Related Research Articles

The Commodore 1581 is a 3½-inch double-sided double-density floppy disk drive that was released by Commodore Business Machines (CBM) in 1987, primarily for its C64 and C128 home/personal computers. The drive stores 800 kilobytes using an MFM encoding but formats different from the MS-DOS, Amiga, and Mac Plus formats. With special software it's possible to read C1581 disks on an x86 PC system, and likewise, read MS-DOS and other formats of disks in the C1581, provided that the PC or other floppy handles the "720 kB" size format. This capability was most frequently used to read MS-DOS disks. The drive was released in the summer of 1987 and quickly became popular with bulletin board system (BBS) operators and other users.
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on hard disks and other devices. It is often supported for compatibility reasons by current operating systems for personal computers and many mobile devices and embedded systems, allowing interchange of data between disparate systems. The increase in disk drives capacity required three major variants: FAT12, FAT16 and FAT32. The FAT standard has also been expanded in other ways while generally preserving backward compatibility with existing software.

The Amiga 600, also known as the A600, is a home computer introduced in March 1992. It is the final Amiga model based on the Motorola 68000 and the 1990 Amiga Enhanced Chip Set. A redesign of the Amiga 500 Plus, it adds the option of an internal hard disk drive and a PCMCIA port. Lacking a numeric keypad, the A600 is only slightly larger than an IBM PC keyboard and weighing approximately 6 pounds. It shipped with AmigaOS 2.0, which was considered more user-friendly than earlier versions of the operating system.
AmigaDOS is the disk operating system of the AmigaOS, which includes file systems, file and directory manipulation, the command-line interface, and file redirection.
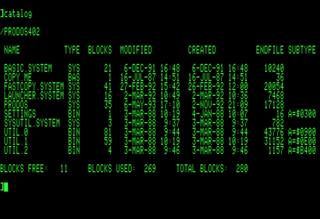
ProDOS is the name of two similar operating systems for the Apple II series of personal computers. The original ProDOS, renamed ProDOS 8 in version 1.2, is the last official operating system usable by all 8-bit Apple II series computers, and was distributed from 1983 to 1993. The other, ProDOS 16, was a stop-gap solution for the 16-bit Apple IIGS that was replaced by GS/OS within two years.
Disk formatting is the process of preparing a data storage device such as a hard disk drive, solid-state drive, floppy disk or USB flash drive for initial use. In some cases, the formatting operation may also create one or more new file systems. The first part of the formatting process that performs basic medium preparation is often referred to as "low-level formatting". Partitioning is the common term for the second part of the process, dividing the device into several sub-devices and, in some cases, writing information to the device allowing an operating system to be booted from it. The third part of the process, usually termed "high-level formatting" most often refers to the process of generating a new file system. In some operating systems all or parts of these three processes can be combined or repeated at different levels and the term "format" is understood to mean an operation in which a new disk medium is fully prepared to store files. Some formatting utilities allow distinguishing between a quick format, which does not erase all existing data and a long option that does erase all existing data.

TRSDOS is the operating system for the Tandy TRS-80 line of eight-bit Zilog Z80 microcomputers that were sold through Radio Shack from 1977 through 1991. Tandy's manuals recommended that it be pronounced triss-doss. TRSDOS should not be confused with Tandy DOS, a version of MS-DOS licensed from Microsoft for Tandy's x86 line of personal computers (PCs).
The Amiga Fast File System is a file system used on the Amiga personal computer. The previous Amiga filesystem was never given a specific name and known originally simply as "DOS" or AmigaDOS. Upon the release of FFS, the original filesystem became known as Amiga Old File System (OFS). OFS, which was primarily designed for use with floppy disks, had been proving slow to keep up with hard drives of the era. FFS was designed as a full replacement for the original Amiga filesystem. FFS differs from its predecessor mainly in the removal of redundant information. Data blocks contain nothing but data, allowing the filesystem to manage the transfer of large chunks of data directly from the host adapter to the final destination.
On the Amiga, the Old File System was the filesystem for AmigaOS before the Amiga Fast File System. Even though it used 512-byte blocks, it reserved the first small portion of each block for metadata, leaving an actual data block capacity of 488 bytes per block. It wasn't very suitable for anything except floppy disks, and it was soon replaced.
Long filename (LFN) support is Microsoft's backward compatible extension of the 8.3 filename naming scheme used in DOS. Long filenames can be more descriptive, including longer filename extensions such as .jpeg, .tiff, .html, and .xhtml that are common on other operating systems, rather than specialized shortened names such as .jpg, .tif, .htm, or .xht. The standard has been common with File Allocation Table (FAT) filesystems since its first implementation in Windows NT 3.5 of 1994.
IMG, in computing, refers to binary files with the .img filename extension that store raw disk images of floppy disks, hard drives, and optical discs or a bitmap image – .img.
Amiga software is computer software engineered to run on the Amiga personal computer. Amiga software covers many applications, including productivity, digital art, games, commercial, freeware and hobbyist products. The market was active in the late 1980s and early 1990s but then dwindled. Most Amiga products were originally created directly for the Amiga computer, and were not ported from other platforms.
AmigaOS is the proprietary native operating system of the Amiga personal computer. Since its introduction with the launch of the Amiga 1000 in 1985, there have been four major versions and several minor revisions of the operating system.
Amiga support and maintenance software performs service functions such as formatting media for a specific filesystem, diagnosing failures that occur on formatted media, data recovery after media failure, and installation of new software for the Amiga family of personal computers—as opposed to application software, which performs business, education, and recreation functions.
Kickstart is the bootstrap firmware of the Amiga computers developed by Commodore International. Its purpose is to initialize the Amiga hardware and core components of AmigaOS and then attempt to boot from a bootable volume, such as a floppy disk. Most Amiga models were shipped with the Kickstart firmware stored on ROM chips.

AmigaOS is a family of proprietary native operating systems of the Amiga and AmigaOne personal computers. It was developed first by Commodore International and introduced with the launch of the first Amiga, the Amiga 1000, in 1985. Early versions of AmigaOS required the Motorola 68000 series of 16-bit and 32-bit microprocessors. Later versions were developed by Haage & Partner and then Hyperion Entertainment. A PowerPC microprocessor is required for the most recent release, AmigaOS 4.

The Amiga 1200, or A1200, is a personal computer in the Amiga computer family released by Commodore International, aimed at the home computer market. It was launched on October 21, 1992, at a base price of £399 in the United Kingdom and $599 in the United States.

DOS is a platform-independent acronym for disk operating system which later became a common shorthand for disk-based operating systems on IBM PC compatibles. DOS primarily consists of Microsoft's MS-DOS and a rebranded version under the name IBM PC DOS, both of which were introduced in 1981. Later compatible systems from other manufacturers include DR DOS (1988), ROM-DOS (1989), PTS-DOS (1993), and FreeDOS (1998). MS-DOS dominated the IBM PC compatible market between 1981 and 1995.

The floppy disk is a data storage and transfer medium that was ubiquitous from the mid-1970s well into the 2000s. Besides the 3½-inch and 5¼-inch formats used in IBM PC compatible systems, or the 8-inch format that preceded them, many proprietary floppy disk formats were developed, either using a different disk design or special layout and encoding methods for the data held on the disk.
A FAT file system is a specific type of computer file system architecture and a family of industry-standard file systems utilizing it.