Telnet is a client/server application protocol that provides access to virtual terminals of remote systems on local area networks or the Internet. It is a protocol for bidirectional 8-bit communications. Its main goal was to connect terminal devices and terminal-oriented processes.

Wake-on-LAN is an Ethernet or Token Ring computer networking standard that allows a computer to be turned on or awakened from sleep mode by a network message. It is based upon AMD's Magic Packet Technology, which was co-developed by AMD and Hewlett-Packard, following its proposal as a standard in 1995 – The standard saw quick adoption thereafter through IBM, Intel and others.

An email client, email reader or, more formally, message user agent (MUA) or mail user agent is a computer program used to access and manage a user's email.
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard communication protocol used for the transfer of computer files from a server to a client on a computer network. FTP is built on a client–server model architecture using separate control and data connections between the client and the server. FTP users may authenticate themselves with a plain-text sign-in protocol, normally in the form of a username and password, but can connect anonymously if the server is configured to allow it. For secure transmission that protects the username and password, and encrypts the content, FTP is often secured with SSL/TLS (FTPS) or replaced with SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP).

A packet analyzer is a computer program or computer hardware such as a packet capture appliance that can analyze and log traffic that passes over a computer network or part of a network. Packet capture is the process of intercepting and logging traffic. As data streams flow across the network, the analyzer captures each packet and, if needed, decodes the packet's raw data, showing the values of various fields in the packet, and analyzes its content according to the appropriate RFC or other specifications.
Virtual private network (VPN) is a network architecture for virtually extending a private network across one or multiple other networks which are either untrusted or need to be isolated.

tcpdump is a data-network packet analyzer computer program that runs under a command line interface. It allows the user to display TCP/IP and other packets being transmitted or received over a network to which the computer is attached. Distributed under the BSD license, tcpdump is free software.
SOCKS is an Internet protocol that exchanges network packets between a client and server through a proxy server. SOCKS5 optionally provides authentication so only authorized users may access a server. Practically, a SOCKS server proxies TCP connections to an arbitrary IP address, and provides a means for UDP packets to be forwarded. A SOCKS server accepts incoming client connection on TCP port 1080, as defined in RFC 1928.
In computer networking, promiscuous mode is a mode for a wired network interface controller (NIC) or wireless network interface controller (WNIC) that causes the controller to pass all traffic it receives to the central processing unit (CPU) rather than passing only the frames that the controller is specifically programmed to receive. This mode is normally used for packet sniffing that takes place on a router or on a computer connected to a wired network or one being part of a wireless LAN. Interfaces are placed into promiscuous mode by software bridges often used with hardware virtualization.
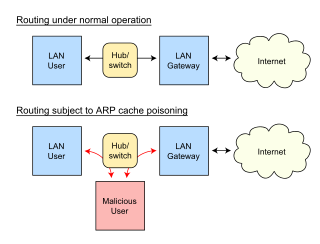
In computer networking, ARP spoofing, ARP cache poisoning, or ARP poison routing, is a technique by which an attacker sends (spoofed) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) messages onto a local area network. Generally, the aim is to associate the attacker's MAC address with the IP address of another host, such as the default gateway, causing any traffic meant for that IP address to be sent to the attacker instead.
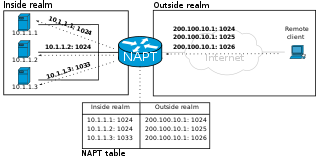
In computer networking, port forwarding or port mapping is an application of network address translation (NAT) that redirects a communication request from one address and port number combination to another while the packets are traversing a network gateway, such as a router or firewall. This technique is most commonly used to make services on a host residing on a protected or masqueraded (internal) network available to hosts on the opposite side of the gateway, by remapping the destination IP address and port number of the communication to an internal host.

Ettercap is a free and open source network security tool for man-in-the-middle attacks on a LAN. It can be used for computer network protocol analysis and security auditing. It runs on various Unix-like operating systems including Linux, Mac OS X, BSD and Solaris, and on Microsoft Windows. It is capable of intercepting traffic on a network segment, capturing passwords, and conducting active eavesdropping against a number of common protocols. Its original developers later founded Hacking Team.
In the field of computer network administration, pcap is an application programming interface (API) for capturing network traffic. While the name is an abbreviation of packet capture, that is not the API's proper name. Unix-like systems implement pcap in the libpcap library; for Windows, there is a port of libpcap named WinPcap that is no longer supported or developed, and a port named Npcap for Windows 7 and later that is still supported.

Wireshark is a free and open-source packet analyzer. It is used for network troubleshooting, analysis, software and communications protocol development, and education. Originally named Ethereal, the project was renamed Wireshark in May 2006 due to trademark issues.
Omnipeek is a packet analyzer software tool from Savvius, a LiveAction company, for network troubleshooting and protocol analysis. It supports an application programming interface (API) for plugins.

EtherApe is a packet sniffer/network traffic monitoring tool, developed for Unix. EtherApe is free, open source software developed under the GNU General Public License.
ngrep is a network packet analyzer written by Jordan Ritter. It has a command-line interface, and relies upon the pcap library and the GNU regex library.
Justniffer is a TCP packet sniffer. It can log network traffic in a 'standard' or in a customized way. It can also log response times, useful for tracking network services performances . The output format of the traffic can be easily customized. An example written in Python stores the transferred contents in an output directory separated by domains. This means that the transferred files like html, css, javascript, images, sounds, etc. can be saved to a directory.
Xplico is a network forensics analysis tool (NFAT), which is a software that reconstructs the contents of acquisitions performed with a packet sniffer.
Sniffing attack in context of network security, corresponds to theft or interception of data by capturing the network traffic using a packet sniffer. When data is transmitted across networks, if the data packets are not encrypted, the data within the network packet can be read using a sniffer. Using a sniffer application, an attacker can analyze the network and gain information to eventually cause the network to crash or to become corrupted, or read the communications happening across the network.








