Related Research Articles

In computing, a data warehouse, also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for reporting and data analysis and is considered a core component of business intelligence. Data warehouses are central repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources. They store current and historical data in one single place that are used for creating reports. This is beneficial for companies as it enables them to interrogate and draw insights from their data and make decisions.
Data mining is the process of extracting and discovering patterns in large data sets involving methods at the intersection of machine learning, statistics, and database systems. Data mining is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and statistics with an overall goal of extracting information from a data set and transforming the information into a comprehensible structure for further use. Data mining is the analysis step of the "knowledge discovery in databases" process, or KDD. Aside from the raw analysis step, it also involves database and data management aspects, data pre-processing, model and inference considerations, interestingness metrics, complexity considerations, post-processing of discovered structures, visualization, and online updating.
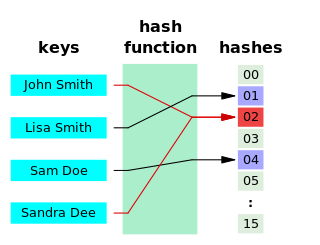
In computer science, a hash collision or hash clash is when two distinct pieces of data in a hash table share the same hash value. The hash value in this case is derived from a hash function which takes a data input and returns a fixed length of bits.

Db2 is a family of data management products, including database servers, developed by IBM. It initially supported the relational model, but was extended to support object–relational features and non-relational structures like JSON and XML. The brand name was originally styled as DB2 until 2017, when it changed to its present form.
In software engineering, a software design pattern is a general, reusable solution to a commonly occurring problem within a given context in software design. It is not a finished design that can be transformed directly into source or machine code. Rather, it is a description or template for how to solve a problem that can be used in many different situations. Design patterns are formalized best practices that the programmer can use to solve common problems when designing an application or system.
Information architecture (IA) is the structural design of shared information environments; the art and science of organizing and labelling websites, intranets, online communities and software to support usability and findability; and an emerging community of practice focused on bringing principles of design, architecture and information science to the digital landscape. Typically, it involves a model or concept of information that is used and applied to activities which require explicit details of complex information systems. These activities include library systems and database development.
Artificial consciousness (AC), also known as machine consciousness (MC), synthetic consciousness or digital consciousness, is the consciousness hypothesized to be possible in artificial intelligence. It is also the corresponding field of study, which draws insights from philosophy of mind, philosophy of artificial intelligence, cognitive science and neuroscience. The same terminology can be used with the term "sentience" instead of "consciousness" when specifically designating phenomenal consciousness.

Data modeling in software engineering is the process of creating a data model for an information system by applying certain formal techniques. It may be applied as part of broader Model-driven engineering (MDE) concept.
William H. Inmon is an American computer scientist, recognized by many as the father of the data warehouse. Inmon wrote the first book, held the first conference, wrote the first column in a magazine and was the first to offer classes in data warehousing. Inmon created the accepted definition of what a data warehouse is - a subject oriented, nonvolatile, integrated, time variant collection of data in support of management's decisions. Compared with the approach of the other pioneering architect of data warehousing, Ralph Kimball, Inmon's approach is often characterized as a top-down approach.

Data analysis is the process of inspecting, cleansing, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, informing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. Data analysis has multiple facets and approaches, encompassing diverse techniques under a variety of names, and is used in different business, science, and social science domains. In today's business world, data analysis plays a role in making decisions more scientific and helping businesses operate more effectively.
Ralph Kimball is an author on the subject of data warehousing and business intelligence. He is one of the original architects of data warehousing and is known for long-term convictions that data warehouses must be designed to be understandable and fast. His bottom-up methodology, also known as dimensional modeling or the Kimball methodology, is one of the two main data warehousing methodologies alongside Bill Inmon.

Data and information visualization is the practice of designing and creating easy-to-communicate and easy-to-understand graphic or visual representations of a large amount of complex quantitative and qualitative data and information with the help of static, dynamic or interactive visual items. Typically based on data and information collected from a certain domain of expertise, these visualizations are intended for a broader audience to help them visually explore and discover, quickly understand, interpret and gain important insights into otherwise difficult-to-identify structures, relationships, correlations, local and global patterns, trends, variations, constancy, clusters, outliers and unusual groupings within data. When intended for the general public to convey a concise version of known, specific information in a clear and engaging manner, it is typically called information graphics.
Predictive analytics is a form of business analytics applying machine learning to generate a predictive model for certain business applications. As such, it encompasses a variety of statistical techniques from predictive modeling and machine learning that analyze current and historical facts to make predictions about future or otherwise unknown events. It represents a major subset of machine learning applications; in some contexts, it is synonymous with machine learning.
Dimensional modeling (DM) is part of the Business Dimensional Lifecycle methodology developed by Ralph Kimball which includes a set of methods, techniques and concepts for use in data warehouse design. The approach focuses on identifying the key business processes within a business and modelling and implementing these first before adding additional business processes, as a bottom-up approach. An alternative approach from Inmon advocates a top down design of the model of all the enterprise data using tools such as entity-relationship modeling (ER).

Dan Ariely is an Israeli-American professor and author. He serves as a James B. Duke Professor of psychology and behavioral economics at Duke University. Ariely is the co-founder of several companies implementing insights from behavioral science. Ariely wrote an advice column called Ask Ariely in the WSJ from June 2012 until September 2022. Ariely is the author of the three New York Times best selling books Predictably Irrational, The Upside of Irrationality and The Honest Truth about Dishonesty. He co-produced the 2015 documentary (Dis)Honesty: The Truth About Lies.

Datavault or data vault modeling is a database modeling method that is designed to provide long-term historical storage of data coming in from multiple operational systems. It is also a method of looking at historical data that deals with issues such as auditing, tracing of data, loading speed and resilience to change as well as emphasizing the need to trace where all the data in the database came from. This means that every row in a data vault must be accompanied by record source and load date attributes, enabling an auditor to trace values back to the source. The concept was published in 2000 by Dan Linstedt.

Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user. Large clouds often have functions distributed over multiple locations, each of which is a data center. Cloud computing relies on sharing of resources to achieve coherence and typically uses a pay-as-you-go model, which can help in reducing capital expenses but may also lead to unexpected operating expenses for users.
Stephen Brobst is an American technology executive.
Business metadata is data that adds business context to other data. It provides information authored by business people and/or used by business people. It is in contrast to technical metadata, which is data used in the storage and structure of the data in a database or system. Technical metadata includes the database table name and column name, data type, indexes referencing the data, ETL jobs involving the data, when the data was last updated, accessed, etc.
Data mesh is a sociotechnical approach to building a decentralized data architecture by leveraging a domain-oriented, self-serve design, and borrows Eric Evans’ theory of domain-driven design and Manuel Pais’ and Matthew Skelton’s theory of team topologies. Data mesh mainly concerns itself with the data itself, taking the data lake and the pipelines as a secondary concern. The main proposition is scaling analytical data by domain-oriented decentralization. With data mesh, the responsibility for analytical data is shifted from the central data team to the domain teams, supported by a data platform team that provides a domain-agnostic data platform. This enables a decrease in data disorder or the existence of isolated data silos, due to the presence of a centralized system that ensures the consistent sharing of fundamental principles across various nodes within the data mesh and allows for the sharing of data across different areas.
References
- ↑ "Data Vault Series 1 – Data Vault Overview" . Retrieved 2023-03-03.
- ↑ "Data Vault Modeling & Methodology - Data Warehouse Architecture". 2012-08-21. Archived from the original on 2012-08-21. Retrieved 2023-03-03.
- ↑ "Dan Linstedt: books, biography, latest update" . Retrieved 2023-03-03.