The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest, called the mediastinum.

Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the arteries and veins that supply the heart muscle (myocardium). Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. Cardiac veins then drain away the blood after it has been deoxygenated. Because the rest of the body, and most especially the brain, needs a steady supply of oxygenated blood that is free of all but the slightest interruptions, the heart is required to function continuously. Therefore its circulation is of major importance not only to its own tissues but to the entire body and even the level of consciousness of the brain from moment to moment. Interruptions of coronary circulation quickly cause heart attacks, in which the heart muscle is damaged by oxygen starvation. Such interruptions are usually caused by coronary ischemia linked to coronary artery disease, and sometimes to embolism from other causes like obstruction in blood flow through vessels.
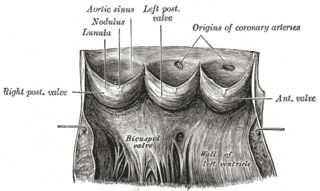
An aortic sinus, also known as a sinus of Valsalva, is one of the anatomic dilations of the ascending aorta, which occurs just above the aortic valve. These widenings are between the wall of the aorta and each of the three cusps of the aortic valve.

The atrium is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves.

The chordae tendineae or tendinous cords, colloquially known as the heart strings, are inelastic cords of fibrous connective tissue that connect the papillary muscles to the tricuspid valve and the mitral valve in the heart.

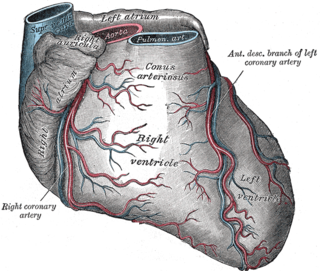
In the blood supply of the heart, the right coronary artery (RCA) is an artery originating above the right cusp of the aortic valve, at the right aortic sinus in the heart. It travels down the right coronary sulcus, towards the crux of the heart. It gives off many branches, including the sinoatrial nodal artery, right marginal artery, posterior interventricular artery, conus artery, and atrioventricular nodal branch. It contributes the right side of the heart, and parts of the interventricular septum.

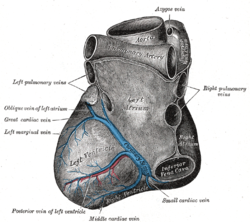
The coronary sinus is the largest vein of the heart. It drains over half of the deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle into the right atrium. It begins on the backside of the heart, in between the left atrium, and left ventricle; it begins at the junction of the great cardiac vein, and oblique vein of the left atrium. It receives multiple tributaries. It passes across the backside of the heart along a groove between left atrium and left ventricle, then drains into the right atrium at the orifice of the coronary sinus.

The great cardiac vein is a vein of the heart. It begins at the apex of the heart and ascends along the anterior interventricular sulcus before joining the oblique vein of the left atrium to form the coronary sinus upon the posterior surface of the heart.

The small cardiac vein, also known as the right coronary vein, is a coronary vein that drains parts of the right atrium and right ventricle of the heart. Despite its size, it is one of the major drainage vessels for the heart.

The pericardial sinuses are impressions in the pericardial sac formed between the points where great vessels enter it.
The coronary sulcus is a groove on the surface of the heart at the base of right auricle that separates the atria from the ventricles. The structure contains the trunks of the nutrient vessels of the heart, and is deficient in front, where it is crossed by the root of the pulmonary trunk. On the posterior surface of the heart, the coronary sulcus contains the coronary sinus. The right coronary artery, circumflex branch of left coronary artery, and small cardiac vein all travel along parts of the coronary sulcus.

The circumflex branch of left coronary artery is a branch of the left coronary artery. It winds around the left side of the heart along the atrioventricular groove. It supplies the posterolateral portion of the left ventricle.

The anterior interventricular sulcus is one of two grooves separating the ventricles of the heart. They can also be known as paraconal interventricular groove or subsinosal interventricular groove respectively. It is situated on the sternocostal surface of the heart, close to the left margin of the heart. It extends between the coronary sulcus, and the apex of the heart; upon reaching the diaphragmatic surface of the heart, it ends at the notch of cardiac apex. It contains the anterior interventricular branch of the left coronary artery, and great cardiac vein.

The posterior interventricular sulcus or posterior longitudinal sulcus is one of the two grooves separating the ventricles of the heart. They can be known as subsinosal interventricular groove or paraconal interventricular groove respectively. It is located on the diaphragmatic surface of the heart near the right margin. It extends between the coronary sulcus, and the apex of the heart. It contains the posterior interventricular artery, and middle cardiac vein.

The left marginal vein is a vein of the heart which courses near or over the left margin of the heart. It drains venous blood from much of the myocardium of the left ventricle. It usually empties into the great cardiac vein.

The right marginal vein is a vein of the heart running along the inferior margin of the heart. It drains adjacent region of the right ventricle. It usually opens directly into the right atrium, but may sometimes instead empty into the anterior cardiac veins, or the coronary sinus.

The left anterior descending artery is a branch of the left coronary artery. It supplies the anterior portion of the left ventricle. It provides about half of the arterial supply to the left ventricle and is thus considered the most important vessel supplying the left ventricle. Blockage of this artery is often called the widow-maker infarction due to a high risk of death.

The smallest cardiac veins are small, valveless veins in the walls of all four heart chambers that drain venous blood from the myocardium directly into any of the heart chambers.

Cardiac resynchronisation therapy is the insertion of electrodes in the left and right ventricles of the heart, as well as on occasion the right atrium, to treat heart failure by coordinating the function of the left and right ventricles via a pacemaker, a small device inserted into the anterior chest wall.
The heart is a muscular organ situated in the mediastinum. It consists of four chambers, four valves, two main arteries, and the conduction system. The left and right sides of the heart have different functions: the right side receives de-oxygenated blood through the superior and inferior venae cavae and pumps blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery, and the left side receives saturated blood from the lungs.