Related Research Articles
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word intron is derived from the term intragenic region, i.e., a region inside a gene. The term intron refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and the corresponding RNA sequence in RNA transcripts. The non-intron sequences that become joined by this RNA processing to form the mature RNA are called exons.
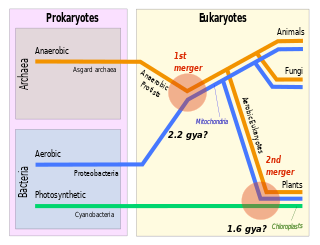
Symbiogenesis is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms. The theory holds that mitochondria, plastids such as chloroplasts, and possibly other organelles of eukaryotic cells are descended from formerly free-living prokaryotes taken one inside the other in endosymbiosis. Mitochondria appear to be phylogenetically related to Rickettsiales bacteria, while chloroplasts are thought to be related to cyanobacteria.
Molecular evolution is the process of change in the sequence composition of cellular molecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins across generations. The field of molecular evolution uses principles of evolutionary biology and population genetics to explain patterns in these changes. Major topics in molecular evolution concern the rates and impacts of single nucleotide changes, neutral evolution vs. natural selection, origins of new genes, the genetic nature of complex traits, the genetic basis of speciation, the evolution of development, and ways that evolutionary forces influence genomic and phenotypic changes.

In molecular biology, RNA polymerase, or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions that synthesize RNA from a DNA template.
Gene knockdown is an experimental technique by which the expression of one or more of an organism's genes is reduced. The reduction can occur either through genetic modification or by treatment with a reagent such as a short DNA or RNA oligonucleotide that has a sequence complementary to either gene or an mRNA transcript.

A primary transcript is the single-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) product synthesized by transcription of DNA, and processed to yield various mature RNA products such as mRNAs, tRNAs, and rRNAs. The primary transcripts designated to be mRNAs are modified in preparation for translation. For example, a precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) is a type of primary transcript that becomes a messenger RNA (mRNA) after processing.

Human mitochondrial genetics is the study of the genetics of human mitochondrial DNA. The human mitochondrial genome is the entirety of hereditary information contained in human mitochondria. Mitochondria are small structures in cells that generate energy for the cell to use, and are hence referred to as the "powerhouses" of the cell.
Nuclear DNA (nDNA), or nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid, is the DNA contained within each cell nucleus of a eukaryotic organism. It encodes for the majority of the genome in eukaryotes, with mitochondrial DNA and plastid DNA coding for the rest. It adheres to Mendelian inheritance, with information coming from two parents, one male and one female—rather than matrilineally as in mitochondrial DNA.

In genetics, an insertion is the addition of one or more nucleotide base pairs into a DNA sequence. This can often happen in microsatellite regions due to the DNA polymerase slipping. Insertions can be anywhere in size from one base pair incorrectly inserted into a DNA sequence to a section of one chromosome inserted into another. The mechanism of the smallest single base insertion mutations is believed to be through base-pair separation between the template and primer strands followed by non-neighbor base stacking, which can occur locally within the DNA polymerase active site. On a chromosome level, an insertion refers to the insertion of a larger sequence into a chromosome. This can happen due to unequal crossover during meiosis.

RNA editing is a molecular process through which some cells can make discrete changes to specific nucleotide sequences within an RNA molecule after it has been generated by RNA polymerase. It occurs in all living organisms and is one of the most evolutionarily conserved properties of RNAs. RNA editing may include the insertion, deletion, and base substitution of nucleotides within the RNA molecule. RNA editing is relatively rare, with common forms of RNA processing not usually considered as editing. It can affect the activity, localization as well as stability of RNAs, and has been linked with human diseases.
A guide RNA (gRNA) is a piece of RNA that functions as a guide for RNA- or DNA-targeting enzymes, with which it forms complexes. Very often these enzymes will delete, insert or otherwise alter the targeted RNA or DNA. They occur naturally, serving important functions, but can also be designed to be used for targeted editing, such as with CRISPR-Cas9 and CRISPR-Cas12.
In genetics, a sense strand, or coding strand, is the segment within double-stranded DNA that carries the translatable code in the 5′ to 3′ direction, and which is complementary to the antisense strand of DNA, or template strand, which does not carry the translatable code in the 5′ to 3′ direction. The sense strand is the strand of DNA that has the same sequence as the mRNA, which takes the antisense strand as its template during transcription, and eventually undergoes translation into a protein. The antisense strand is thus responsible for the RNA that is later translated to protein, while the sense strand possesses a nearly identical makeup to that of the mRNA.

