately to the north in central Indiana, which features flat to gently rolling landscape. Interstates 64 and 69 pass through this rugged section of the state with sections of both cut deep into the rock and others towering over the treetops.

Twin Caves is a pair of cave entrances connected by a short river at the bottom of a sinkhole within the boundaries of Spring Mill State Park in Lawrence County, Indiana. The river is an exposed section of a mostly-underground stream that originates as Mosquito Creek several miles southeast of the park, which sinks into the Upper Twin Cave system. The stream then comes out briefly at Twin Caves, and flows into the Lower Twin Cave, re-emerging briefly at Bronson Cave shortly to the northwest, then flowing into the Shawnee Cave System. The stream finally emerges at the Donaldson Cave entrance as a short tributary of Mill Creek, still within the park.
The Knobstone Escarpment is a rugged geologic region in Southern Indiana. Physically, the Knobstone Escarpment is the most rugged terrain in Indiana. The highest hill in the area is Weed Patch Hill, with an elevation of 1,060 feet above sea level.

Shawswick Township is one of nine townships in Lawrence County, Indiana, United States. As of the 2010 census, its population was 20,469 and it contained 9,653 housing units.

The Stone Forest or Shilin is a notable set of limestone formations about 500 km2 located in Shilin Yi Autonomous County, Yunnan Province, People's Republic of China, near Shilin approximately 90 km (56 mi) from the provincial capital Kunming.
The Lost River is a river that rises in Vernon Township, Washington County, Indiana, and discharges into the East Fork of the White River in Lost River Township, Martin County, Indiana. The river's unusual hydrology has led to two of its features being named as National Natural Landmarks.
The Mitchell Plain is a karst area in Indiana of relatively low relief. The extensive underlying cave system developed in Mississippian age limestone bedrock. Surface drainage is rare due to most streams in the area disappearing into caves or joints within the rock.
The Ozark Highlands is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in four U.S. states. Most of the region is within Missouri, with a part in Arkansas and small sections in Oklahoma and Kansas. It is the largest subdivision of the region known as the Ozark Mountains, less rugged in comparison to the Boston Mountains in Arkansas, the highest part of the Ozarks.

Clear Creek is an American creek in Monroe County, Indiana. Flowing in the general south-western and southern direction, it is a tributary of Salt Creek, which in its turn flows into the East Fork of Indiana's White River.
The Marengo warehouse and distribution center is a subterranean storage facility located in Marengo, Indiana, located about 35 miles northwest of Louisville, Kentucky. It is one of the largest underground storage facilities in the United States.

Cedar Sink is a vertical-walled large depression, or sinkhole, in the ground, that is located in Edmonson County, Kentucky and contained within and managed by Mammoth Cave National Park. The sinkhole measures 300 feet (91.4 m) from the top sandstone plateau to the bottom of the sink and was caused by collapse of the surface soil. The landscape is karst topography, which means the region is influenced by the dissolution of soluble rocks. Sinkholes, caves, and dolines typically characterize these underground drainage systems. Cedar Sink has a bottom area of about 7 acres (2.8 ha) and has more fertile soil compared to the ridgetops.
References
- ↑ "Landscapes of Indiana".
- ↑ Lakey, B., Krothe, N.C. (1996). Stable isotopic variation of storm discharge from a perennial karst spring, Indiana. Water Resources Research 32(3), 721-731