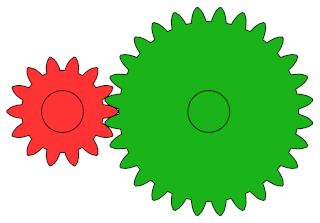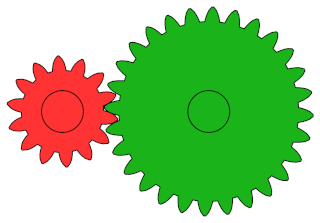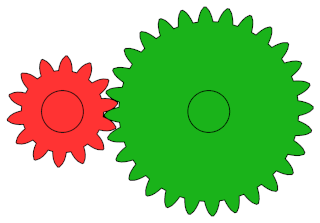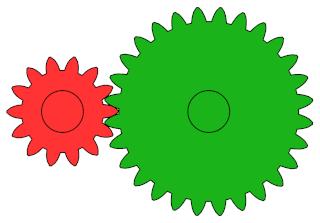
A gear or gearwheel is a rotating machine part typically used to transmit rotational motion and/or torque by means of a series of teeth that engage with compatible teeth of another gear or other part. The teeth can be integral saliences or cavities machined on the part, or separate pegs inserted into it. In the latter case, the gear is usually called a cogwheel. A cog may be one of those pegs or the whole gear. Two or more meshing gears are called a gear train.

Astrophotography, also known as astronomical imaging, is the photography or imaging of astronomical objects, celestial events, or areas of the night sky. The first photograph of an astronomical object was taken in 1840, but it was not until the late 19th century that advances in technology allowed for detailed stellar photography. Besides being able to record the details of extended objects such as the Moon, Sun, and planets, modern astrophotography has the ability to image objects outside of the visible spectrum of the human eye such as dim stars, nebulae, and galaxies. This is accomplished through long time exposure as both film and digital cameras can accumulate and sum photons over long periods of time or using specialized optical filters which limit the photons to a certain wavelength.

A rack railway is a steep grade railway with a toothed rack rail, usually between the running rails. The trains are fitted with one or more cog wheels or pinions that mesh with this rack rail. This allows the trains to operate on steep gradients of 100% or more, well above the 10% maximum for friction-based rail. The rack and pinion mechanism also provides more controlled braking and reduces the effects of snow or ice on the rails. Most rack railways are mountain railways, although a few are transit railways or tramways built to overcome a steep gradient in an urban environment. The first cog railway was the Middleton Railway between Middleton and Leeds in West Yorkshire, England, United Kingdom, where the first commercially successful steam locomotive, Salamanca, ran in 1812. This used a rack and pinion system designed and patented in 1811 by John Blenkinsop.

A Dobsonian telescope is an altazimuth-mounted Newtonian telescope design popularized by John Dobson in 1965 and credited with vastly increasing the size of telescopes available to amateur astronomers. Dobson's telescopes featured a simplified mechanical design that was easy to manufacture from readily available components to create a large, portable, low-cost telescope. The design is optimized for observing faint deep-sky objects such as nebulae and galaxies. This type of observation requires a large objective diameter of relatively short focal length and portability for travel to less light-polluted locations.

A ratchet is a mechanical device that allows continuous linear or rotary motion in only one direction while preventing motion in the opposite direction. Ratchets are widely used in machinery and tools. The word ratchet is also used informally to refer to a ratcheting socket wrench.

An eyepiece, or ocular lens, is a type of lens that is attached to a variety of optical devices such as telescopes and microscopes. It is named because it is usually the lens that is closest to the eye when someone looks through an optical device to observe an object or sample. The objective lens or mirror collects light from an object or sample and brings it to focus creating an image of the object. The eyepiece is placed near the focal point of the objective to magnify this image to the eyes. The amount of magnification depends on the focal length of the eyepiece.

Digiscoping is a neologism for afocal photography, using a (digital) camera to record distant images through the eyepiece of an optical telescope.
An interference fit, also known as a pressed fit or friction fit, is a form of fastening between two tightfitting mating parts that produces a joint which is held together by friction after the parts are pushed together.
This is an alphabetical list of articles pertaining specifically to mechanical engineering. For a broad overview of engineering, please see List of engineering topics. For biographies please see List of engineers.

Leviathan of Parsonstown, or Rosse six-foot telescope, is a historic reflecting telescope of 72 inches (1.83 m) aperture, which was the largest telescope in the world from 1845 until the construction of the 100-inch (2.5 m) Hooker Telescope in California in 1917. The Rosse six-foot telescope was built by William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse on his estate, Birr Castle, at Parsonstown in Ireland.
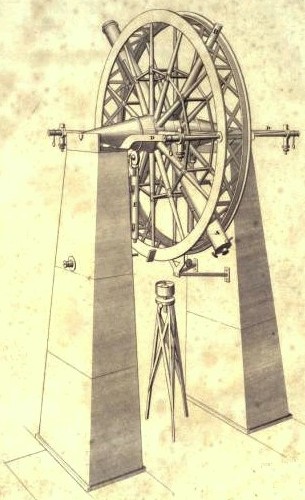
The meridian circle is an instrument for timing of the passage of stars across the local meridian, an event known as a culmination, while at the same time measuring their angular distance from the nadir. These are special purpose telescopes mounted so as to allow pointing only in the meridian, the great circle through the north point of the horizon, the north celestial pole, the zenith, the south point of the horizon, the south celestial pole, and the nadir. Meridian telescopes rely on the rotation of the sky to bring objects into their field of view and are mounted on a fixed, horizontal, east–west axis.
A linear-motion bearing or linear slide is a bearing designed to provide free motion in one direction. There are many different types of linear motion bearings.

In an automobile, ball joints are spherical bearings that connect the control arms to the steering knuckles, and are used on virtually every automobile made. They bionically resemble the ball-and-socket joints found in most tetrapod animals.

A ball screw is a mechanical linear actuator that translates rotational motion to linear motion with little friction. A threaded shaft provides a helical raceway for ball bearings which act as a precision screw. As well as being able to apply or withstand high thrust loads, they can do so with minimum internal friction. They are made to close tolerances and are therefore suitable for high-precision applications. The ball assembly acts as the nut while the threaded shaft is the screw.

A reduction drive is a mechanical device to shift rotational speed. A planetary reduction drive is a small scale version using ball bearings in an epicyclic arrangement instead of toothed gears.
Questar Corporation is a company based in New Hope, Pennsylvania. It manufactures precision optical devices for consumer, industrial, aerospace, and military markets. Its telescopes produced for the consumer market are sold under the brand name "Questar".

The Dual speed focuser is a focusing mechanism used in precision optics such as advanced amateur astronomical telescopes and laboratory microscopes.

The yaw bearing is the most crucial and cost intensive component of a yaw system found on modern horizontal axis wind turbines. The yaw bearing must cope with enormous static and dynamic loads and moments during the wind turbine operation, and provide smooth rotation characteristics for the orientation of the nacelle under all weather conditions. It has also to be corrosion and wear resistant and extremely long lasting. It should last for the service life of the wind turbine) while being cost effective.

Afocal photography, also called afocal imaging or afocal projection is a method of photography where the camera with its lens attached is mounted over the eyepiece of another image forming system such as an optical telescope or optical microscope, with the camera lens taking the place of the human eye.

John Wall was an English design engineer, amateur astronomer, amateur telescope maker and member of the British Astronomical Association. He lived in Coventry, England.






















