
Systolic heart murmurs are heart murmurs heard during systole, [1] [2] [3] i.e. they begin and end between S1 and S2. Many involve stenosis of the semilunar valves or regurgitation of the atrioventricular valves.

Systolic heart murmurs are heart murmurs heard during systole, [1] [2] [3] i.e. they begin and end between S1 and S2. Many involve stenosis of the semilunar valves or regurgitation of the atrioventricular valves.
| Time | Condition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mid-systolic ejection | Aortic outflow obstruction (Aortic stenosis) | Can be due to aortic valve stenosis or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), with a harsh and rough quality. ** Valvular aortic stenosis can produce a harsh, or even a musical murmur over the right second intercostal space which radiates into the neck over the two carotid arteries. The most common cause of AS (Aortic stenosis) is calcified valves due to aging. The second most common cause is congenital bicuspid aortic valves (normal valve is tricuspid). In aortic stenosis, heaving apical impulse is present. The distinguishing feature between these two causes is that bicuspid AS has little or no radiation. It can be confirmed if it also has an aortic ejection sound, a short early diastolic murmur, and normal carotid pulse. The murmur in valvular AS decreases with standing and straining with Valsalva maneuver. ** Supravalvular aortic stenosis is loudest at a point slightly higher than in that of valvular AS and may radiate more to the right carotid artery. ** Subvalvular aortic stenosis is usually due to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), with murmur loudest over the left sternal border or the apex. The murmur in HCM increases in intensity with a standing position as well as straining with Valsalva maneuver. |
| Mid-systolic ejection | Pulmonic outflow obstruction (Pulmonic stenosis) | A harsh murmur usually on left second intercostal space radiating to left neck and accompanied by palpable thrill. It can be distinguished from a VSD (ventricular septal defect) by listening to the S2, which is normal in VSD but it is widely split in pulmonary stenosis. However, VSD is almost always pansystolic where the murmur of pulmonary stenosis is diamond-shaped and ends clearly before S2. Many innocent murmurs also arise from this location but S1 and S2 must split normally. |
| Mid-systolic ejection | Dilation of aortic root or pulmonary artery | Produces an ejection sound, with a short ejection systolic murmur and a relatively wide split S2. There is no hemodynamic abnormality. This is similar to pulmonary hypertension except the latter has hemodynamic instabilities. |
| Mid-systolic ejection | Increased semilunar blood flow | This can occur in situations such as anemia, pregnancy, or hyperthyroidism. |
| Mid-systolic ejection | Aortic valve sclerosis | This is due to degenerative thickening of the roots of the aortic cusps but produces no obstruction and no hemodynamic instability and thus should be differentiated from aortic stenosis. It is heard over right second intercostal space with a normal carotid pulse and normal S2. |
| Mid-systolic ejection | Innocent midsystolic murmurs | These murmurs are not accompanied by other abnormal findings. One example of a benign paediatric heart murmur is Still's murmur in children. |
| Time | Condition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Late systolic | Mitral valve prolapse | This is the most common cause of late systolic murmurs. It can be heard best over the apex of the heart, usually preceded by clicks. The most common cause of mitral valve prolapse is "floppy" valve (Barlow's) syndrome. If the prolapse becomes severe enough, mitral regurgitation may occur. Any maneuver that decreases left ventricular volume — such as standing, sitting, Valsalva maneuver, and amyl nitrate inhalation — can produce earlier onset of clicks, longer murmur duration, and decreased murmur intensity. Any maneuver that increases left ventricular volume — such as squatting, elevation of legs, hand grip, and phenylephrine — can delay the onset of clicks, shorten murmur duration, and increase murmur intensity. |
| Late systolic | Tricuspid valve prolapse | Uncommon without concomitant mitral valve prolapse. Best heard over left lower sternal border. |
| Late systolic | Papillary muscle dysfunction | Usually due to acute myocardial infarction or ischemia, which causes mild mitral regurgitation. |
| Time | Condition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Holosystolic (pansystolic) | Tricuspid regurgitation | Intensifies upon inspiration. Can be best heard over the fourth left sternal border. The intensity can be accentuated following inspiration (Carvallo's sign) due to increased regurgitant flow in right ventricular volume. Tricuspid regurgitation is most often secondary to pulmonary hypertension. Primary tricuspid regurgitation is less common and can be due to bacterial endocarditis following IV drug use, Ebstein's anomaly, carcinoid disease, or prior right ventricular infarction. |
| Holosystolic (pansystolic) | Mitral regurgitation or MR | No intensification upon inspiration. In the presence of incompetent mitral valve, the pressure in the L ventricle becomes greater than that in the L atrium at the onset of isovolumic contraction, which corresponds to the closing of the mitral valve (S1). This explains why the murmur in MR starts at the same time as S1. This difference in pressure extends throughout systole and can even continue after the aortic valve has closed, explaining how it can sometimes drown the sound of S2. The murmur in MR is high pitched and best heard at the apex with diaphragm of the stethoscope with patient in the lateral decubitus position. Left ventricular function can be assessed by determining the apical impulse. A normal or hyperdynamic apical impulse suggests good ejection fraction and primary MR. A displaced and sustained apical impulse suggests decreased ejection fraction and chronic and severe MR. This type of murmur is known as the Castex Murmur. |
| Holosystolic (pansystolic) | Ventricular septal defect | No intensification upon inspiration. VSD is a defect in the ventricular wall, producing a shunt between the left and right ventricles. Since the L ventricle has a higher pressure than the R ventricle, flow during systole occurs from the L to R ventricle, producing the holosystolic murmur. It can be best heard over the left third and fourth intercostal spaces and along the sternal border. It is associated with normal pulmonary artery pressure and thus S2 is normal. This fact can be used to distinguish from pulmonary stenosis, which has a wide splitting S2. When the shunt becomes reversed ("Eisenmenger syndrome"), the murmur may be absent and S2 can become markedly accentuated and single. |

A heart valve is a one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. Four valves are usually present in a mammalian heart and together they determine the pathway of blood flow through the heart. A heart valve opens or closes according to differential blood pressure on each side.

