Related Research Articles

The dorsal scapular nerve is a branch of the brachial plexus, usually derived from the ventral ramus of cervical nerve C5. It provides motor innervation to the rhomboid major muscle, rhomboid minor muscle, and levator scapulae muscle.

In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax. On the left side of the body, the subclavian comes directly off the aortic arch, while on the right side it arises from the relatively short brachiocephalic artery when it bifurcates into the subclavian and the right common carotid artery.

The pulmonary veins are the veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The largest pulmonary veins are the four main pulmonary veins, two from each lung that drain into the left atrium of the heart. The pulmonary veins are part of the pulmonary circulation.

The rhomboid major is a skeletal muscle of the back that connects the scapula with the vertebrae of the spinal column. It originates from the spinous processes of the thoracic vertebrae T2–T5 and supraspinous ligament; it inserts onto the lower portion of the medial border of the scapula. It acts together with the rhomboid minor to keep the scapula pressed against thoracic wall and to retract the scapula toward the vertebral column.

In human anatomy, the rhomboid minor is a small skeletal muscle of the back that connects the scapula to the vertebrae of the spinal column. It arises from the nuchal ligament, and the 7th cervical and 1st thoracic vertebrae and intervening supraspinous ligaments; it inserts onto the medial border of the scapula. It is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve.

The external jugular vein receives the greater part of the blood from the exterior of the cranium and the deep parts of the face, being formed by the junction of the posterior division of the retromandibular vein with the posterior auricular vein.
The small saphenous vein is a relatively large superficial vein of the posterior leg.

The subscapular artery, the largest branch of the axillary artery, arises from the third part of the axillary artery at the lower border of the subscapularis muscle, which it follows to the inferior angle of the scapula, where it anastomoses with the lateral thoracic and intercostal arteries, and with the descending branch of the dorsal scapular artery, and ends in the neighboring muscles.
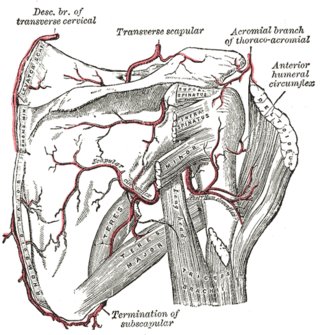
The circumflex scapular artery is a branch of the subscapular artery and part of the scapular anastomoses.

The transverse cervical artery is an artery in the neck and a branch of the thyrocervical trunk, running at a higher level than the suprascapular artery.
Dorsal scapular may refer to:
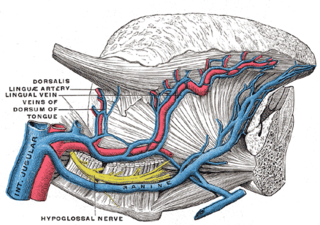
The lingual veins are multiple veins of the tongue with two distinct courses: one group drains into the lingual artery; another group drains either into the lingual artery, (common) facial vein, or internal jugular vein.

The vitelline veins are veins that drain blood from the yolk sac and the gut tube during gestation.

The scapular anastomosis is a system connecting certain subclavian artery and their corresponding axillary artery, forming a circulatory anastomosis around the scapula. It allows blood to flow past the joint in case of occlusion, damage, or pinching of the following scapular arteries:

The cerebellar veins are veins which drain the cerebellum. They consist of the superior cerebellar veins and the inferior cerebellar veins. The superior cerebellar veins drain to the straight sinus and the internal cerebral veins. The inferior cerebellar veins drain to the transverse sinus, the superior petrosal sinus, and the occipital sinus.

The posterior intercostal veins are veins that drain the intercostal spaces posteriorly. They run with their corresponding posterior intercostal artery on the underside of the rib, the vein superior to the artery. Each vein also gives off a dorsal branch that drains blood from the muscles of the back.

In human male anatomy, the dorsal veins of the penis are blood vessels that drain the shaft, the skin and the glans of the human penis. They are typically located in the midline on the dorsal aspect of the penis and they comprise the superficial dorsal veinof the penis, that lies in the subcutaneous tissue of the shaft, and the deep dorsal veinof the penis, that lies beneath the deep fascia.
The deep dorsal vein of clitoris is a vein which drains to the vesical plexus.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
References
- ↑ "Definition: dorsal scapular vein from Online Medical Dictionary" . Retrieved 2007-08-30.