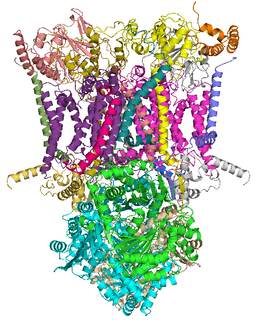
The coenzyme Q : cytochrome c – oxidoreductase, sometimes called the cytochrome bc1 complex, and at other times complex III, is the third complex in the electron transport chain, playing a critical role in biochemical generation of ATP. Complex III is a multisubunit transmembrane protein encoded by both the mitochondrial and the nuclear genomes. Complex III is present in the mitochondria of all animals and all aerobic eukaryotes and the inner membranes of most eubacteria. Mutations in Complex III cause exercise intolerance as well as multisystem disorders. The bc1 complex contains 11 subunits, 3 respiratory subunits, 2 core proteins and 6 low-molecular weight proteins.

Stearoyl-CoA desaturase (Δ-9-desaturase) is an endoplasmic reticulum enzyme that catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the formation of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), specifically oleate and palmitoleate from stearoyl-CoA and palmitoyl-CoA. Oleate and palmitoleate are major components of membrane phospholipids, cholesterol esters and alkyl-diacylglycerol. In humans, the enzyme is encoded by the SCD gene.
Ascorbate peroxidase (or L-ascorbate peroxidase, APX) (EC 1.11.1.11) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Cytochrome-b5 reductase is a NADH-dependent enzyme that converts ferricytochrome from a Fe3+ form to a Fe2+ form. It contains FAD and catalyzes the reaction:
Formate dehydrogenases are a set of enzymes that catalyse the oxidation of formate to carbon dioxide, donating the electrons to a second substrate, such as NAD+ in formate:NAD+ oxidoreductase (EC 1.17.1.9) or to a cytochrome in formate:ferricytochrome-b1 oxidoreductase (EC 1.2.2.1).
In enzymology, a CMP-N-acetylneuraminate monooxygenase (EC 1.14.18.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a stearoyl-CoA 9-desaturase (EC 1.14.19.1) is an enzyme used to produce the monounsaturated fatty acid oleic acid from the saturated fatty acid stearic acid. It catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a carbon-monoxide dehydrogenase (cytochrome b-561) (EC 1.2.2.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cytochrome-c3 hydrogenase (EC 1.12.2.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycine dehydrogenase (cytochrome) (EC 1.4.2.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an iron—cytochrome-c reductase (created 1972 as EC 1.9.99.1, transferred 2014 to EC 1.9.98.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a NADPH—cytochrome-c2 reductase (EC 1.6.2.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NADPH—hemoprotein reductase (EC 1.6.2.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Cytochrome c nitrite reductase (ccNiR) is a bacterial enzyme that catalyzes the six electron reduction of nitrite to ammonia; an important step in the biological nitrogen cycle. The enzyme catalyses the second step in the two step conversion of nitrate to ammonia, which allows certain bacteria to use nitrite as a terminal electron acceptor, rather than oxygen, during anaerobic conditions. During this process, ccNiR draws electrons from the quinol pool, which are ultimately provided by a dehydrogenase such as formate dehydrogenase or hydrogenase. These dehydrogenases are responsible for generating a proton motive force.
In enzymology, a nitrite reductase (NO-forming) (EC 1.7.2.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Thiosulfate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a trimethylamine-N-oxide reductase (cytochrome c) (EC 1.7.2.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Nitric oxide reductase (cytochrome c) (EC 1.7.2.5) is an enzyme with systematic name nitrous oxide:ferricytochrome-c oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Hydroxylamine dehydrogenase (EC 1.7.2.6, HAO (ambiguous)) is an enzyme with systematic name hydroxylamine:ferricytochrome-c oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Dimethyl sulfide:cytochrome c2 reductase (EC 1.8.2.4) is an enzyme with systematic name dimethyl sulfide:cytochrome-c2 oxidoreductase. It is also known by the name dimethylsulfide dehydrogenase (Ddh). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction









