Related Research Articles

Astrobiology, and the related field of exobiology, is an interdisciplinary scientific field that studies the origins, early evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe. Astrobiology is the multidisciplinary field that investigates the deterministic conditions and contingent events with which life arises, distributes, and evolves in the universe. It considers the question of whether extraterrestrial life exists, and if it does, how humans can detect it.

Extraterrestrial life, sometimes colloquially referred to as alien life, is life that may occur outside Earth and which did not originate on Earth. No extraterrestrial life has yet been conclusively detected, although efforts are underway. Such life might range from simple forms comparable to prokaryotes, to intelligent beings, possibly bringing forth civilizations that might be far more advanced than humankind. The Drake equation speculates about the existence of sapient life elsewhere in the universe. The science of extraterrestrial life in all its forms is known as astrobiology, the multidisciplinary field that investigates the deterministic conditions and contingent events with which life arises, distributes, and evolves in the universe.

Europa, or Jupiter II, is the smallest of the four Galilean moons orbiting Jupiter, and the sixth-closest to the planet of all the 80 known moons of Jupiter. It is also the sixth-largest moon in the Solar System. Europa was discovered in 1610 by Galileo Galilei and was named after Europa, the Phoenician mother of King Minos of Crete and lover of Zeus.

The Jupiter Icy Moons Orbiter (JIMO) was a proposed NASA spacecraft designed to explore the icy moons of Jupiter. The main target was Europa, where an ocean of liquid water may harbor alien life. Ganymede and Callisto, which are now thought to have liquid, salty oceans beneath their icy surfaces, were also targets of interest for the probe.

Linda A. Morabito, also known as Linda Kelly, Linda Hyder, and Linda Morabito-Meyer, is the astronomer who discovered volcanic activity on Io, a moon of Jupiter. She made this finding on March 9, 1979, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. At the time of her discovery, she was serving as Cognizant Engineer over the Optical Navigation Image Processing System (ONIPS) on the Voyager deep space mission Navigation Team. While performing image processing analysis of a Voyager 1 picture taken for spacecraft navigation, she detected a 270 kilometres (170 mi) tall cloud off the limb of Io. The cloud was of volcanic origin. This was the first time in history that active volcanism was detected off of Earth. Her discovery is considered by some planetary scientists as the largest discovery of the planetary exploration program that has come out of Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Morabito is currently an associate professor of astronomy at Victor Valley College. Linda Morabito Meyer is also the author of a memoir, Parallel Universes, a Memoir from the Edges of Space and Time.

The Europa Jupiter System Mission – Laplace (EJSM-Laplace) was a proposed joint NASA/ESA uncrewed space mission slated to launch around 2020 for the in-depth exploration of Jupiter's moons with a focus on Europa, Ganymede and Jupiter's magnetosphere. The mission would have comprised at least two independent elements, NASA's Jupiter Europa Orbiter (JEO) and ESA's Jupiter Ganymede Orbiter (JGO), to perform coordinated studies of the Jovian system.

NASA's large strategic science missions or large strategic missions, formerly known as Flagship missions or Flagship-class missions, are the costliest and most capable NASA science spacecraft. Flagship missions exist within all four divisions of NASA's Science Mission Directorate (SMD): the astrophysics, Earth science, heliophysics and planetary science divisions.
Laplace-P is a proposed orbiter and lander by the Russian Federal Space Agency designed to study the Jovian moon system and explore Ganymede with a lander.

Mark Robert Showalter is a Senior Research Scientist at the SETI Institute. He is the discoverer of six moons and three planetary rings. He is the Principal Investigator of NASA's Planetary Data System Rings Node, a co-investigator on the Cassini–Huygens mission to Saturn, and works closely with the New Horizons mission to Pluto.

Adriana C. Ocampo Uria is a Colombian planetary geologist and a Science Program Manager at NASA Headquarters. In 1970, Ocampo emigrated to California and completed her Master in Sciences at California State University, Northridge and finished her PhD at the Vrije Universiteit in the Netherlands. During high school and graduate studies she worked that the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, where she serves as the science coordinator for many planetary missions.

