
Transport in Belgium is facilitated with well-developed road, air, rail and water networks. The rail network has 2,950 km (1,830 mi) of electrified tracks. There are 118,414 km (73,579 mi) of roads, among which there are 1,747 km (1,086 mi) of motorways, 13,892 km (8,632 mi) of main roads and 102,775 km (63,861 mi) of other paved roads. There is also a well-developed urban rail network in Brussels, Antwerp, Ghent and Charleroi. The ports of Antwerp and Bruges-Zeebrugge are two of the biggest seaports in Europe. Brussels Airport is Belgium's biggest airport.

The Scheldt is a 435-kilometre-long (270 mi) river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corresponding to Old English sċeald ("shallow"), Modern English shoal, Low German schol, West Frisian skol, and obsolete Swedish skäll ("thin").

Damme is a city and municipality located in the Belgian province of West Flanders, six kilometres northeast of Brugge (Bruges). The municipality comprises the city of Damme proper and the villages of Hoeke, Lapscheure, Moerkerke, Oostkerke, Sijsele, Vivenkapelle, and Sint-Rita. On 1 January 2006, the municipality had a population of 10,899. The total area is 89.52 km2, giving a population density of 122 inhabitants per km2.

Zuid-Beveland is part of the province of Zeeland in the Netherlands north of the Western Scheldt and south of the Eastern Scheldt.

The siege of Antwerp was an engagement between the German and the Belgian, British and French armies around the fortified city of Antwerp during the First World War. German troops besieged a garrison of Belgian fortress troops, the Belgian field army and the British Royal Naval Division in the Antwerp area, after the German invasion of Belgium in August 1914. The city, which was ringed by forts known as the National Redoubt, was besieged to the south and east by German forces.

The Zwin is a nature reserve at the North Sea coast, on the Belgian–Dutch border. It consists of the entrance area of a former tidal inlet which during the Middle Ages connected the North Sea with the ports of Sluis and Bruges inland.
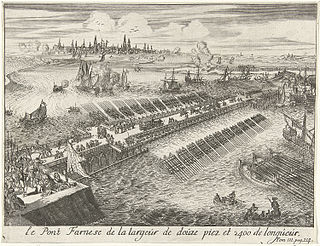
The fall of Antwerp on 17 August 1585 took place during the Eighty Years' War, after a siege lasting over a year from July 1584 until August 1585. The city of Antwerp was the focal point of the Protestant-dominated Dutch Revolt, but was forced to surrender to the Spanish forces under the command of Alessandro Farnese. Under the terms agreed, all the Protestants of Antwerp were given four years to settle their affairs and leave the city. Many migrated north, especially to Amsterdam. Apart from losing a high proportion of its middle class and mercantile population, Antwerp's trade suffered for two centuries afterwards as Dutch forts blockaded the River Scheldt until 1795.

The Port of Ghent is the third busiest seaport in Belgium, located in Ghent, East Flanders in the Flemish Region. The first port of Ghent was situated at the river Scheldt and later on at the Leie. Since the Middle Ages Ghent has sought for a connection to the sea. In the 13th century via the Lieve canal to the Zwin near Damme, in the 16th century via the Sassevaart, in the 17th century via the Ghent–Bruges canal. Since the 19th century, the Ghent–Terneuzen Canal connects the port via the Western Scheldt to the North Sea. The port of Ghent is accessible by ships of the Panamax size, and in February 2015 the construction of a new lock at Terneuzen was announced, which will maintain near-parity with those of the Panama Canal expansion project.

The Brussels–Charleroi Canal, also known as the Charleroi Canal amongst other similar names, is an important canal in Belgium. The canal is quite large, with a Class IV Freycinet gauge, and its Walloon portion is 47.9 kilometres (29.8 mi) long. It runs from Charleroi (Wallonia) in the south to Brussels in the north.

Brussels has an extensive network of both private or public transportation means. Public transportation includes Brussels buses, trams, and metro, as well as a set of railway lines and railway stations served by public trains. Air transport is available via one of the city's two airports, and boat transport is available via the Port of Brussels. Bicycle-sharing and car-sharing public systems are also available. The city is relatively car-dependent by northern European standards and is considered to be the most congested city in the world according to the INRIX traffic survey.

The Schipdonk Canal is a canal in the Belgian provinces of East Flanders and West Flanders. With a length of 56 km (35 mi), the canal runs in a northerly direction from Deinze, turning to a north-western direction roughly halfway along its route to the North Sea with which it meets on the coast near to Heist. It crosses both the Ghent-Bruges Canal and for its final 20 km (12 mi) runs parallel with the Leopold Canal as it approaches the north Belgian coast. For most of this final section the two canals are separated only by a dyke.

The history of Flanders concerns not only the modern Dutch-speaking part of Belgium, which is now called "Flanders", but also several neighbouring territories and populations. Its historical core territory was in western Belgium between the coast and the Scheldt river.

Belgium was heavily involved in the early development of railway transport. Belgium was the second country in Europe, after Great Britain, to open a railway and produce locomotives. The first line, between the cities of Brussels and Mechelen opened in 1835. Belgium was the first state in Europe to create a national railway network and the first to possess a nationalised railway system. The network expanded fast as Belgium industrialised, and by the early 20th century was increasingly under state-control. The nationalised railways, under the umbrella organisation National Railway Company of Belgium (NMBS/SNCB), retained their monopoly until liberalisation in the 2000s.

The Franco-Flemish War was a conflict between the Kingdom of France and the County of Flanders between 1297 and 1305.

Bruges is the capital and largest city of the province of West Flanders, in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is in the northwest of the country, and is the sixth most populous city in the country.

Blankenberge railway station is a railway station in Blankenberge, West Flanders, Belgium. The station opened on 16 August 1863 on railway line 51. It is run by the National Railway Company of Belgium (NMBS/SNCB) as a terminal station located on the railway line from Brugge and has services to Brussels-South and beyond to Leuven.

The Bocholt–Herentals Canal is a canal in Belgium that links the Zuid-Willemsvaart at Bocholt with the Albert Canal in Herentals, with a length of slightly over 60 kilometres. It is one of the seven canals linking the rivers Meuse and Scheldt.

The siege of Sluis (1604), also known as the Sluis campaign or the Battle of the Oostburg Line, was a series of military actions that took place during the Eighty Years' War and the Anglo–Spanish War from 19 May to 19 August 1604. A States and English army under Prince Maurice of Orange and Horace Vere respectively crossed the Scheldt estuary and advanced on land taking Cadzand, Aardenburg, and IJzendijke in the Spanish Netherlands. This soon led to the culmination of the siege of the Spanish-held inland port of Sluis.
The Kontor of Bruges was the Hanseatic kontor, one of the Hanseatic League's four major trading posts, in Bruges, County of Flanders. A kontor was a corporation (universitas) with a level of legal autonomy in a foreign non-Hanseatic city, the one of Bruges was formally organised in the 14th century. Bruges was a major Flemish port in the high and late Middle Ages. Flanders was a fiefdom of France until the Treaty of Senlis was signed in 1493, after that it belonged to the Holy Roman Empire.



















