
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a set of communication standards for simultaneous digital transmission of voice, video, data, and other network services over the digitalised circuits of the public switched telephone network. Work on the standard began in 1980 at Bell Labs and was formally standardized in 1988 in the CCITT "Red Book". By the time the standard was released, newer networking systems with much greater speeds were available, and ISDN saw relatively little uptake in the wider market. One estimate suggests ISDN use peaked at a worldwide total of 25 million subscribers at a time when 1.3 billion analog lines were in use. ISDN has largely been replaced with digital subscriber line (DSL) systems of much higher performance.
In telecommunications, a customer-premises equipment or customer-provided equipment (CPE) is any terminal and associated equipment located at a subscriber's premises and connected with a carrier's telecommunication circuit at the demarcation point ("demarc"). The demarc is a point established in a building or complex to separate customer equipment from the equipment located in either the distribution infrastructure or central office of the communications service provider.
Digital subscriber line is a family of technologies that are used to transmit digital data over telephone lines. In telecommunications marketing, the term DSL is widely understood to mean asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL), the most commonly installed DSL technology, for Internet access.
Telephony is the field of technology involving the development, application, and deployment of telecommunication services for the purpose of electronic transmission of voice, fax, or data, between distant parties. The history of telephony is intimately linked to the invention and development of the telephone.
A symmetric digital subscriber line (SDSL) is a digital subscriber line (DSL) that transmits digital data over the copper wires of the telephone network, where the bandwidth in the downstream direction, from the network to the subscriber, is identical to the bandwidth in the upstream direction, from the subscriber to the network. This symmetric bandwidth can be considered to be the opposite of the asymmetric bandwidth offered by asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) technologies, where the upstream bandwidth is lower than the downstream bandwidth. SDSL is generally marketed at business customers, while ADSL is marketed at private as well as business customers.
The HomePNA Alliance is an incorporated non-profit industry association of companies that develops and standardizes technology for home networking over the existing coaxial cables and telephone wiring within homes, so new wires do not need to be installed.
Very high-speed digital subscriber line (VDSL) and very high-speed digital subscriber line 2 (VDSL2) are digital subscriber line (DSL) technologies providing data transmission faster than the earlier standards of asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) G.992.1, G.992.3 (ADSL2) and G.992.5 (ADSL2+).

A digital subscriber line access multiplexer is a network device, often located in telephone exchanges, that connects multiple customer digital subscriber line (DSL) interfaces to a high-speed digital communications channel using multiplexing techniques. Its cable internet (DOCSIS) counterpart is the cable modem termination system.
In telephony, pair gain is the transmission of multiple plain old telephone service (POTS) channels over the twisted pair local loop traditionally used for a single subscriber line in telephone systems. Pair gain has the effect of creating additional subscriber lines. This is typically used as an expedient way to solve subscriber line shortages at a location by using existing wiring, instead of installing new wires from the central office to the customer premises. The term was invented in the middle 20th century by analogy with earlier use of gain to extend telephone local loops far from the telephone exchange.

A telephone line or telephone circuit is a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system. It is designed to reproduce speech of a quality that is understandable. It is the physical wire or other signaling medium connecting the user's telephone apparatus to the telecommunications network, and usually also implies a single telephone number for billing purposes reserved for that user. Telephone lines are used to deliver landline telephone service and digital subscriber line (DSL) phone cable service to the premises. Telephone overhead lines are connected to the public switched telephone network. The voltage at a subscriber's network interface is typically 48 V between the ring and tip wires, with tip near ground and ring at –48 V.
A naked DSL, also known as standalone or dry loop DSL, is a digital subscriber line (DSL) without a PSTN service — or the associated dial tone. In other words, only a standalone DSL Internet service is provided on the local loop.
In telecommunications, ITU G.992.2 is an ITU standard for ADSL using discrete multitone modulation. G.lite does not strictly require the use of DSL filters, but like all variants of ADSL generally functions better with splitters.

A digital subscriber line (DSL) modem is a device used to connect a computer or router to a telephone line which provides the digital subscriber line (DSL) service for connection to the Internet, which is often called DSL broadband. The modem connects to a single computer or router, through an Ethernet port, USB port, or is installed in a computer PCI slot.

SpeedTouch is the brand name of a line of networking equipment produced by Alcatel and Technicolor SA. Before 27 January 2010 Technicolor was known as Thomson SA.
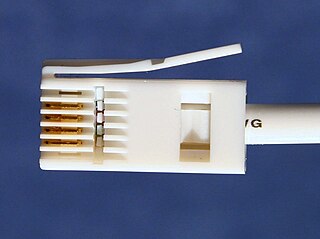
British telephone sockets were introduced in their current plug and socket form on 19 November 1981 by British Telecom to allow subscribers to connect their own telephones. The connectors are specified in British Standard BS 6312. Electrical characteristics of the telephone interface are specified by individual network operators, e.g. in British Telecom's SIN 351. Electrical characteristics required of British telephones used to be specified in BS 6305.

Annex J is a specification in ITU-T Recommendations G.992.3 and G.992.5 for all digital mode ADSL with improved spectral compatibility with ADSL over ISDN, which means that it is a type of naked DSL which will not disturb existing Annex B ADSL services in the same cable binder.

Asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) is a type of digital subscriber line (DSL) technology, a data communications technology that enables faster data transmission over copper telephone lines than a conventional voiceband modem can provide. ADSL differs from the less common symmetric digital subscriber line (SDSL). In ADSL, bandwidth and bit rate are said to be asymmetric, meaning greater toward the customer premises (downstream) than the reverse (upstream). Providers usually market ADSL as an Internet access service primarily for downloading content from the Internet, but not for serving content accessed by others.

A modulator-demodulator or modem is a computer hardware device that converts data from a digital format into a format suitable for an analog transmission medium such as telephone or radio. A modem transmits data by modulating one or more carrier wave signals to encode digital information, while the receiver demodulates the signal to recreate the original digital information. The goal is to produce a signal that can be transmitted easily and decoded reliably. Modems can be used with almost any means of transmitting analog signals, from light-emitting diodes to radio.
Homes typically have several kinds of home wiring, including electrical wiring for lighting and power distribution, permanently installed and portable appliances, telephone, heating or ventilation system control, and increasingly for home theatre and computer networks.

G.fast is a digital subscriber line (DSL) protocol standard for local loops shorter than 500 meters, with performance targets between 100 Mbit/s and 1 Gbit/s, depending on loop length. High speeds are only achieved over very short loops. Although G.fast was initially designed for loops shorter than 250 meters, Sckipio in early 2015 demonstrated G.fast delivering speeds over 100 Mbit/s at nearly 500 meters and the EU announced a research project.











