Related Research Articles

Retroviral integrase (IN) is an enzyme produced by a retrovirus that integrates its genetic information into that of the host cell it infects. Retroviral INs are not to be confused with phage integrases (recombinases) used in biotechnology, such as λ phage integrase, as discussed in site-specific recombination.

Luciferase is a generic term for the class of oxidative enzymes that produce bioluminescence, and is usually distinguished from a photoprotein. The name was first used by Raphaël Dubois who invented the words luciferin and luciferase, for the substrate and enzyme, respectively. Both words are derived from the Latin word lucifer, meaning "lightbearer", which in turn is derived from the Latin words for "light" (lux) and "to bring or carry" (ferre).

Helix-turn-helix is a DNA-binding protein (DBP). The helix-turn-helix (HTH) is a major structural motif capable of binding DNA. Each monomer incorporates two α helices, joined by a short strand of amino acids, that bind to the major groove of DNA. The HTH motif occurs in many proteins that regulate gene expression. It should not be confused with the helix–loop–helix motif.

In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is a redox-active coenzyme associated with various proteins, which is involved with several enzymatic reactions in metabolism. A flavoprotein is a protein that contains a flavin group, which may be in the form of FAD or flavin mononucleotide (FMN). Many flavoproteins are known: components of the succinate dehydrogenase complex, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, and a component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
Cryptochromes are a class of flavoproteins found in plants and animals that are sensitive to blue light. They are involved in the circadian rhythms and the sensing of magnetic fields in a number of species. The name cryptochrome was proposed as a portmanteau combining the chromatic nature of the photoreceptor, and the cryptogamic organisms on which many blue-light studies were carried out.

Flavoproteins are proteins that contain a nucleic acid derivative of riboflavin. These proteins are involved in a wide array of biological processes, including removal of radicals contributing to oxidative stress, photosynthesis, and DNA repair. The flavoproteins are some of the most-studied families of enzymes.
Photolyases are DNA repair enzymes that repair damage caused by exposure to ultraviolet light. These enzymes require visible light both for their own activation and for the actual DNA repair. The DNA repair mechanism involving photolyases is called photoreactivation. They mainly convert pyrimidine dimers into a normal pair of pyrimidine bases.
Thermus thermophilus is a Gram-negative bacterium used in a range of biotechnological applications, including as a model organism for genetic manipulation, structural genomics, and systems biology. The bacterium is extremely thermophilic, with an optimal growth temperature of about 65 °C (149 °F). Thermus thermophilus was originally isolated from a thermal vent within a hot spring in Izu, Japan by Tairo Oshima and Kazutomo Imahori. The organism has also been found to be important in the degradation of organic materials in the thermogenic phase of composting. T. thermophilus is classified into several strains, of which HB8 and HB27 are the most commonly used in laboratory environments. Genome analyses of these strains were independently completed in 2004.

Ku is a dimeric protein complex that binds to DNA double-strand break ends and is required for the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA repair. Ku is evolutionarily conserved from bacteria to humans. The ancestral bacterial Ku is a homodimer. Eukaryotic Ku is a heterodimer of two polypeptides, Ku70 (XRCC6) and Ku80 (XRCC5), so named because the molecular weight of the human Ku proteins is around 70 kDa and 80 kDa. The two Ku subunits form a basket-shaped structure that threads onto the DNA end. Once bound, Ku can slide down the DNA strand, allowing more Ku molecules to thread onto the end. In higher eukaryotes, Ku forms a complex with the DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) to form the full DNA-dependent protein kinase, DNA-PK. Ku is thought to function as a molecular scaffold to which other proteins involved in NHEJ can bind, orienting the double-strand break for ligation.

A DNA clamp, also known as a sliding clamp, is a protein complex that serves as a processivity-promoting factor in DNA replication. As a critical component of the DNA polymerase III holoenzyme, the clamp protein binds DNA polymerase and prevents this enzyme from dissociating from the template DNA strand. The clamp-polymerase protein–protein interactions are stronger and more specific than the direct interactions between the polymerase and the template DNA strand; because one of the rate-limiting steps in the DNA synthesis reaction is the association of the polymerase with the DNA template, the presence of the sliding clamp dramatically increases the number of nucleotides that the polymerase can add to the growing strand per association event. The presence of the DNA clamp can increase the rate of DNA synthesis up to 1,000-fold compared with a nonprocessive polymerase.

EF-Tu is a prokaryotic elongation factor responsible for catalyzing the binding of an aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) to the ribosome. It is a G-protein, and facilitates the selection and binding of an aa-tRNA to the A-site of the ribosome. As a reflection of its crucial role in translation, EF-Tu is one of the most abundant and highly conserved proteins in prokaryotes. It is found in eukaryotic mitochondria as TUFM.

Type II topoisomerases are topoisomerases that cut both strands of the DNA helix simultaneously in order to manage DNA tangles and supercoils. They use the hydrolysis of ATP, unlike Type I topoisomerase. In this process, these enzymes change the linking number of circular DNA by ±2. Topoisomerases are ubiquitous enzymes, found in all living organisms.
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DHODH gene on chromosome 16. The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the fourth enzymatic step, the ubiquinone-mediated oxidation of dihydroorotate to orotate, in de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis. This protein is a mitochondrial protein located on the outer surface of the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM). Inhibitors of this enzyme are used to treat autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.

