
macOS Server, formerly Mac OS X Server and OS X Server, is a series of Unix-like server operating systems developed by Apple Inc. and based on macOS. macOS Server adds server functionality and system administration tools to macOS and provides tools to manage both macOS-based computers and iOS-based devices.

GNOME Evolution is the official personal information manager for GNOME. It has been an official part of GNOME since Evolution 2.0 was included with the GNOME 2.8 release in September 2004. It combines e-mail, address book, calendar, task list and note-taking features. Its user interface and functionality is similar to Microsoft Outlook. Evolution is free software licensed under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL).
WebDAV is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) that allows clients to perform remote Web content authoring operations. WebDAV is defined in RFC 4918 by a working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force.

SOGo is an open source collaborative software (groupware) server with a focus on simplicity and scalability.
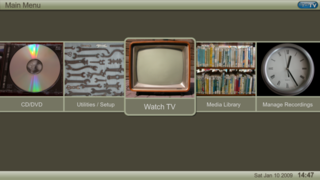
MythTV is a free and open-source home entertainment application with a simplified "10-foot user interface" design for the living room TV. It turns a computer with the necessary hardware into a network streaming digital video recorder, a digital multimedia home entertainment system, or home theater personal computer. It can be considered a free and open-source alternative to TiVo or Windows Media Center. It runs on various operating systems, primarily Linux, macOS, and FreeBSD.
Calendaring Extensions to WebDAV, or CalDAV, is an Internet standard allowing a client to access scheduling information on a remote server. It extends WebDAV specification and uses iCalendar format for the data. The access protocol is defined by RFC 4791. It allows multiple client access to the same information thus allowing cooperative planning and information sharing. Many server and client applications support the protocol. Extensions to CalDAV for automated scheduling are also standardized, as RFC 6638.

m23 is a software distribution and management system for the Debian, Ubuntu, Kubuntu Linux, Xubuntu, Linux Mint, elementary OS, Fedora, CentOS and openSUSE distributions.
PulseAudio is a network-capable sound server program distributed via the freedesktop.org project. It runs mainly on Linux, various BSD distributions such as FreeBSD and OpenBSD, macOS, as well as Illumos distributions and the Solaris operating system. Microsoft Windows was previously supported via MinGW. The Windows port has not been updated since 2011, however.
The Calendar and Contacts Server project is an Apple-developed standards-compliant server implementing the CalDAV and CardDAV protocols. It provides a shared location on the network allowing multiple users to store and edit calendaring and contact information. The server was publicly released during Apple's Worldwide Developers Conference on August 7, 2006 as iCal Server and Address Book Server.

CNR, or One-Click & Run, was a free one-click software delivery service that was created to make finding and installing Linux software easier. It assists the user in finding and installing software on their computer, it sits dormant in the system tray when not in use.
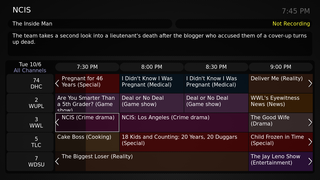
Mythbuntu is a discontinued media center operating system based on Ubuntu, which integrated the MythTV media center software as its main function, and did not install with all of the programs included with Ubuntu.
EGroupware is free open-source groupware software intended for businesses from small to enterprises. Its primary functions allow users to manage contacts, appointments, projects and to-do lists. EGroupware is based on PHP. The projects spreads its software under the terms of GNU General Public License (GPL).
The Linux Schools Project is an operating system designed for schools. It is a Linux distribution based on Ubuntu. The project maintains two custom distributions, with one designed for use on servers and the other for use with the server version on client machines. The server distribution is the official Karoshi, while the client is known as Karoshi Client.

Ubuntu One is an OpenID-based single sign-on service operated by Canonical Ltd. to allow users to log onto many Canonical-owned Web sites. Until April 2014, Ubuntu One was also a file hosting service and music store that allowed users to store data "in the cloud".
vCard Extensions to WebDAV (CardDAV) is an address book client/server protocol designed to allow users to access and share contact data on a server.

ownCloud is a suite of client–server software for creating and using file hosting services. ownCloud functionally has similarities to the widely used Dropbox. The primary functional difference between ownCloud and Dropbox is that ownCloud does not offer data centre capacity to host stored files. The Server Edition of ownCloud is free and open-source, thereby allowing anyone to install and operate it without charge on their own private server.
A comparison of CalDAV and CardDAV implementations offers two overviews of client and server computer software implementations of the CalDAV and CardDAV protocols.
Snap is a software packaging and deployment system developed by Canonical for the operating systems that use the Linux kernel. The packages, called snaps, and the tool for using them, snapd, work across a range of Linux distributions and allow upstream software developers to distribute their applications directly to users. Snaps are self-contained applications running in a sandbox with mediated access to the host system. Snap was originally released for cloud applications but was later ported to work for Internet of Things devices and desktop applications too.

Flatpak is a utility for software deployment and package management for Linux. It is advertised as offering a sandbox environment in which users can run application software in isolation from the rest of the system.

Nextcloud is a suite of client-server software for creating and using file hosting services. Nextcloud is free and open-source, which means that anyone is allowed to install and operate it on their own private server devices.










