
The Ramayana, also known as Valmiki Ramayana, as traditionally attributed to Valmiki, is a smriti text from ancient India, one of the 2 important epics of Hinduism known as the Itihasas, the other being the Mahabharata. The epic narrates the life of Rama, a prince of Ayodhya in the kingdom of Kosala. The epic follows his fourteen-year exile to the forest urged by his father King Dasharatha, on the request of Rama's stepmother Kaikeyi; his travels across forests in the Indian subcontinent with his wife Sita and brother Lakshmana; the kidnapping of Sita by Ravana, the king of Lanka, that resulted in war; and Rama's eventual return to Ayodhya along with Sita to be crowned king amidst jubilation and celebration.

Sanskrit literature broadly comprises all literature in the Sanskrit language. This includes texts composed in the earliest attested descendant of the Proto-Indo-Aryan language known as Vedic Sanskrit, texts in Classical Sanskrit as well as some mixed and non-standard forms of Sanskrit. Literature in the older language begins with the composition of the Ṛg·veda between about 1500 and 1000 BCE, followed by other Vedic works right up to the time of the grammarian Pāṇini around 6th or 4th century BCE.

Vidarbha is a geographical region in the west Indian state of Maharashtra. Forming the eastern part of the state, it comprises Amravati and Nagpur divisions. As per the 2011 Census, the region had a population of 23,003,179. The region occupies 31.6% of the total area and is home to 21.3% of the total population of Maharashtra. Situated in central India, it borders the state of Madhya Pradesh to the north, Chhattisgarh to the east, Telangana to the south and Marathwada and Uttar Maharashtra regions of Maharashtra to the west.
Keļallur Nīlakaṇṭha Somayāji, also referred to as Keļallur Comatiri, was a major mathematician and astronomer of the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics. One of his most influential works was the comprehensive astronomical treatise Tantrasamgraha completed in 1501. He had also composed an elaborate commentary on Aryabhatiya called the Aryabhatiya Bhasya. In this Bhasya, Nilakantha had discussed infinite series expansions of trigonometric functions and problems of algebra and spherical geometry. Grahapariksakrama is a manual on making observations in astronomy based on instruments of the time.
Vatasseri Parameshvara Nambudiri was a major Indian mathematician and astronomer of the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics founded by Madhava of Sangamagrama. He was also an astrologer. Parameshvara was a proponent of observational astronomy in medieval India and he himself had made a series of eclipse observations to verify the accuracy of the computational methods then in use. Based on his eclipse observations, Parameshvara proposed several corrections to the astronomical parameters which had been in use since the times of Aryabhata. The computational scheme based on the revised set of parameters has come to be known as the Drgganita or Drig system. Parameshvara was also a prolific writer on matters relating to astronomy. At least 25 manuscripts have been identified as being authored by Parameshvara.
Munishvara or Munīśvara Viśvarūpa was an Indian mathematician who wrote several commentaries including one on astronomy, the Siddhanta Sarvabhauma (1646), which included descriptions of astronomical instruments such as the pratoda yantra. Another commentary he wrote was the Lilavativivruti. Very little is known about him other than that he came from a family of astronomers including his father Ranganatha who wrote a commentary called the Gụ̄hārthaprakaśa/Gūḍhārthaprakāśikā, a commentary on the Suryasiddhanta. His grandfather Ballala had his origins in Dadhigrama in Vidharba and had moved to Benares. Ballala had several sons who wrote commentaries on astronomy and mathematics. Munisvara's Siddhantasarvabhauma had the patronage of Shah Jahan like his paternal uncle Krishna Daivagna did. He was opposed to fellow mathematician Kamalakara, whose brother also wrote a critique of Munisvara's bhangi-vibhangi method for planetary motions. He was also opposed to the adoption of some mathematical ideas in spherical trigonometry from Arab scholars. An edition of his Siddhanta Sarvabhauma was published in the Princess of Wales Sarasvati Bhavana Granthamala series edited by Gopinath Kaviraj. Munisvara's book had twelve chapters in two parts. The second part had notes on astronomical instruments. He was a follower of Bhaskara II.
Mahanubhava refers to Krishnaite Hindu denomination in India that was founded by Sarvadnya Shri Chakradhar Swami, an ascetic and philosopher who is considered as a reincarnation of Krishna by his devotees Some sources list the founders as Chakrapani and Govinda Prabhu with Chakradhara as the first "apostle" and propagator of Mahanubhava Pantha. Mahanubhava Sampradaya was formally formed in modern-day Varhad region of Maharashtra in 1267 CE. It has different names such as Jai Krishni Pantha in Punjab and Achyuta Pantha in Gujarat. Mahanubhava Pantha was also known as Paramarga by its followers in 13th century. Nagadevacharya, also known as Bhatobas, became the head of Sampradaya after Chakradhara.