Physarum polycephalum, an acellular slime mold or myxomycete popularly known as "the blob", is a protist with diverse cellular forms and broad geographic distribution. The “acellular” moniker derives from the plasmodial stage of the life cycle: the plasmodium is a bright yellow macroscopic multinucleate coenocyte shaped in a network of interlaced tubes. This stage of the life cycle, along with its preference for damp shady habitats, likely contributed to the original mischaracterization of the organism as a fungus. P. polycephalum is used as a model organism for research into motility, cellular differentiation, chemotaxis, cellular compatibility, and the cell cycle.

A kinetoplast is a network of circular DNA inside a mitochondrion that contains many copies of the mitochondrial genome. The most common kinetoplast structure is a disk, but they have been observed in other arrangements. Kinetoplasts are only found in Excavata of the class Kinetoplastida. The variation in the structures of kinetoplasts may reflect phylogenic relationships between kinetoplastids. A kinetoplast is usually adjacent to the organism's flagellar basal body, suggesting that it is bound to some components of the cytoskeleton. In Trypanosoma brucei this cytoskeletal connection is called the tripartite attachment complex and includes the protein p166.
NUMT, pronounced "new might", is an acronym for "nuclear mitochondrial DNA" segment or genetic locus coined by evolutionary geneticist, Jose V. Lopez, which describes a transposition of any type of cytoplasmic mitochondrial DNA into the nuclear genome of eukaryotic organisms.

Eukaryotic transcription is the elaborate process that eukaryotic cells use to copy genetic information stored in DNA into units of transportable complementary RNA replica. Gene transcription occurs in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Unlike prokaryotic RNA polymerase that initiates the transcription of all different types of RNA, RNA polymerase in eukaryotes comes in three variations, each translating a different type of gene. A eukaryotic cell has a nucleus that separates the processes of transcription and translation. Eukaryotic transcription occurs within the nucleus where DNA is packaged into nucleosomes and higher order chromatin structures. The complexity of the eukaryotic genome necessitates a great variety and complexity of gene expression control.
Numerous key discoveries in biology have emerged from studies of RNA, including seminal work in the fields of biochemistry, genetics, microbiology, molecular biology, molecular evolution and structural biology. As of 2010, 30 scientists have been awarded Nobel Prizes for experimental work that includes studies of RNA. Specific discoveries of high biological significance are discussed in this article.
Somatic hypermutation is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it, as seen during class switching. A major component of the process of affinity maturation, SHM diversifies B cell receptors used to recognize foreign elements (antigens) and allows the immune system to adapt its response to new threats during the lifetime of an organism. Somatic hypermutation involves a programmed process of mutation affecting the variable regions of immunoglobulin genes. Unlike germline mutation, SHM affects only an organism's individual immune cells, and the mutations are not transmitted to the organism's offspring. Because this mechanism is merely selective and not precisely targeted, somatic hypermutation has been strongly implicated in the development of B-cell lymphomas and many other cancers.
This glossary of genetics is a list of definitions of terms and concepts commonly used in the study of genetics and related disciplines in biology, including molecular biology, cell biology, and evolutionary biology. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical detail, see the article corresponding to each term. For related terms, see Glossary of evolutionary biology.
This glossary of cell and molecular biology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts commonly used in the study of cell biology, molecular biology, and related disciplines, including genetics, microbiology, and biochemistry. It is split across two articles:
References
- ↑ Tyagi, Rajiv (2009). Computational Molecular Biology. Discovery Publishing House. ISBN 9788183564656.
- ↑ Vargas-Parada, L. (2010). "Kinetoplastids and their networks of interlocked DNA". Nature Education. 3 (9): 63. Retrieved 2015-11-26.
- ↑ Hammar, Freya; Miller, Dennis L. (2023-03-02). "Genetic Diversity in the mtDNA of Physarum polycephalum". Genes. 14 (3): 628. doi: 10.3390/genes14030628 . ISSN 2073-4425. PMC 10048350 . PMID 36980901.
- ↑ Mahendran, R.; Spottswood, M. R.; Miller, D. L. (1991). "RNA editing by cytidine insertion in mitochondria of Physarum polycephalum". Nature. 349 (6308): 434–438. Bibcode:1991Natur.349..434M. doi:10.1038/349434a0. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 1825131. S2CID 4342992.