Related Research Articles

In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases spans formal techniques and practical considerations, including data modeling, efficient data representation and storage, query languages, security and privacy of sensitive data, and distributed computing issues, including supporting concurrent access and fault tolerance.

Microsoft Access is a database management system (DBMS) from Microsoft that combines the relational Access Database Engine (ACE) with a graphical user interface and software-development tools. It is a member of the Microsoft 365 suite of applications, included in the Professional and higher editions or sold separately.
A relational database is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970. A system used to maintain relational databases is a relational database management system (RDBMS). Many relational database systems are equipped with the option of using the SQL for querying and maintaining the database.
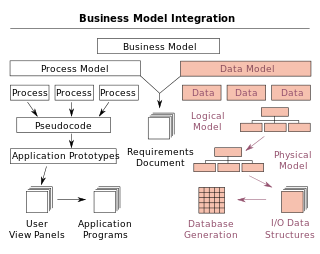
A data model is an abstract model that organizes elements of data and standardizes how they relate to one another and to the properties of real-world entities. For instance, a data model may specify that the data element representing a car be composed of a number of other elements which, in turn, represent the color and size of the car and define its owner.
ABAP is a high-level programming language created by the German software company SAP SE. It is currently positioned, alongside Java, as the language for programming the SAP NetWeaver Application Server, which is part of the SAP NetWeaver platform for building business applications.
A stored procedure is a subroutine available to applications that access a relational database management system (RDBMS). Such procedures are stored in the database data dictionary.
Transact-SQL (T-SQL) is Microsoft's and Sybase's proprietary extension to the SQL used to interact with relational databases. T-SQL expands on the SQL standard to include procedural programming, local variables, various support functions for string processing, date processing, mathematics, etc. and changes to the DELETE and UPDATE statements.
WinFS was the code name for a canceled data storage and management system project based on relational databases, developed by Microsoft and first demonstrated in 2003 as an advanced storage subsystem for the Microsoft Windows operating system, designed for persistence and management of structured, semi-structured and unstructured data.
In software, a data access object (DAO) is a pattern that provides an abstract interface to some type of database or other persistence mechanism. By mapping application calls to the persistence layer, the DAO provides some specific data operations without exposing details of the database. This isolation supports the single responsibility principle. It separates what data access the application needs, in terms of domain-specific objects and data types, from how these needs can be satisfied with a specific DBMS, database schema, etc..
A database abstraction layer is an application programming interface which unifies the communication between a computer application and databases such as SQL Server, IBM Db2, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle or SQLite. Traditionally, all database vendors provide their own interface that is tailored to their products. It is up to the application programmer to implement code for the database interfaces that will be supported by the application. Database abstraction layers reduce the amount of work by providing a consistent API to the developer and hide the database specifics behind this interface as much as possible. There exist many abstraction layers with different interfaces in numerous programming languages. If an application has such a layer built in, it is called database-agnostic.
ADO.NET is a data access technology from the Microsoft .NET Framework that provides communication between relational and non-relational systems through a common set of components. ADO.NET is a set of computer software components that programmers can use to access data and data services from a database. It is a part of the base class library that is included with the Microsoft .NET Framework. It is commonly used by programmers to access and modify data stored in relational database systems, though it can also access data in non-relational data sources. ADO.NET is sometimes considered an evolution of ActiveX Data Objects (ADO) technology, but was changed so extensively that it can be considered an entirely new product.
The Access Database Engine is a database engine on which several Microsoft products have been built. The first version of Jet was developed in 1992, consisting of three modules which could be used to manipulate a database.
In a database, a view is the result set of a stored query on the data, which the database users can query just as they would in a persistent database collection object. This pre-established query command is kept in the database dictionary. Unlike ordinary base tables in a relational database, a view does not form part of the physical schema: as a result set, it is a virtual table computed or collated dynamically from data in the database when access to that view is requested. Changes applied to the data in a relevant underlying table are reflected in the data shown in subsequent invocations of the view. In some NoSQL databases, views are the only way to query data.
The object–relational impedance mismatch is a set of conceptual and technical difficulties that are often encountered when a relational database management system (RDBMS) is being served by an application program written in an object-oriented programming language or style, particularly because objects or class definitions must be mapped to database tables defined by a relational schema.
Microsoft SQL Server is a relational database management system developed by Microsoft. As a database server, it is a software product with the primary function of storing and retrieving data as requested by other software applications—which may run either on the same computer or on another computer across a network. Microsoft markets at least a dozen different editions of Microsoft SQL Server, aimed at different audiences and for workloads ranging from small single-machine applications to large Internet-facing applications with many concurrent users.
Apache Empire-db is a Java library that provides a high level object-oriented API for accessing relational database management systems (RDBMS) through JDBC. Apache Empire-db is open source and provided under the Apache License 2.0 from the Apache Software Foundation.
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) is an application programming interface (API) for the programming language Java, which defines how a client may access a database. It is a Java-based data access technology used for Java database connectivity. It is part of the Java Standard Edition platform, from Oracle Corporation. It provides methods to query and update data in a database, and is oriented toward relational databases. A JDBC-to-ODBC bridge enables connections to any ODBC-accessible data source in the Java virtual machine (JVM) host environment.
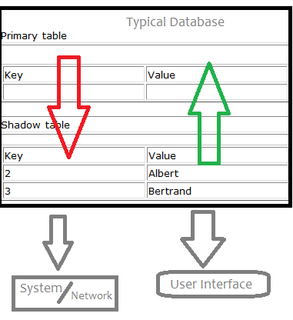
Shadow tables are objects in computer science used to improve the way machines, networks and programs handle information. More specifically, a shadow table is an object that is read and written by a processor and contains data similar to its primary table, which is the table it's "shadowing". Shadow tables usually contain data that is relevant to the operation and maintenance of its primary table, but not within the subset of data required for the primary table to exist. Shadow tables are related to the data type "trails" in data storage systems. Trails are very similar to shadow tables but instead of storing identically formatted information that is different, they store a history of modifications and functions operated on a table.
The following is provided as an overview of and topical guide to databases:
Oracle TopLink is a mapping and persistence framework for Java developers. TopLink is produced by Oracle and is a part of Oracle's OracleAS, WebLogic, and OC4J servers. It is an object-persistence and object-transformation framework. TopLink provides development tools and run-time functionalities that ease the development process and help increase functionality. Persistent object-oriented data is stored in relational databases which helps build high-performance applications. Storing data in either XML or relational databases is made possible by transforming it from object-oriented data.