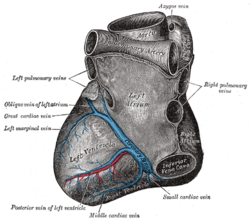
The crux cordis or crux of the heart (from Latin "crux" meaning "cross") is the area on the lower back side of the heart where the coronary sulcus (the groove separating the atria from the ventricles) and the posterior interventricular sulcus (the groove separating the left from the right ventricle) meet. [1] It is important surgically because the atrioventricular nodal artery, a small but vital vessel, passes in proximity to the crux of the heart. [2] It is the anastomotic point of right and left coronary artery.