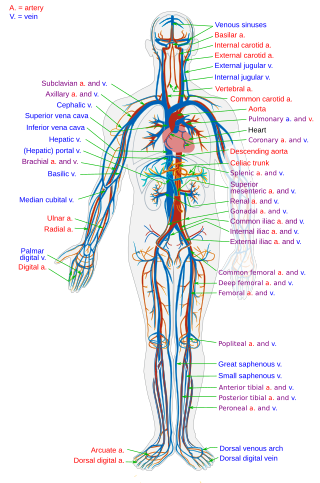
The circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels. The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms cardiovascular system and vascular system interchangeably with circulatory system.

Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the arteries and veins that supply the heart muscle (myocardium). Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. Cardiac veins then drain away the blood after it has been deoxygenated. Because the rest of the body, and most especially the brain, needs a steady supply of oxygenated blood that is free of all but the slightest interruptions, the heart is required to function continuously. Therefore its circulation is of major importance not only to its own tissues but to the entire body and even the level of consciousness of the brain from moment to moment. Interruptions of coronary circulation quickly cause heart attacks, in which the heart muscle is damaged by oxygen starvation. Such interruptions are usually caused by coronary ischemia linked to coronary artery disease, and sometimes to embolism from other causes like obstruction in blood flow through vessels.

The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra.

Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a medical condition in which the ductus arteriosus fails to close after birth: this allows a portion of oxygenated blood from the left heart to flow back to the lungs through the aorta, which has a higher blood pressure, to the pulmonary artery, which has a lower blood pressure. Symptoms are uncommon at birth and shortly thereafter, but later in the first year of life there is often the onset of an increased work of breathing and failure to gain weight at a normal rate. With time, an uncorrected PDA usually leads to pulmonary hypertension followed by right-sided heart failure.

The umbilical vein is a vein present during fetal development that carries oxygenated blood from the placenta into the growing fetus. The umbilical vein provides convenient access to the central circulation of a neonate for restoration of blood volume and for administration of glucose and drugs.
At the end of pregnancy, the fetus must take the journey of childbirth to leave the reproductive mother. Upon its entry to the air-breathing world, the newborn must begin to adjust to life outside the uterus. This is true for all viviparous animals; this article discusses humans as the most-researched example.

The atrium is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves.

In the fetus, the ductus venosus shunts a portion of umbilical vein blood flow directly to the inferior vena cava. Thus, it allows oxygenated blood from the placenta to bypass the liver. Compared to the 50% shunting of umbilical blood through the ductus venosus found in animal experiments, the degree of shunting in the human fetus under physiological conditions is considerably less, 30% at 20 weeks, which decreases to 18% at 32 weeks, suggesting a higher priority of the fetal liver than previously realized. In conjunction with the other fetal shunts, the foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus, it plays a critical role in preferentially shunting oxygenated blood to the fetal brain. It is a part of fetal circulation.

Tricuspid atresia is a form of congenital heart disease whereby there is a complete absence of the tricuspid valve. Therefore, there is an absence of right atrioventricular connection. This leads to a hypoplastic (undersized) or absent right ventricle. This defect occurs during prenatal development, when the heart does not finish developing. It causes the systemic circulation to be filled with relatively deoxygenated blood. The causes of tricuspid atresia are unknown.

The fossa ovalis is a depression in the right atrium of the heart, at the level of the interatrial septum, the wall between right and left atrium. The fossa ovalis is the remnant of a thin fibrous sheet that covered the foramen ovale during fetal development.
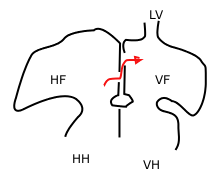
In the fetal heart, the foramen ovale, also foramen Botalli or the ostium secundum of Born, allows blood to enter the left atrium from the right atrium. It is one of two fetal cardiac shunts, the other being the ductus arteriosus. Another similar adaptation in the fetus is the ductus venosus. In most individuals, the foramen ovale closes at birth. It later forms the fossa ovalis.
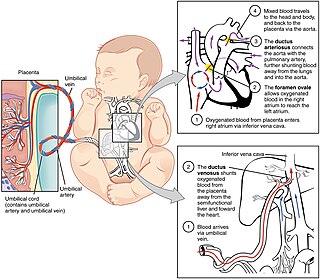
In humans, the circulatory system is different before and after birth. The fetal circulation is composed of the placenta, umbilical blood vessels encapsulated by the umbilical cord, heart and systemic blood vessels. A major difference between the fetal circulation and postnatal circulation is that the lungs are not used during the fetal stage resulting in the presence of shunts to move oxygenated blood and nutrients from the placenta to the fetal tissue. At birth, the start of breathing and the severance of the umbilical cord prompt various changes that quickly transform fetal circulation into postnatal circulation.

The sinus venosus is a large quadrangular cavity which precedes the atrium on the venous side of the chordate heart.

The crista terminalis is a vertical ridge on the posterolateral inner surface of the adult right atrium extending between the superior vena cava, and the inferior vena cava. The crista terminalis denotes where the junction of the embryologic sinus venosus and the right atrium occurred during embryonic development. It forms a boundary between the rough trabecular portion and the smooth, sinus venosus-derived portion of the internal surface of the right atrium. The sinoatrial node is located within the crista terminalis.

The valve of the inferior vena cava is a venous valve that lies at the junction of the inferior vena cava and right atrium.
A fetus or foetus is the unborn mammalian offspring that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Prenatal development is a continuum, with no clear defining feature distinguishing an embryo from a fetus. However, in general a fetus is characterized by the presence of all the major body organs, though they will not yet be fully developed and functional, and some may not yet be situated in their final anatomical location.

Hypoplastic right heart syndrome (HRHS) is a congenital heart defect in which the structures on the right side of the heart, particularly the right ventricle, are underdeveloped. This defect causes inadequate blood flow to the lungs, and thus a cyanotic infant.

In anatomy, the venae cavae are two large veins that return deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart. In humans they are the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava, and both empty into the right atrium. They are located slightly off-center, toward the right side of the body.

Heart development, also known as cardiogenesis, refers to the prenatal development of the heart. This begins with the formation of two endocardial tubes which merge to form the tubular heart, also called the primitive heart tube. The heart is the first functional organ in vertebrate embryos.
The heart is a muscular organ situated in the mediastinum. It consists of four chambers, four valves, two main arteries, and the conduction system. The left and right sides of the heart have different functions: the right side receives de-oxygenated blood through the superior and inferior venae cavae and pumps blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery, and the left side receives saturated blood from the lungs.











