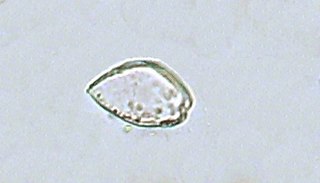
The Prorocentrales are a small order of dinoflagellates. They are distinguished by having their two flagella inserted apically, rather than ventrally as in other groups. One flagellum extends forward and the other circles its base, and there are no flagellar grooves. This arrangement is called desmokont, in contrast to the dinokont arrangement found in other groups. Accordingly, the Prorocentrales may be called desmoflagellates, and in some classifications were treated as a separate class Desmophyceae.

Fucus vesiculosus, known by the common names bladder wrack, black tang, rockweed, bladder fucus, sea oak, black tany, cut weed, dyers fucus, red fucus, and rock wrack is a seaweed found on the coasts of the North Sea, the western Baltic Sea, and the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. It was the original source of iodine, discovered in 1811, and was used extensively to treat goitre, a swelling of the thyroid gland related to iodine deficiency.

Laminaria is a genus of 31 species of brown algae commonly called "kelp". Some species are also referred to as tangle. This economically important genus is characterized by long, leathery laminae and relatively large size. Some species are referred to by the common name Devil's apron, due to their shape, or sea colander, due to the perforations present on the lamina. It is found in the north Atlantic Ocean and the northern Pacific Ocean at depths from 8 to 30 m. Laminaria form a habitat for many fish and invertebrates.

AlgaeBase is a global species database of information on all groups of algae, as well as one group of flowering plants, the sea-grasses.
Bryopsidella is a genus of green algae in the family Bryopsidaceae.

The Rivulariaceae are a family of cyanobacteria within the Nostocales in which the filaments (trichomes) are tapered from wider at the base to narrower at the tip.
Pyrenomonas is a genus of cryptomonad.
Dinophysis norvegica is a species of dinoflagellate most commonly associated with diarrheal shellfish poisoning.

Chorda is a genus of thalloid brown algae including two species. Its members are known by a number of common names including: mermaid's fishing line, tsurumo, ruálach, doruithe briain, sea laces, mermaids line, roccálach, ruadhálach, gemeine meersaite, bootlace weed, seatwine, zottige meersaite, dead men's ropes, mermaid's tresses, cat gut and sea lace.

Erythrotrichiaceae is a red algae family in the order Erythropeltidales.

Erythrotrichia is a red algae genus in the family Erythrotrichiaceae.
Amphidinium carterae is a species of dinoflagellates. It was first described by Edward M. Hulburt in 1957, and was named in honour of the British phycologist Nellie Carter-Montford. The type locality is Great Pond, Barnstable County, Massachusetts, USA. It is a toxic species.

Cystoseira foeniculacea is a species of brown alga in the genus Cystoseira.
Cyanonephron elegans is a freshwater species of cyanobacteria in the family Synechococcaceae. It is described in the Netherlands, Siberia, Russia and Queensland, Australia.

Acetabularia acetabulum is a species of green alga in the family Polyphysaceae.

Palmariales is an order of marine algae. It includes the edible seaweed dulse.









