
Lemierre's syndrome is infectious thrombophlebitis of the internal jugular vein. It most often develops as a complication of a bacterial sore throat infection in young, otherwise healthy adults. The thrombophlebitis is a serious condition and may lead to further systemic complications such as bacteria in the blood or septic emboli.
An embolism is the lodging of an embolus, a blockage-causing piece of material, inside a blood vessel. The embolus may be a blood clot (thrombus), a fat globule, a bubble of air or other gas, amniotic fluid, or foreign material. An embolism can cause partial or total blockage of blood flow in the affected vessel. Such a blockage may affect a part of the body distant from the origin of the embolus. An embolism in which the embolus is a piece of thrombus is called a thromboembolism.
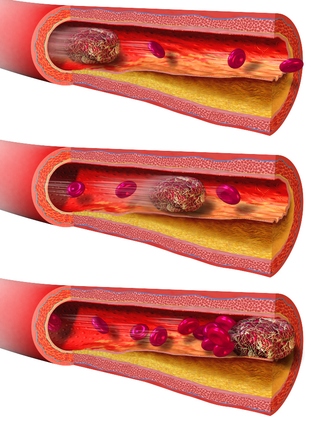
Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss. Even when a blood vessel is not injured, blood clots may form in the body under certain conditions. A clot, or a piece of the clot, that breaks free and begins to travel around the body is known as an embolus.
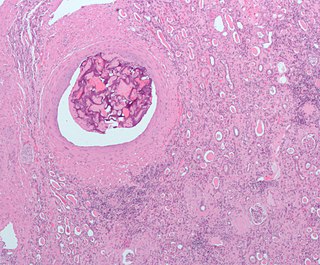
An embolus is an unattached mass that travels through the bloodstream and is capable of creating blockages. When an embolus occludes a blood vessel, it is called an embolism or embolic event. There are a number of different types of emboli, including blood clots, cholesterol plaque or crystals, fat globules, gas bubbles, and foreign bodies, which can result in different types of embolisms.

A thrombus, colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cross-linked fibrin protein. The substance making up a thrombus is sometimes called cruor. A thrombus is a healthy response to injury intended to stop and prevent further bleeding, but can be harmful in thrombosis, when a clot obstructs blood flow through healthy blood vessels in the circulatory system.

Platelets or thrombocytes are a component of blood whose function is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby initiating a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm derived from the megakaryocytes of the bone marrow or lung, which then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates, thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells.
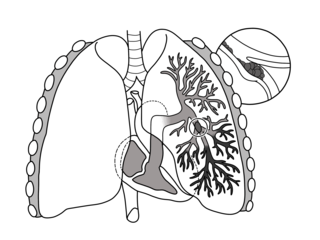
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include shortness of breath, chest pain particularly upon breathing in, and coughing up blood. Symptoms of a blood clot in the leg may also be present, such as a red, warm, swollen, and painful leg. Signs of a PE include low blood oxygen levels, rapid breathing, rapid heart rate, and sometimes a mild fever. Severe cases can lead to passing out, abnormally low blood pressure, obstructive shock, and sudden death.

Venous thrombosis is blockage of a vein caused by a thrombus. A common form of venous thrombosis is deep vein thrombosis (DVT), when a blood clot forms in the deep veins. If a thrombus breaks off (embolizes) and flows to the lungs to lodge there, it becomes a pulmonary embolism (PE), a blood clot in the lungs. The conditions of DVT only, DVT with PE, and PE only, are all captured by the term venous thromboembolism (VTE).

Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems moving parts of the body. As clotting factors and platelets are used up, bleeding may occur. This may include blood in the urine, blood in the stool, or bleeding into the skin. Complications may include organ failure.
Fibrinolysis is a process that prevents blood clots from growing and becoming problematic. Primary fibrinolysis is a normal body process, while secondary fibrinolysis is the breakdown of clots due to a medicine, a medical disorder, or some other cause.

Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enlarged veins in the affected area, but some DVTs have no symptoms. The most common life-threatening concern with DVT is the potential for a clot to embolize, travel as an embolus through the right side of the heart, and become lodged in a pulmonary artery that supplies blood to the lungs. This is called a pulmonary embolism (PE). DVT and PE comprise the cardiovascular disease of venous thromboembolism (VTE). About two-thirds of VTE manifests as DVT only, with one-third manifesting as PE with or without DVT. The most frequent long-term DVT complication is post-thrombotic syndrome, which can cause pain, swelling, a sensation of heaviness, itching, and in severe cases, ulcers. Recurrent VTE occurs in about 30% of those in the ten years following an initial VTE.

