Related Research Articles

In computer architecture, a bus is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. This expression covers all related hardware components and software, including communication protocols.
Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a logic family built from bipolar junction transistors. Its name signifies that transistors perform both the logic function and the amplifying function, as opposed to earlier resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and diode–transistor logic (DTL).

In computing, an expansion card is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot on a computer's motherboard to add functionality to a computer system. Sometimes the design of the computer's case and motherboard involves placing most of these slots onto a separate, removable card. Typically such cards are referred to as a riser card in part because they project upward from the board and allow expansion cards to be placed above and parallel to the motherboard.

The Intel 8085 ("eighty-eighty-five") is an 8-bit microprocessor produced by Intel and introduced in March 1976. It is software-binary compatible with the more-famous Intel 8080 with only two minor instructions added to support its added interrupt and serial input/output features. However, it requires less support circuitry, allowing simpler and less expensive microcomputer systems to be built. The "5" in the part number highlighted the fact that the 8085 uses a single +5-volt (V) power supply by using depletion-mode transistors, rather than requiring the +5 V, −5 V and +12 V supplies needed by the 8080. This capability matched that of the competing Z80, a popular 8080-derived CPU introduced the year before. These processors could be used in computers running the CP/M operating system.

VMEbus is a computer bus standard, originally developed for the Motorola 68000 line of CPUs, but later widely used for many applications and standardized by the IEC as ANSI/IEEE 1014-1987. It is physically based on Eurocard sizes, mechanicals and connectors, but uses its own signalling system, which Eurocard does not define. It was first developed in 1981 and continues to see widespread use today.

The DIN connector is an electrical connector that was standardized by the Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN), the German Institute for Standards, in the mid 1950's, initial with 3 pins for mono, but when stereo connections and gear appeared in late 1950's, versions with 5 pins or more were launched. The male DIN connectors (plugs) feature a 13.2 mm diameter metal shield with a notch that limits the orientation in which plug and socket can mate. The range of DIN connectors, different only in the configuration of the pins, have been standardized as DIN 41524 / IEC/DIN EN 60130-9 ; DIN 45322 ; DIN 45329 / IEC/DIN EN 60130–9 ; and DIN 45326 / IEC/DIN EN 60130-9.
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a de facto standard for synchronous serial communication, used primarily in embedded systems for short-distance wired communication between integrated circuits.

The D-subminiature or D-sub is a common type of electrical connector. They are named for their characteristic D-shaped metal shield. When they were introduced, D-subs were among the smallest connectors used on computer systems.

A remote terminal unit (RTU) is a microprocessor-controlled electronic device that interfaces objects in the physical world to a distributed control system or SCADA system by transmitting telemetry data to a master system, and by using messages from the master supervisory system to control connected objects. Other terms that may be used for RTU are remote telemetry unit and remote telecontrol unit.
A general-purpose input/output (GPIO) is an uncommitted digital signal pin on an integrated circuit or electronic circuit board which may be used as an input or output, or both, and is controllable by software.
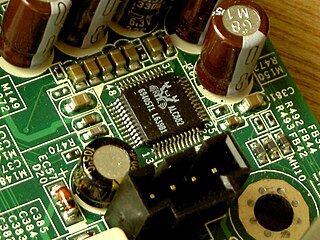
Intel High Definition Audio (IHDA) (also called HD Audio or development codename Azalia) is a specification for the audio sub-system of personal computers. It was released by Intel in 2004 as the successor to their AC'97 PC audio standard.

Multibus is a computer bus standard used in industrial systems. It was developed by Intel Corporation and was adopted as the IEEE 796 bus.

The STEbus is a non-proprietary, processor-independent, computer bus with 8 data lines and 20 address lines. It was popular for industrial control systems in the late 1980s and early 1990s before the ubiquitous IBM PC dominated this market. STE stands for STandard Eurocard.

In computer hardware, a port serves as an interface between the computer and other computers or peripheral devices. In computer terms, a port generally refers to the part of a computing device available for connection to peripherals such as input and output devices. Computer ports have many uses, to connect a monitor, webcam, speakers, or other peripheral devices. On the physical layer, a computer port is a specialized outlet on a piece of equipment to which a plug or cable connects. Electronically, the several conductors where the port and cable contacts connect, provide a method to transfer signals between devices.

The DAI personal computer is an early home computer from the Belgian company Data Applications International.The DAI came to market in 1980. It provided many pioneering features such as high resolution color graphics, a maths co-processor, and a pre-compiling BASIC interpreter. However, it never became a commercial success.
RM Nimbus was a range of personal computers from British company Research Machines sold from 1985 until the early 1990s, after which the designation Nimbus was discontinued. The first of these computers, the RM Nimbus PC-186, was not IBM PC compatible, but its successors the PC-286 and PC-386 were. RM computers were predominantly sold to schools and colleges in the United Kingdom for use as LAN workstations in classrooms.

The Intel 8255 Programmable Peripheral Interface (PPI) chip was developed and manufactured by Intel in the first half of the 1970s for the Intel 8080 microprocessor. The 8255 provides 24 parallel input/output lines with a variety of programmable operating modes.
Audio connectors and video connectors are electrical or optical connectors for carrying audio or video signals. Audio interfaces or video interfaces define physical parameters and interpretation of signals. For digital audio and digital video, this can be thought of as defining the physical layer, data link layer, and most or all of the application layer. For analog audio and analog video these functions are all represented in a single signal specification like NTSC or the direct speaker-driving signal of analog audio.
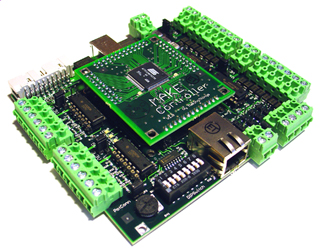
A single-board microcontroller is a microcontroller built onto a single printed circuit board. This board provides all of the circuitry necessary for a useful control task: a microprocessor, I/O circuits, a clock generator, RAM, stored program memory and any necessary support ICs. The intention is that the board is immediately useful to an application developer, without requiring them to spend time and effort to develop controller hardware.

The Arduino Uno is an open-source microcontroller board based on the Microchip ATmega328P microcontroller (MCU) and developed by Arduino.cc and initially released in 2010. The microcontroller board is equipped with sets of digital and analog input/output (I/O) pins that may be interfaced to various expansion boards (shields) and other circuits. The board has 14 digital I/O pins, 6 analog I/O pins, and is programmable with the Arduino IDE, via a type B USB cable. It can be powered by a USB cable or a barrel connector that accepts voltages between 7 and 20 volts, such as a rectangular 9-volt battery. It has the same microcontroller as the Arduino Nano board, and the same headers as the Leonardo board. The hardware reference design is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike 2.5 license and is available on the Arduino website. Layout and production files for some versions of the hardware are also available.