
The left and right brachiocephalic veins are major veins in the upper chest, formed by the union of the ipsilateral internal jugular vein and subclavian vein behind the sternoclavicular joint. The left brachiocephalic vein is more than twice the length of the right brachiocephalic vein.
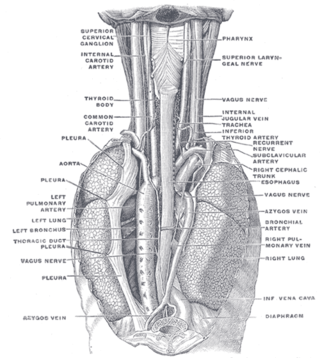
The azygos vein is a vein running up the right side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superior vena cava and inferior vena cava and can provide an alternative path for blood to the right atrium when either of the venae cavae is blocked.

The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.

In human anatomy, the internal thoracic vein is the vein that drains the chest wall and breasts.

The hemiazygos vein is a vein running superiorly in the lower thoracic region, just to the left side of the vertebral column.

The accessory hemiazygos vein, also called the superior hemiazygous vein, is a vein on the left side of the vertebral column that generally drains the fourth through eighth intercostal spaces on the left side of the body.

The supreme intercostal vein is a paired vein that drains the first intercostal space on its corresponding side.

The lumbar arteries are arteries located in the lower back or lumbar region. The lumbar arteries are in parallel with the intercostals.

The intercostal space (ICS) is the anatomic space between two ribs. Since there are 12 ribs on each side, there are 11 intercostal spaces, each numbered for the rib superior to it.
The subcostal arteries, so named because they lie below the last ribs, constitute the lowest pair of branches derived from the thoracic aorta, and are in series with the intercostal arteries.

The costocervical trunk arises from the upper and back part of the second part of subclavian artery, behind the scalenus anterior on the right side, and medial to that muscle on the left side.

The carotid triangle is a portion of the anterior triangle of the neck.
The bronchial veins are small vessels that return blood from the larger bronchi and structures at the roots of the lungs. The right side drains into the azygos vein, while the left side drains into the left superior intercostal vein or the accessory hemiazygos vein. Bronchial veins are thereby part of the bronchial circulation, carrying waste products away from the cells that constitute the lungs.

The superior intercostal veins are two veins that drain the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th intercostal spaces, one vein for each side of the body.

The intercostal arteries are a group of arteries passing within an intercostal space. There are 9 anterior and 11 posterior intercostal arteries on each side of the body. The anterior intercostal arteries are branches of the internal thoracic artery and its terminal branch - the musculophrenic artery. The posterior intercostal arteries are branches of the supreme intercostal artery and thoracic aorta.

The lumbar veins are four pairs of veins running along the inside of the posterior abdominal wall, and drain venous blood from parts of the abdominal wall. Each lumbar vein accompanies a single lumbar artery. The lower two pairs of lumbar veins all drain directly into the inferior vena cava, whereas the fate of the upper two pairs is more variable.
The esophageal veins drain blood from the esophagus to the azygos vein, in the thorax, and to the inferior thyroid vein in the neck. It also drains, although with less significance, to the hemiazygos vein, posterior intercostal vein and bronchial veins.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The posterior cardinal veins or postcardinal veins join with the corresponding right and left cardinal veins to form the left common cardinal veins, which empty in the sinus venosus. In the development of a human embryo, most of the posterior cardinal veins regress, and what remains of them forms the renal segment of the inferior vena cava and the common iliac veins. Later in the development stages, the posterior cardinal veins are replaced by the subcardinal and supracardinal veins. The subcardinal veins form part of the inferior vena cava, the renal veins and the gonadal veins. The supracardinal veins form part of the inferior vena cava, the intercostal veins, the hemiazygos vein and the azygos vein.