Europa Clipper is an interplanetary mission in development by NASA comprising an orbiter. Planned for launch in October 2024, the spacecraft is being developed to study the Galilean moon Europa through a series of flybys while in orbit around Jupiter.
Journey to Enceladus and Titan (JET) is an astrobiology mission concept to assess the habitability potential of Enceladus and Titan, moons of Saturn.
THEO is a feasibility study for a New Frontiers class orbiter mission to Enceladus that would directly sample its south pole water plumes in order to study its internal habitability and to search for biosignatures. Specifically, it would take advantage of the direct sampling opportunities of a subsurface ocean.

Christina "Chrissy" Richey is an American planetary scientist and astrophysicist working at Jet Propulsion Laboratory in La Cañada Flintridge, California. Richey is a project staff scientist for the Europa Clipper mission and is a research technologist in the Astrophysics and Space Sciences Section. Prior to working at JPL, Richey worked as contractor for Arctic Slope Regional Corporation at NASA Headquarters in Washington, D.C. They were a program officer in NASA's Planetary Science Division, the deputy program scientist for the OSIRIS-REx mission, and the deputy science advisor for research and analysis for the Science Mission Directorate.

The Europa Lander is a proposed astrobiology mission concept by NASA to send a lander to Europa, an icy moon of Jupiter. If funded and developed as a large strategic science mission, it would be launched in 2027 to complement the studies by the Europa Clipper orbiter mission and perform analyses on site.
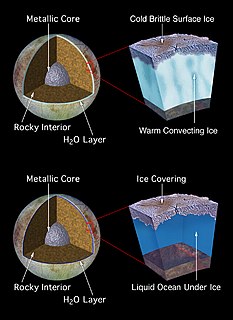
The Ocean Worlds Exploration Program (OWEP) is a NASA program to explore ocean worlds in the outer Solar System that could possess subsurface oceans to assess their habitability and to seek biosignatures of simple extraterrestrial life.
The Mapping Imaging Spectrometer for Europa (MISE) is an imaging near infrared spectrometer on board the Europa Clipper mission to Jupiter's moon Europa. MISE will examine Europa's surface composition and relate it to the habitability of its internal water ocean.
The Interior Characterization of Europa using Magnetometry (ICEMAG) is a multi-frequency magnetometer that was proposed to be flown on board the Europa Clipper mission to Jupiter's moon Europa, but its inclusion was cancelled in March 2019. Magnetic induction is a powerful tool for probing the subsurface and determine Europa's ocean depth, salinity, and ice shell thickness, as well as detecting erupting plume activity.

The Planetary Missions Program Office is a division of NASA headquartered at the Marshall Space Flight Center, formed by the agency's Science Mission Directorate (SMD). Succeeding the Discovery and New Frontiers Program Office, it was established in 2014 to manage the Discovery and New Frontiers programs of low and medium-cost missions by third-party institutions, and the Solar System Exploration program of NASA-led missions that focus on prioritized planetary science objectives. The Discovery and New Frontiers programs were established in 1992 and 2001 respectively, and have launched fourteen primary missions together, along with two missions launched under the administration of the Planetary Missions Program Office. The Solar System Exploration Program was established alongside the office, with three missions planned for launch under the new program.
Melissa McGrath is an astronomer whose expertise is the atmosphere and magnetosphere of our Solar System planets and their moon. Her main interest has focused on imaging and spectroscopic studies of Jupiter’s Galilean moons. She is currently co-investigator on the ultraviolet spectrometer instrument on ESA JUICE mission to Ganymede, and co-investigator on two proposed instruments on the NASA Europa Clipper mission. McGrath is senior scientist at SETI Institute in Mountain View, California.
References
- ↑ Birth year from Library of Congress catalog entry, retrieved 2022-08-14
- 1 2 3 "Cynthia Phillips: Planetary Geologist, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL)", NASA Science: Solar System Exploration, NASA, retrieved 2022-08-14
- 1 2 "Cynthia Phillips", Meet Our Scientists, SETI Institute, archived from the original on 2015-09-10
- ↑ Surface of Jupiter’s Moon Europa Churned by Small Impacts, NASA, July 12, 2021, retrieved 2022-08-14
- ↑ Conditt, J. (March 11, 2018), "NASA wants to change the way we think about the habitable zone", Engadget, retrieved 2022-08-14
- ↑ Biographical sketch (PDF), SETI Institute, 2010, archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-08-10
- ↑ PTYS/LPL Alumni Directory, University of Arizona Lunar & Planetary Laboratory, retrieved 2022-08-14
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Cynthia Phillips", About the author, Simon & Schuster, retrieved 2022-08-14