
A short take-off and vertical landing aircraft is a fixed-wing aircraft that is able to take off from a short runway and land vertically. The formal NATO definition is:
A Short Take-Off and Vertical Landing aircraft is a fixed-wing aircraft capable of clearing a 15 m obstacle within 450 m of commencing take-off run, and capable of landing vertically.

A delta wing is a wing shaped in the form of a triangle. It is named for its similarity in shape to the Greek uppercase letter delta (Δ).

The Dassault Mirage III is a family of single/dual-seat, single-engine, fighter aircraft developed and manufactured by French aircraft company Dassault Aviation. It was the first Western European combat aircraft to exceed Mach 2 in horizontal flight, which it achieved on 24 October 1958.

A vertical and/or short take-off and landing (V/STOL) aircraft is an airplane able to take-off or land vertically or on short runways. Vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) aircraft are a subset of V/STOL craft that do not require runways at all. Generally, a V/STOL aircraft needs to be able to hover. Helicopters are not considered under the V/STOL classification as the classification is only used for aeroplanes, aircraft that achieve lift (force) in forward flight by planing the air, thereby achieving speed and fuel efficiency that is typically greater than the capability of helicopters.

The Dassault Mirage 2000 is a French multirole, single-engine, delta wing, fourth-generation jet fighter manufactured by Dassault Aviation. It was designed in the late 1970s as a lightweight fighter to replace the Mirage III for the French Air Force. The Mirage 2000 evolved into a multirole aircraft with several variants developed, with sales to a number of nations. It was later developed into the Mirage 2000N and 2000D strike variants, the improved Mirage 2000-5, and several export variants. Over 600 aircraft were built and it has been in service with nine nations.

The Atlas Cheetah is a South African fighter aircraft designed and produced by the aviation company Atlas Aircraft Corporation. It was primarily designed and developed to be operated by the South African Air Force (SAAF).

The Israel Aircraft Industries Kfir is an Israeli all-weather multirole combat aircraft based on the French Dassault Mirage 5, with Israeli avionics and an Israeli-built version of the General Electric J79 turbojet engine.

The Israel Aircraft Industries Nesher was the Israeli version of the French Dassault Mirage 5 multirole fighter.

The Dassault Mirage 5 is a French supersonic attack aircraft/fighter-bomber designed by Dassault Aviation during the 1960s and manufactured in France and other countries. It was derived from Dassault's popular Mirage III fighter and spawned several variants of its own, including the IAI Kfir. In Pakistan's service, the Mirage 5s are modified and are capable of nuclear weapons delivery.

The Dassault Mirage G, also known as the Mirage IIIG, was a variant of the French Dassault Mirage series of supersonic warplanes, but with a variable-sweep wing. Three prototypes were flown; one single-engined G and two twin-engined G8 examples. Various roles, equipment fits and other variants were proposed, but none entered production.

A supersonic aircraft is an aircraft capable of supersonic flight, that is, flying faster than the speed of sound. Supersonic aircraft were developed in the second half of the twentieth century. Supersonic aircraft have been used for research and military purposes, but only two supersonic aircraft, the Tupolev Tu-144 and the Concorde, ever entered service for civil use as airliners. Fighter jets are the most common example of supersonic aircraft.

The Dassault Super Mystère is a French supersonic fighter-bomber and was the first Western European supersonic aircraft to enter mass production.

The Dassault Mirage IIIV, also spelled Mirage III V, was a French vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) prototype fighter aircraft of the mid-1960s developed and produced by Dassault Aviation.
The Hawker Siddeley P.1154 was a planned supersonic vertical/short take-off and landing (V/STOL) fighter aircraft designed by Hawker Siddeley Aviation (HSA).

In aeronautics, a canard is a wing configuration in which a small forewing or foreplane is placed forward of the main wing of a fixed-wing aircraft or a weapon. The term "canard" may be used to describe the aircraft itself, the wing configuration, or the foreplane. Canard wings are also extensively used in guided missiles and smart bombs.
The Atlas Carver was a proposed South African twin-engine, delta wing fourth-generation fighter aircraft. In development during the 1980s and early 1990s, the Carver was ultimately cancelled during 1991.
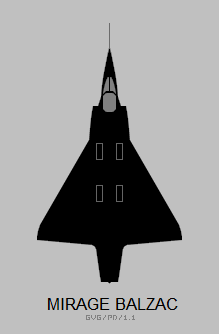
The Dassault Balzac V was a French vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) testbed of the early 1960s. It was built by Dassault Aviation from a prototype Mirage III aircraft to test the configuration for the Mirage IIIV. The sole example was involved in two major accidents that killed the aircraft's pilot, and was not repaired after the second crash.

The IAI Nammer was a fighter aircraft developed in the Israeli aerospace manufacturing Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) during the late 1980s and early 1990s. The programme was pursued as a private venture and the resultant aircraft was intended for the export market.

NBMR-3 or NATO Basic Military Requirement 3 was a document produced by a North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) committee in the early 1960s detailing the specification of future combat aircraft designs. The requirement was for aircraft in two performance groups, supersonic fighter aircraft (NBMR-3a) and subsonic fighter-bomber aircraft (NBMR-3b). Both requirements specifically stated the need for V/STOL performance as the contemporary fear was that airfields could be overrun or disabled through Eastern Bloc hostile actions and that dispersed operating bases would be needed. Germany was planning replacements for the Fiat G.91 and Lockheed F-104G Starfighter using the new aircraft types.

















