This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page . (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
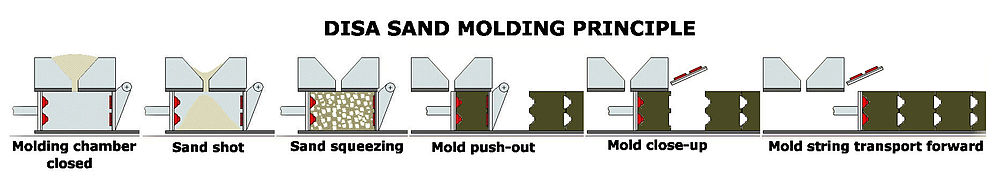
DISAMATIC is an automatic production line used for fast manufacturing of sand molds for sand casting. This process is often used to mass manufacture metal castings for the automotive and machine industries.