Heart sounds are the noises generated by the beating heart and the resultant flow of blood through it. Specifically, the sounds reflect the turbulence created when the heart valves snap shut. In cardiac auscultation, an examiner may use a stethoscope to listen for these unique and distinct sounds that provide important auditory data regarding the condition of the heart.

The mitral valve, also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two cusps or flaps and lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle of the heart. The heart valves are all one-way valves allowing blood flow in just one direction. The mitral valve and the tricuspid valve are known as the atrioventricular valves because they lie between the atria and the ventricles.

Heart murmurs are unique heart sounds produced when blood flows across a heart valve or blood vessel. This occurs when turbulent blood flow creates a sound loud enough to hear with a stethoscope. Turbulent blood flow is not smooth. The sound differs from normal heart sounds by their characteristics. For example, heart murmurs may have a distinct pitch, duration and timing. The major way health care providers examine the heart on physical exam is heart auscultation; another clinical technique is palpation, which can detect by touch when such turbulence causes the vibrations called cardiac thrill. A murmur is a sign found during the cardiac exam. Murmurs are of various types and are important in the detection of cardiac and valvular pathologies.

Systole is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. The term originates, via New Latin, from Ancient Greek συστολή (sustolē), from συστέλλειν, and is similar to the use of the English term to squeeze.

Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a valvular heart disease characterized by the displacement of an abnormally thickened mitral valve leaflet into the left atrium during systole. It is the primary form of myxomatous degeneration of the valve. There are various types of MVP, broadly classified as classic and nonclassic. In severe cases of classic MVP, complications include mitral regurgitation, infective endocarditis, congestive heart failure, and, in rare circumstances, cardiac arrest.

Diastole is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are re-filling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventricular diastole the relaxing of the ventricles.

Mitral stenosis is a valvular heart disease characterized by the narrowing of the opening of the mitral valve of the heart. It is almost always caused by rheumatic valvular heart disease. Normally, the mitral valve is about 5 cm2 during diastole. Any decrease in area below 2 cm2 causes mitral stenosis. Early diagnosis of mitral stenosis in pregnancy is very important as the heart cannot tolerate increased cardiac output demand as in the case of exercise and pregnancy. Atrial fibrillation is a common complication of resulting left atrial enlargement, which can lead to systemic thromboembolic complications like stroke.

Aortic regurgitation (AR), also known as aortic insufficiency (AI), is the leaking of the aortic valve of the heart that causes blood to flow in the reverse direction during ventricular diastole, from the aorta into the left ventricle. As a consequence, the cardiac muscle is forced to work harder than normal.
A stenosis is an abnormal narrowing in a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture.
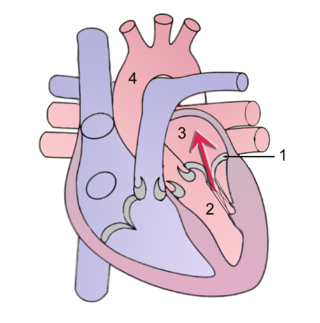
Mitral regurgitation(MR), also known as mitral insufficiency or mitral incompetence, is a form of valvular heart disease in which the mitral valve is insufficient and does not close properly when the heart pumps out blood. It is the abnormal leaking of blood backwards – regurgitation from the left ventricle, through the mitral valve, into the left atrium, when the left ventricle contracts. Mitral regurgitation is the most common form of valvular heart disease.
A transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) is the most common type of echocardiogram, which is a still or moving image of the internal parts of the heart using ultrasound. In this case, the probe is placed on the chest or abdomen of the subject to get various views of the heart. It is used as a non-invasive assessment of the overall health of the heart, including a patient's heart valves and degree of heart muscle contraction. The images are displayed on a monitor for real-time viewing and then recorded.

Valvular heart disease is any cardiovascular disease process involving one or more of the four valves of the heart. These conditions occur largely as a consequence of aging, but may also be the result of congenital (inborn) abnormalities or specific disease or physiologic processes including rheumatic heart disease and pregnancy.
Regurgitation is blood flow in the opposite direction from normal, as the backward flowing of blood into the heart or between heart chambers. It is the circulatory equivalent of backflow in engineered systems. It is sometimes called reflux.
Tricuspid regurgitation (TR), also called tricuspid insufficiency, is a type of valvular heart disease in which the tricuspid valve of the heart, located between the right atrium and right ventricle, does not close completely when the right ventricle contracts (systole). TR allows the blood to flow backwards from the right ventricle to the right atrium, which increases the volume and pressure of the blood both in the right atrium and the right ventricle, which may increase central venous volume and pressure if the backward flow is sufficiently severe.

Diastolic heart murmurs are heart murmurs heard during diastole, i.e. they start at or after S2 and end before or at S1. Many involve stenosis of the atrioventricular valves or regurgitation of the semilunar valves.

Heart murmurs are most frequently organized by timing, into systolic heart murmurs and diastolic heart murmurs. However, continuous murmurs can not be directly placed into either category.
With newer, non-invasive imaging techniques, the origin of other, so-called adventitial sounds or heart clicks has been appreciated. These are short, high-pitched sounds.
Cardiac physiology or heart function is the study of healthy, unimpaired function of the heart: involving blood flow; myocardium structure; the electrical conduction system of the heart; the cardiac cycle and cardiac output and how these interact and depend on one another.