
BMW AG is a German multinational company which currently produces automobiles and motorcycles, and also produced aircraft engines until 1945.

Bentley Motors Limited is a British manufacturer and marketer of luxury cars and SUVs—and a subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group since 1998.

A V12 engine is a V engine with 12 cylinders mounted on the crankcase in two banks of six cylinders each, usually but not always at a 60° angle to each other, with all 12 pistons driving a common crankshaft. Since each cylinder bank is essentially a straight-six which is by itself in both primary and secondary balance, a V12 inherits perfect primary and secondary balance no matter which V angle is used, and therefore it needs no balance shafts. A four-stroke 12 cylinder engine has an even firing order if cylinders fire every 60° of crankshaft rotation, so a V12 with cylinder banks at a multiples of 60° will have even firing intervals without using split crankpins. By using split crankpins or ignoring minor vibrations, any V angle is possible. The 180° configuration is usually referred to as a "flat-twelve engine" or a "boxer" although it is in reality a 180° V since the pistons can and normally do use shared crankpins. It may also be written as "V-12", although this is less common.

Rolls-Royce Holdings plc is a British multinational engineering company incorporated in February 2011 that owns Rolls-Royce, a business established in 1904 which today designs, manufactures and distributes power systems for aviation and other industries. Rolls-Royce is the world’s second-largest maker of aircraft engines and has major businesses in the marine propulsion and energy sectors.

Maybach Motorenbau is a defunct German car manufacturer that today exists as a sub-brand of Mercedes-Benz. The company was founded in 1909 by Wilhelm Maybach and his son, originally as a subsidiary of Luftschiffbau Zeppelin GmbH, and it was known as Luftfahrzeug-Motorenbau GmbH until 1999.

The Rolls-Royce BR700 family of turbofan engines powers regional jets and corporate jets. It was developed by BMW and Rolls-Royce plc through the joint venture BMW Rolls-Royce AeroEngines GmbH, established in 1990. The BR710 first ran in 1995. It is manufactured in Dahlewitz, Germany. Rolls-Royce took full control of the company in 2000, which is now known as Rolls-Royce Deutschland. The military designation of the series is F130.

Märkisches Museum is a Berlin U-Bahn station located on the U 2 in the Mitte district. Since 1935 it has been named after the nearby Märkisches Museum, the municipal museum of the history of Berlin and the Mark Brandenburg.

Bundesautobahn 9 is an autobahn in Germany, connecting Berlin and Munich via Leipzig and Nuremberg. It's the fifth longest autobahn spanning 529 km (328.71 mi).

Rolls-Royce Motor Cars Limited is a British luxury automobile maker. A wholly owned subsidiary of German group BMW, it was established in 1998 after BMW was licensed the rights to the Rolls-Royce brand name and logo from Rolls-Royce plc and acquired the rights to the Spirit of Ecstasy and Rolls-Royce grill shape trademarks from Volkswagen AG. Rolls-Royce Motor Cars Limited operates from purpose-built administrative and production facilities opened in 2003 across from the historic Goodwood Circuit in Goodwood, West Sussex, England, United Kingdom. Rolls-Royce Motors Cars Limited is the exclusive manufacturer of Rolls-Royce branded motor cars since 2003.

Berlin-Wittenau is a railway station in the Wittenau district of Berlin, Germany. It is served by the Berlin S-Bahn and numerous local buses. It is also the northern terminus of the Berlin U-Bahn line U 8.

The Border checkpoint Helmstedt–Marienborn, named Grenzübergangsstelle Marienborn (GÜSt) by the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was the largest and most important border crossing on the Inner German border during the division of Germany. Due to its geographical location, allowing for the shortest land route between West Germany and West Berlin, most transit traffic to and from West Berlin used the Helmstedt-Marienborn crossing. Most travel routes from West Germany to East Germany and Poland also used this crossing. The border crossing existed from 1945 to 1990 and was situated near the East German village of Marienborn at the edge of the Lappwald. The crossing interrupted the Bundesautobahn 2 (A 2) between the junctions Helmstedt-Ost and Ostingersleben.
An official state car is a vehicle used by a government to transport its head of state or head of government in an official capacity, which may also be used occasionally to transport other members of the government or visiting dignitaries from other countries. A few countries bring their own official state car for state visits to other countries, for instance, the United States, Russia and the United Kingdom. It also may serve as an automotive symbol of the head of state and their country. Part of the criteria for an official state car is to have adequate security, capability and stateliness for its duty. A limousine, executive car or sport utility vehicle is usually selected.

The Eberswalde Hoard or Treasure of Eberswalde is a Bronze Age hoard of 81 gold objects with a total weight of 2.59 kg (83 ozt). The largest prehistoric assembly of gold objects ever found in Germany, it is considered to be one of the most important finds from the Central European Bronze Age. Today, it is in Russia, as part of the group of artifacts and works of art looted from Germany at the end of the Second World War.

The AG Märkische Kleinbahn or MKB in Berlin is a German railway museum and heritage railway, founded in 1981, with legal status as a society since 1982. It has set itself the task of preserving historical railway vehicles and other items of railway technology in an operational state or for museum display and to make them accessible to the public. Their centre of operations is the locomotive shed at Schönow.
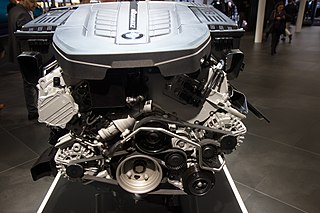
The BMW N74 is a twin-turbo V12 petrol engine which replaced the N73 and has been produced from 2008 to present. It is BMW's first turbocharged V12 engine and is also used in several Rolls-Royce models.

The Goodwood plant serves as the headquarters, design, manufacturing and assembly centre for Rolls-Royce Motor Cars.

The Rolls-Royce–Bentley L-series V8 engine was introduced in 1959 and is still in production. Built in Crewe, it was used on most Rolls-Royce and Bentley automobiles in the four decades after its introduction and is still used in the Bentley Mulsanne.

The Rolls-Royce Cullinan is a full-sized luxury SUV produced by Rolls-Royce Motor Cars. The Cullinan is the first SUV to be launched by the Rolls-Royce marque, and is also the brand's first all-wheel drive vehicle.

The Rolls-Royce Phantom VIII is a full-sized luxury saloon manufactured by Rolls-Royce Motor Cars. It is the eighth and current generation of the Rolls-Royce Phantom, and the second launched by Rolls-Royce under BMW ownership. It is offered in two wheelbase lengths.

