The Ranganathaswamy Temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to Ranganatha and is located in Srirangam, Tiruchirapalli, Tamil Nadu, India. Constructed in the Dravidian architectural style, the temple is glorified by the Tamil poet-saints called the Alvars in their canon, the Naalayira Divya Prabhandam, and has the unique distinction of being the foremost among the 108 Divya Desams dedicated to the god Vishnu. The Srirangam temple is the largest temple compound in India and is one of the largest religious complexes in the world. Some of these structures have been renovated, expanded and rebuilt over the centuries as a living temple. The latest addition is the outer tower that is approximately 73 metres (240 ft) tall, it was completed in 1987. Srirangam temple is often listed as the largest functioning Hindu temple in the world, the still larger Angkor Wat being the largest existing temple. The temple is an active Hindu house of worship and follows the Tenkalai tradition of Sri Vaishnavism. The annual 21-day festival conducted during the Tamil month of Margali (December–January) attracts 1 million visitors. The temple complex has been nominated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and is in UNESCO's tentative list. In 2017 the temple won the UNESCO Asia Pacific Award of Merit 2017 for cultural heritage conservation, making it the first temple in Tamil Nadu to receive the award from the UNESCO.

The Vidarbha Kingdom in the Sanskrit epic Mahabharata is among the many kingdoms ruled by Yadu kings . It was situated in the region still known as Vidarbha in what is now Maharashtra in central India.

Depending on the methods of counting, as many as three hundred versions of the Indian Hindu epic poem, the Ramayana, are known to exist. The oldest version is generally recognized to be the Sanskrit version attributed to the sage Narada, the Mula Ramayana. Narada passed on the knowledge to Valmiki, who authored Valmiki Ramayana, the present oldest available version of Ramayana.
Nashik is a historically, mythologically, socially and culturally important city in the northern part of the state of Maharashtra in India. It is known for the temples on the banks of the Godavari and it has historically been one of the holy sites of the Hindu religion. It is one of the four cities that hosts the massive Sinhastha Kumbh Mela once every twelve years.
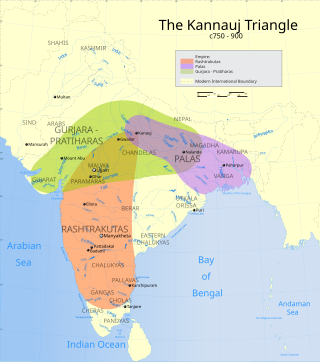
The Tripartite Struggle (785–816), also called the Kannauj Triangle Wars, was a conflict in northern India involving the three Indian great powers of the era – Gurjaratra, Bengal, and Manyakheta under the Pratiharas, the Palas and the Rashtrakutas respectively. The war was fought over the control of the Kingdom of Kannauj.
Govinda Bhaṭṭathiri was an Indian astrologer and astronomer who flourished in Kerala during the thirteenth century CE.
Jambusāgaranagara is a place or region in India where a school of astronomers and mathematicians flourished during the fifteenth to eighteenth centuries CE. The location of this place has not been definitely identified.
Golagrama is a village or region in India associated with several medieval Indian astronomers, astrologers and mathematicians. Presently there is no place bearing the name Golagrama anywhere in India. It is known that Golagrama was situated in Maharashtra State on the northern banks of river Godavari, was near Partha-puri (Pathari) in Maharashtra and was about 320 km away from Amravati town in Maharashtra. It is sometimes identified as a place named Golgam at latitude 18° N longitude 78° E. The name Golagrama considered as a word in Sanskrit could literally be translated as sphere-village.
Nila-kantha was a 16th-century astrologer and astronomer and Sanskrit writer from the Mughal Empire of present-day India. He was a royal astrologer to emperor Akbar, and contributed to Todarananda, an encyclopedia sponsored by Akbar's minister Todara-malla. He wrote Tajika-Nilakanthi, the most popular work on the Tajika astrology, and possibly compiled Prashna-tantra, a work on interrogational astrology, based on an earlier text.
Nandigrama is the name of a location, place or region somewhere in Western India where a school of astronomers and mathematicians flourished during the thirteenth-eighteenth centuries CE. David Pingree, one of America's leading historians of the exact sciences in antiquity, identified Nandigrama with Nandod in Gujarat. However, modern scholarship has identified Nandigrama as the Nandgaon village in the Raigad district in Maharashtra State. It lies about 64 km south of Mumbai on the Konkan coast.
Tattvachintamani is a treatise in Sanskrit authored by 14th-century CE Indian logician and philosopher Gangesa. The title may be translated into English as "A Thought-jewel of Truth." The treatise is also known as Pramāṇa-chintāmaṇi.
Keshava was an astrologer and astronomer from Nandigrama in present-day western India.






