
Frost is a thin layer of ice on a solid surface, which forms from water vapor in an above-freezing atmosphere coming in contact with a solid surface whose temperature is below freezing, and resulting in a phase change from water vapor to ice as the water vapor reaches the freezing point. In temperate climates, it most commonly appears on surfaces near the ground as fragile white crystals; in cold climates, it occurs in a greater variety of forms. The propagation of crystal formation occurs by the process of nucleation.

Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets, though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailstone. Ice pellets generally fall in cold weather, while hail growth is greatly inhibited during cold surface temperatures.

Snow comprises individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes. It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout its life cycle, starting when, under suitable conditions, the ice crystals form in the atmosphere, increase to millimeter size, precipitate and accumulate on surfaces, then metamorphose in place, and ultimately melt, slide or sublimate away.

Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influenced by nearby bodies of water, topography, and wind conditions. In turn, fog affects many human activities, such as shipping, travel, and warfare.

An avalanche is a rapid flow of snow down a slope, such as a hill or mountain.

A winter storm is an event in which wind coincides with varieties of precipitation that only occur at freezing temperatures, such as snow, mixed snow and rain, or freezing rain. In temperate continental climates, these storms are not necessarily restricted to the winter season, but may occur in the late autumn and early spring as well. A snowstorm with strong winds and other conditions meeting certain criteria is called a blizzard.

In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzling, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor, so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation but colloids, because the water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called showers.

Black ice, sometimes called clear ice, is a thin coating of glaze ice on a surface, especially on roads. The ice itself is not black, but visually transparent, allowing the often black road below to be seen through it. The typically low levels of noticeable ice pellets, snow, or sleet surrounding black ice means that areas of the ice are often practically invisible to drivers or people stepping on it. There is, thus, a risk of slippage and subsequent accident due to the unexpected loss of traction.

Rime ice forms when supercooled water liquid droplets freeze onto surfaces. Meteorologists distinguish between three basic types of ice forming on vertical and horizontal surfaces by deposition of supercooled water droplets. There are also intermediate formations.

This is a list of meteorology topics. The terms relate to meteorology, the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere that focuses on weather processes and forecasting.
A pilot report or PIREP is a report of actual weather conditions encountered by an aircraft in flight. This information is usually relayed by radio to the nearest ground station, but other options also exist in some regions. The message would then be encoded and relayed to other weather offices and air traffic service units.

A snowsquall, or snow squall, is a sudden moderately heavy snow fall with blowing snow and strong, gusty surface winds. It is often referred to as a whiteout and is similar to a blizzard but is localized in time or in location and snow accumulations may or may not be significant.

Atmospheric icing occurs in the atmosphere when water droplets freeze on objects they come in contact with. Icing conditions can be particularly dangerous to aircraft, as the built-up ice changes the aerodynamics of the flight surfaces, which can increase the risk of a stall. For this reason, on-board ice protection systems have been developed.

It is very rare for snow to fall in the U.S. state of Florida, especially in the central and southern portions of the state. With the exception of the far northern areas of the state, most of the major cities in Florida have never recorded measurable snowfall, though trace amounts have been recorded, or flurries in the air observed few times each century. According to the National Weather Service, in the Florida Keys and Key West there is no known occurrence of snow flurries since the European colonization of the region more than 300 years ago. In Miami, Fort Lauderdale, and Palm Beach there has been only one known report of snow flurries observed in the air in more than 200 years; this occurred in January 1977. In any event, Miami, Fort Lauderdale, and Palm Beach have not seen snow flurries before or since this 1977 event.

Severe weather is any dangerous meteorological phenomenon with the potential to cause damage, serious social disruption, or loss of human life. Types of severe weather phenomena vary, depending on the latitude, altitude, topography, and atmospheric conditions. High winds, hail, excessive precipitation, and wildfires are forms and effects of severe weather, as are thunderstorms, downbursts, tornadoes, waterspouts, tropical cyclones, and extratropical cyclones. Regional and seasonal severe weather phenomena include blizzards (snowstorms), ice storms, and duststorms. Extreme weather phenomena which cause extreme heat, cold, wetness or drought often will bring severe weather events. One of the principle effects of anthropogenic climate change is changes in severe and extreme weather patterns.

Airport weather stations are automated sensor suites which are designed to serve aviation and meteorological operations, weather forecasting and climatology. Automated airport weather stations have become part of the backbone of weather observing in the United States and Canada and are becoming increasingly more prevalent worldwide due to their efficiency and cost-savings.

The climate of Finland is influenced most by its latitude: Finland is located between 60 and 70 N. Because of Finland's northern location, winter is the longest season. Only on the south coast and the southwest is summer as long as winter. On average, winter lasts from early January to late February in the outermost islands in the archipelago and the warmest locations along the southwestern coast – notably in Hanko, and from early October to mid May in the most elevated locations, such as northwestern Lapland and the lowest valleys in northeastern Lapland. This means that southern portions of the country are snow-covered about three to four months of the year, and the northern for about seven months. The long winter causes about half of the annual 500 to 600 millimetres precipitation in the north to fall as snow. Precipitation in the south amounts to about 600 to 700 millimetres annually. Like that of the north, it occurs all through the year, though not so much of it is snow.

Classifications of snow describe and categorize the attributes of snow-generating weather events, including the individual crystals both in the air and on the ground, and the deposited snow pack as it changes over time. Snow can be classified by describing the weather event that is producing it, the shape of its ice crystals or flakes, how it collects on the ground, and thereafter how it changes form and composition. Depending on the status of the snow in the air or on the ground, a different classification applies.
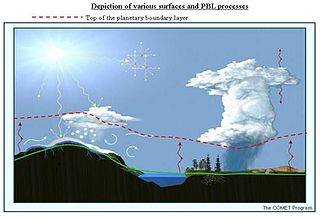
The alpine planetary boundary layer is the planetary boundary layer (PBL) associated with mountainous regions. Due to its high spatial and temporal variability, its behavior is more complex than over a flat terrain. The fast changing local wind system directly linked to topography and the variable land cover that goes from snow to vegetation have a significant effect on the growth of the PBL and make it much harder to predict.

This glossary of meteorology is a list of terms and concepts relevant to meteorology and atmospheric science, their sub-disciplines, and related fields.


