4-hydroxyphenylacetate 3-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.14.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, proline dehydrogenase (PRODH) (EC 1.5.5.2, formerly EC 1.5.99.8) is an enzyme of the oxidoreductase family, active in the oxidation of L-proline to (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate during proline catabolism. The end product of this reaction is then further oxidized in a (S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase (P5CDH)-dependent reaction of the proline metabolism, or spent to produce ornithine, a crucial metabolite of ornithine and arginine metabolism. The systematic name of this enzyme class is L-proline:quinone oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include L-proline dehydrogenase, L-proline oxidase,and L-proline:(acceptor) oxidoreductase. It employs one cofactor, FAD, which requires riboflavin (vitamin B2).
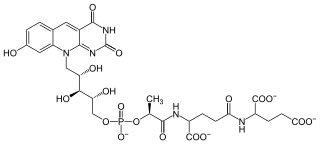
Coenzyme F420 or 8-hydroxy-5-deazaflavin is a coenzyme (sometimes called a cofactor) involved in redox reactions in methanogens, in many Actinomycetota, and sporadically in other bacterial lineages. It is a flavin derivative with an absorption maximum at 420 nm—hence its name. The coenzyme is a substrate for coenzyme F420 hydrogenase, 5,10-methylenetetrahydromethanopterin reductase and methylenetetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenase.

EF-P is an essential protein that in bacteria stimulates the formation of the first peptide bonds in protein synthesis. Studies show that EF-P prevents ribosomes from stalling during the synthesis of proteins containing consecutive prolines. EF-P binds to a site located between the binding site for the peptidyl tRNA and the exiting tRNA. It spans both ribosomal subunits with its amino-terminal domain positioned adjacent to the aminoacyl acceptor stem and its carboxyl-terminal domain positioned next to the anticodon stem-loop of the P site-bound initiator tRNA. The EF-P protein shape and size is very similar to a tRNA and interacts with the ribosome via the exit “E” site on the 30S subunit and the peptidyl-transferase center (PTC) of the 50S subunit. EF-P is a translation aspect of an unknown function, therefore It probably functions indirectly by altering the affinity of the ribosome for aminoacyl-tRNA, thus increasing their reactivity as acceptors for peptidyl transferase.

The prokaryotic riboflavin biosynthesis protein is a bifunctional enzyme found in bacteria that catalyzes the phosphorylation of riboflavin into flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and the adenylylation of FMN into flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). It consists of a C-terminal riboflavin kinase and an N-terminal FMN-adenylyltransferase. This bacterial protein is functionally similar to the monofunctional riboflavin kinases and FMN-adenylyltransferases of eukaryotic organisms, but only the riboflavin kinases are structurally homologous.

In molecular biology, the H2TH domain is a DNA-binding domain found in DNA glycosylase/AP lyase enzymes, which are involved in base excision repair of DNA damaged by oxidation or by mutagenic agents. Most damage to bases in DNA is repaired by the base excision repair pathway. These enzymes are primarily from bacteria, and have both DNA glycosylase activity EC 3.2.2.- and AP lyase activity EC 4.2.99.18. Examples include formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylases and endonuclease VIII (Nei).

Archaeal transcription factor B is a protein family of extrinsic transcription factors that guide the initiation of RNA transcription in organisms that fall under the domain of Archaea. It is homologous to eukaryotic TFIIB and, more distantly, to bacterial sigma factor. Like these proteins, it is involved in forming transcription preinitiation complexes. Its structure includes several conserved motifs which interact with DNA and other transcription factors, notably the single type of RNA polymerase that performs transcription in Archaea.
References
- ↑ Tamada T, Kitadokoro K, Higuchi Y, Inaka K, Yasui A, de Ruiter PE, Eker AP, Miki K (November 1997). "Crystal structure of DNA photolyase from Anacystis nidulans". Nature Structural Biology. 4 (11): 887–91. doi: 10.1038/nsb1197-887 . PMID 9360600. S2CID 7041623.
- 1 2 Sancar A (June 2003). "Structure and function of DNA photolyase and cryptochrome blue-light photoreceptors". Chemical Reviews. 103 (6): 2203–37. doi:10.1021/cr0204348. PMID 12797829.
- 1 2 Scheerer P, Zhang F, Kalms J, von Stetten D, Krauß N, Oberpichler I, Lamparter T (May 2015). "The class III cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer photolyase structure reveals a new antenna chromophore binding site and alternative photoreduction pathways". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 290 (18): 11504–14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.637868 . PMC 4416854 . PMID 25784552.
- 1 2 Kiontke S, Gnau P, Haselsberger R, Batschauer A, Essen LO (July 2014). "Structural and evolutionary aspects of antenna chromophore usage by class II photolyases". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 289 (28): 19659–69. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.542431 . PMC 4094076 . PMID 24849603.
- ↑ Klar T, Kaiser G, Hennecke U, Carell T, Batschauer A, Essen LO (November 2006). "Natural and non-natural antenna chromophores in the DNA photolyase from Thermus thermophilus". ChemBioChem. 7 (11): 1798–806. doi:10.1002/cbic.200600206. PMID 17051659. S2CID 44346656.
- 1 2 Glas AF, Maul MJ, Cryle M, Barends TR, Schneider S, Kaya E, Schlichting I, Carell T (July 2009). "The archaeal cofactor F0 is a light-harvesting antenna chromophore in eukaryotes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 106 (28): 11540–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812665106 . PMC 2704855 . PMID 19570997.
- ↑ Oberpichler I, Pierik AJ, Wesslowski J, Pokorny R, Rosen R, Vugman M, Zhang F, Neubauer O, Ron EZ, Batschauer A, Lamparter T (31 October 2011). "A photolyase-like protein from Agrobacterium tumefaciens with an iron-sulfur cluster". PLOS ONE. 6 (10): e26775. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...626775O. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026775 . PMC 3204975 . PMID 22066008.