Related Research Articles

A chambered cairn is a burial monument, usually constructed during the Neolithic, consisting of a sizeable chamber around and over which a cairn of stones was constructed. Some chambered cairns are also passage-graves. They are found throughout Britain and Ireland, with the largest number in Scotland.

Maeshowe is a Neolithic chambered cairn and passage grave situated on Mainland Orkney, Scotland. It was probably built around 2800 BC. In the archaeology of Scotland, it gives its name to the Maeshowe type of chambered cairn, which is limited to Orkney.

A passage grave or passage tomb consists of one or more burial chambers covered in earth or stone and having a narrow access passage made of large stones. These structures usually date from the Neolithic Age and are found largely in Western Europe. When covered in earth, a passage grave is a type of burial mound which are found in various forms all over the world. When a passage grave is covered in stone, it is a type of cairn.

Newgrange is a prehistoric monument in County Meath in Ireland, located on a rise overlooking the River Boyne, eight kilometres west of the town of Drogheda. It is an exceptionally grand passage tomb built during the Neolithic Period, around 3200 BC, making it older than Stonehenge and the Egyptian pyramids. Newgrange is the main monument in the Brú na Bóinne complex, a World Heritage Site that also includes the passage tombs of Knowth and Dowth, as well as other henges, burial mounds and standing stones.

A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 structures or arrangements in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.

A chamber tomb is a tomb for burial used in many different cultures. In the case of individual burials, the chamber is thought to signify a higher status for the interred than a simple grave. Built from rock or sometimes wood, the chambers could also serve as places for storage of the dead from one family or social group and were often used over long periods for multiple burials.

The court cairn or court tomb is a megalithic type of chambered cairn or gallery grave. During the period, 3900–3500 BC, more than 390 court cairns were built in Ireland and over 100 in southwest Scotland. The Neolithic monuments are identified by an uncovered courtyard connected to one or more roofed and partitioned burial chambers. Many monuments were built in multiple phases in both Ireland and Scotland and later re-used in the Early Bronze Age.

A gallery grave is a form of megalithic tomb built primarily during the Neolithic Age in Europe in which the main gallery of the tomb is entered without first passing through an antechamber or hallway. There are at least four major types of gallery grave, and they may be covered with an earthen mound or rock mound.

Aberffraw is a village and community on the south west coast of the Isle of Anglesey in Wales. The village is 9 miles from the island's county town, Llangefni, and is on the west bank of the Afon Ffraw. The community includes Soar and Dothan. It is on the A4080 and the nearest rail station is Bodorgan.

Carrowmore is a large group of megalithic monuments on the Coolera Peninsula to the west of Sligo, Ireland. They were built in the 4th millennium BC, during the Neolithic. There are thirty surviving tombs, making Carrowmore one of the largest clusters of megalithic tombs in Ireland, and one of the 'big four' along with Carrowkeel, Loughcrew and Brú na Bóinne. Carrowmore is the heart of an ancient ritual landscape which is dominated by the mountain of Knocknarea to the west. It is a protected National Monument.

Barclodiad y Gawres is a Neolithic burial chamber between Rhosneigr and Aberffraw on the south-western coast of the island of Anglesey in North Wales. It is an example of a cruciform passage grave, a notable feature being its decorated stones. Similar graves and marks exist across the Irish Sea in the Boyne Valley.

Prehistoric Wales in terms of human settlements covers the period from about 230,000 years ago, the date attributed to the earliest human remains found in what is now Wales, to the year AD 48 when the Roman army began a military campaign against one of the Welsh tribes. Traditionally, historians have believed that successive waves of immigrants brought different cultures into the area, largely replacing the previous inhabitants, with the last wave of immigrants being the Celts. However, studies of population genetics now suggest that this may not be true, and that immigration was on a smaller scale.

Two Rock is a mountain in Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown, Ireland. It is 536 metres high and is the 382nd highest mountain in Ireland. It is the highest point of the group of hills in the Dublin Mountains which comprises Two Rock, Three Rock, Kilmashogue and Tibradden Mountains. The mountain takes its name from the two granite tors that lie to the south-east of the summit. From the summit, which is called Fairy Castle, there are views of much of the Dublin area from Tallaght to Howth to the north while Bray Head, Killiney Hill, the Great Sugar Loaf and the Wicklow Mountains are visible to the south. The summit area is mostly shallow bog while ferns and gorse cover the lower slopes. The mountain is also an important habitat for red grouse.

Prehistoric Orkney refers only to the prehistory of the Orkney archipelago of Scotland that begins with human occupation. Although some records referring to Orkney survive that were written during the Roman invasions of Scotland, “prehistory” in northern Scotland is defined as lasting until the start of Scotland's Early Historic Period.

51.71025°N 2.29970°W

Nordic megalith architecture is an ancient architectural style found in Northern Europe, especially Scandinavia and North Germany, that involves large slabs of stone arranged to form a structure. It emerged in northern Europe, predominantly between 3500 and 2800 BC. It was primarily a product of the Funnelbeaker culture. Between 1964 and 1974, Ewald Schuldt in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania excavated over 100 sites of different types: simple dolmens, extended dolmens, passage graves, great dolmens, unchambered long barrows, and stone cists. In addition, there are polygonal dolmens and types that emerged later, for example, the Grabkiste and Röse. This nomenclature, which specifically derives from the German, is not used in Scandinavia where these sites are categorised by other, more general, terms, as dolmens, passage graves and stone cists.

The architecture of Scotland in the prehistoric era includes all human building within the modern borders of Scotland, before the arrival of the Romans in Britain in the first century BCE. Stone Age settlers began to build in wood in what is now Scotland from at least 8,000 years ago. The first permanent houses of stone were constructed around 6,000 years ago, as at Knap of Howar, Orkney and settlements like Skara Brae. There are also large numbers of chambered tombs and cairns from this era, particularly in the west and north. In the south and east there are earthen barrows, often linked to timber monuments of which only remnants remain. Related structures include bank barrows, cursus monuments, mortuary enclosures and timber halls. From the Bronze Age there are fewer new buildings, but there is evidence of crannogs, roundhouses built on artificial islands and of Clava cairns and the first hillforts. From the Iron Age there is evidence of substantial stone Atlantic roundhouses, which include broch towers, smaller duns. There is also evidence of about 1,000 hillforts in Scotland, most located below the Clyde-Forth line.
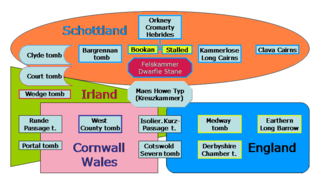
British megalith architecture is the study of those ancient cultures that built megalithic sites on the British Isles, including the research and documentation of these sites. The classification sometimes used of these cultures based on geological criteria is problematic.
Thomas George Eyre Powell was a British archaeologist who specialised in the study of the Neolithic British Isles and the Celts.
References
- ↑ Powell, T. G. E. (December 1938). "The Passage Graves of Ireland". Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society. 4 (2): 239–248. doi:10.1017/S0079497X00020892. ISSN 2050-2729.
- ↑ "Barclodiad y Gawres (Cadw)". VisitWales. 1 January 2000. Retrieved 26 November 2024.