Coronary thrombosis is defined as the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel of the heart. This blood clot may then restrict blood flow within the heart, leading to heart tissue damage, or a myocardial infarction, also known as a heart attack.
D-dimer is a dimer that is a fibrin degradation product, a small protein fragment present in the blood after a blood clot is degraded by fibrinolysis. It is so named because it contains two D fragments of the fibrin protein joined by a cross-link, hence forming a protein dimer.
An embolus, is described as a free-floating mass, located inside blood vessels that can travel from one site in the blood stream to another. An embolus can be made up of solid, liquid, or gas. Once these masses get "stuck" in a different blood vessel, it is then known as an "embolism." An embolism can cause ischemia—damage to an organ from lack of oxygen. A paradoxical embolism is a specific type of embolism in which the embolus travels from the right side of the heart to the left side of the heart and lodges itself in a blood vessel known as an artery. Thus, it is termed "paradoxical" because the embolus lands in an artery, rather than a vein.

Vascular disease is a class of diseases of the vessels of the circulatory system in the body, including blood vessels – the arteries and veins, and the lymphatic vessels. Vascular disease is a subgroup of cardiovascular disease. Disorders in this vast network of blood and lymph vessels can cause a range of health problems that can sometimes become severe, and fatal. Coronary heart disease for example, is the leading cause of death for men and women in the United States.
Embolectomy is the emergency interventional or surgical removal of emboli which are blocking blood circulation. It usually involves removal of thrombi, and is then referred to as thromboembolectomy or thrombectomy. Embolectomy is an emergency procedure often as the last resort because permanent occlusion of a significant blood flow to an organ leads to necrosis. Other involved therapeutic options are anticoagulation and thrombolysis.

Left ventricular thrombus is a blood clot (thrombus) in the left ventricle of the heart. LVT is a common complication of acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Typically the clot is a mural thrombus, meaning it is on the wall of the ventricle. The primary risk of LVT is the occurrence of cardiac embolism, in which the thrombus detaches from the ventricular wall and travels through the circulation and blocks blood vessels. Blockage can be especially damaging in the heart or brain (stroke).

Ultrasonography in suspected deep vein thrombosis focuses primarily on the femoral vein and the popliteal vein, because thrombi in these veins are associated with the greatest risk of harmful pulmonary embolism.

Arterial occlusion is a condition involving partial or complete blockage of blood flow through an artery. Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to body tissues. An occlusion of arteries disrupts oxygen and blood supply to tissues, leading to ischemia. Depending on the extent of ischemia, symptoms of arterial occlusion range from simple soreness and pain that can be relieved with rest, to a lack of sensation or paralysis that could require amputation.

Feline arterial thromboembolism is a disease of the domestic cat in which blood clots (thrombi) block arteries, causing severe circulatory problems. Relative to the total number of feline patients, the disease is rare, but relatively common in cats with heart disease: about one-sixth of cats with heart disease are affected. Heart disease is the most common underlying cause of arterial thromboembolism. It leads to the formation of blood clots in the heart, which leave it with the bloodstream and obstruct larger blood vessels, in cats mainly the aorta at the outlet of the two external iliac arteries. Arterial thromboembolism occurs suddenly and is very painful. The blockage of the terminal portion of the aorta results in an undersupply of blood to the hind legs. The result is paralysis, cold hind extremities and later severe tissue damage. Rarely, other blood vessels are also affected; the symptoms of failure then depend on the supply area of the affected artery. Since drug thrombolysis in cats does not achieve satisfactory results, the focus today is on the self-dissolution of the clot by the body's own repair processes. Accompanying pain therapy and thrombosis prevention are performed and the underlying disease is treated. The mortality of arterial thromboembolism in cats is very high. Fifty to 60% of affected animals are euthanized without attempted treatment, and only one-quarter to one-third of animals survive such an event. In about half of the recovered cats, thromboembolism recurs despite anticoagulation prophylaxis.



















