Cardiology is the study of the heart. Cardiology is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease, and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a sub-specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery.
In medicine, the pulse is the rhythmic throbbing of each artery in response to the cardiac cycle (heartbeat). The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the neck, wrist, at the groin, behind the knee, near the ankle joint, and on foot. The pulse is most commonly measured at the wrist or neck. A sphygmograph is an instrument for measuring the pulse.

Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in a brachial artery, where it is most commonly measured. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure over diastolic pressure in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure, or in kilopascals (kPa). The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures is known as pulse pressure, while the average pressure during a cardiac cycle is known as mean arterial pressure.

Aortic stenosis is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart, such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse over time. Symptoms often come on gradually with a decreased ability to exercise often occurring first. If heart failure, loss of consciousness, or heart related chest pain occur due to AS the outcomes are worse. Loss of consciousness typically occurs with standing or exercising. Signs of heart failure include shortness of breath especially when lying down, at night, or with exercise, and swelling of the legs. Thickening of the valve without causing obstruction is known as aortic sclerosis.

Heart murmurs are unique heart sounds produced when blood flows across a heart valve or blood vessel. This occurs when turbulent blood flow creates a sound loud enough to hear with a stethoscope. The sound differs from normal heart sounds by their characteristics. For example, heart murmurs may have a distinct pitch, duration and timing. The major way health care providers examine the heart on physical exam is heart auscultation; another clinical technique is palpation, which can detect by touch when such turbulence causes the vibrations called cardiac thrill. A murmur is a sign found during the cardiac exam. Murmurs are of various types and are important in the detection of cardiac and valvular pathologies.

Systole is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. Its contrasting phase is diastole, the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are refilling with blood.

Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to fill with and pump blood.

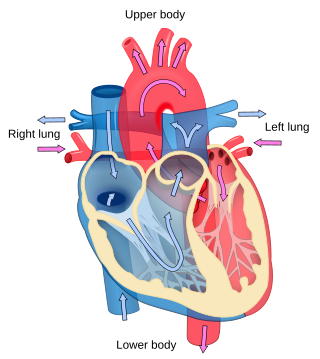
A ventricle is one of two large chambers located toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles, while intraventricular means within one ventricle.
A sphygmomanometer, also known as a blood pressure monitor, or blood pressure gauge, is a device used to measure blood pressure, composed of an inflatable cuff to collapse and then release the artery under the cuff in a controlled manner, and a mercury or aneroid manometer to measure the pressure. Manual sphygmomanometers are used with a stethoscope when using the auscultatory technique.

Pulse pressure is the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). It represents the force that the heart generates each time it contracts. Healthy pulse pressure is around 40 mmHg. A pulse pressure that is consistently 60 mmHg or greater is likely to be associated with disease, and a pulse pressure of 50 mmHg or more increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. Pulse pressure is considered low if it is less than 25% of the systolic. A very low pulse pressure can be a symptom of disorders such as congestive heart failure.

Aortic regurgitation (AR), also known as aortic insufficiency (AI), is the leaking of the aortic valve of the heart that causes blood to flow in the reverse direction during ventricular diastole, from the aorta into the left ventricle. As a consequence, the cardiac muscle is forced to work harder than normal.

Valvular heart disease is any cardiovascular disease process involving one or more of the four valves of the heart. These conditions occur largely as a consequence of aging, but may also be the result of congenital (inborn) abnormalities or specific disease or physiologic processes including rheumatic heart disease and pregnancy.
Pulsus paradoxus, also paradoxic pulse or paradoxical pulse, is an abnormally large decrease in stroke volume, systolic blood pressure and pulse wave amplitude during inspiration. Pulsus paradoxus is not related to pulse rate or heart rate, and it is not a paradoxical rise in systolic pressure. Normally, blood pressure drops less precipitously than 10 mmHg during inhalation. Pulsus paradoxus is a sign that is indicative of several conditions, most commonly pericardial effusion.

Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) is a condition defined by an abnormal enlargement of the cardiac muscle surrounding the right ventricle. The right ventricle is one of the four chambers of the heart. It is located towards the right lower chamber of the heart and it receives deoxygenated blood from the right upper chamber and pumps blood into the lungs.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to cardiology, the branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the human heart. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiology are called cardiologists.

Diabetic cardiomyopathy is a disorder of the heart muscle in people with diabetes. It can lead to inability of the heart to circulate blood through the body effectively, a state known as heart failure(HF), with accumulation of fluid in the lungs or legs. Most heart failure in people with diabetes results from coronary artery disease, and diabetic cardiomyopathy is only said to exist if there is no coronary artery disease to explain the heart muscle disorder.
A plot of a system's pressure versus volume has long been used to measure the work done by the system and its efficiency. This analysis can be applied to heat engines and pumps, including the heart. A considerable amount of information on cardiac performance can be determined from the pressure vs. volume plot. A number of methods have been determined for measuring PV-loop values experimentally.
The cardiovascular examination is a portion of the physical examination that involves evaluation of the cardiovascular system. The exact contents of the examination will vary depending on the presenting complaint but a complete examination will involve the heart, lungs, belly and the blood vessels.

Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a form of heart failure in which the ejection fraction – the percentage of the volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle with each heartbeat divided by the volume of blood when the left ventricle is maximally filled – is normal, defined as greater than 50%; this may be measured by echocardiography or cardiac catheterization. Approximately half of people with heart failure have preserved ejection fraction, while the other half have a reduction in ejection fraction, called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
The main pathophysiology of heart failure is a reduction in the efficiency of the heart muscle, through damage or overloading. As such, it can be caused by a wide number of conditions, including myocardial infarction, hypertension and cardiac amyloidosis. Over time these increases in workload will produce changes to the heart itself:













