Documentation is any communicable material that is used to describe, explain or instruct regarding some attributes of an object, system or procedure, such as its parts, assembly, installation, maintenance, and use. As a form of knowledge management and knowledge organization, documentation can be provided on paper, online, or on digital or analog media, such as audio tape or CDs. Examples are user guides, white papers, online help, and quick-reference guides. Paper or hard-copy documentation has become less common. Documentation is often distributed via websites, software products, and other online applications.

A safety data sheet (SDS), material safety data sheet (MSDS), or product safety data sheet (PSDS) is a document that lists information relating to occupational safety and health for the use of various substances and products. SDSs are a widely used type of fact sheet used to catalogue information on chemical species including chemical compounds and chemical mixtures. SDS information may include instructions for the safe use and potential hazards associated with a particular material or product, along with spill-handling procedures. The older MSDS formats could vary from source to source within a country depending on national requirements; however, the newer SDS format is internationally standardized.
A technical writer is a professional communicator whose task is to convey complex information in simple terms to an audience of the general public or a very select group of readers. Technical writers research and create information through a variety of delivery media. Example types of information include online help, manuals, white papers, design specifications, project plans, and software test plans. With the rise of e-learning, technical writers are increasingly hired to develop online training material.

The Gerber format is an open, ASCII, vector format for printed circuit board (PCB) designs. It is the de facto standard used by PCB industry software to describe the printed circuit board images: copper layers, solder mask, legend, drill data, etc. The standard file extension is .GBR or .gbr though other extensions like .GB, .geb or .gerber are also used. It is documented by The Gerber Layer Format Specification and some related extensions such as XNC drill files and GerberJob to convey information about the entire PCB, as opposed to single layers.

Technical writing is a specialized form of communication used by many of today's industrial and scientific organizations to clearly and accurately convey complex information to a user. An organization's customers, employees, assembly workers, engineers, and scientists are some of the most common users who reference this form of content to complete a task or research a subject. Most technical writing relies on simplified grammar, supported by easy-to-understand visual communication to clearly and accurately explain complex information.
Product literature is a primary subset of business publishing that is geared toward the selection, purchase and subsequent use of a business' products. Product literature is intended to be created and distributed by the manufacturer alongside the product. The two components are designed to work in tandem so as to provide more information to the purchaser regarding factors such as ongoing use, how the product functions and what the expected effects over time might be.
Environmental stress screening (ESS) refers to the process of exposing a newly manufactured or repaired product or component to stresses such as thermal cycling and vibration in order to force latent defects to manifest themselves by permanent or catastrophic failure during the screening process. The surviving population, upon completion of screening, can be assumed to have a higher reliability than a similar unscreened population.
Product information management (PIM) is the process of managing all the information required to market and sell products through distribution channels. This product data is created by an internal organization to support a multichannel marketing strategy. A central hub of product data can be used to distribute information to sales channels such as e-commerce websites, print catalogues, marketplaces such as Amazon and Google Shopping, social media platforms like Instagram and electronic data feeds to trading partners. Moreover, the significant role that PIM plays is reducing the abandonment rate by giving better product information.

The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) is an internationally agreed-upon standard managed by the United Nations that was set up to replace the assortment of hazardous material classification and labelling schemes previously used around the world. Core elements of the GHS include standardized hazard testing criteria, universal warning pictograms, and safety data sheets which provide users of dangerous goods relevant information with consistent organization. The system acts as a complement to the UN numbered system of regulated hazardous material transport. Implementation is managed through the UN Secretariat. Although adoption has taken time, as of 2017, the system has been enacted to significant extents in most major countries of the world. This includes the European Union, which has implemented the United Nations' GHS into EU law as the CLP Regulation, and United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration standards.

An owner's manual is an instructional book or booklet that is supplied with almost all technologically advanced consumer products such as vehicles, home appliances and computer peripherals. Information contained in the owner's manual typically includes:
Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) is used in the Aerospace or automotive supply chain for establishing confidence in suppliers and their production processes. Actual measurements are taken from the parts produced and are used to complete the various test sheets of PPAP.
"All customer engineering design record and specification requirements are properly understood by the supplier and that the process has the potential to produce product consistently meeting these requirements during an actual production run at the quoted production rate." Version 4, 1 March 2006

Submittals in construction management can include: shop drawings, material data, samples, and product data. Submittals are required primarily for the architect and engineer to verify that the correct products will be installed on the project.
Right to know is a human right enshrined in law in several countries. UNESCO defines it as the right for people to "participate in an informed way in decisions that affect them, while also holding governments and others accountable". It pursues universal access to information as essential foundation of inclusive knowledge societies. It is often defined in the context of the right for people to know about their potential exposure to environmental conditions or substances that may cause illness or injury, but it can also refer more generally to freedom of information or informed consent.
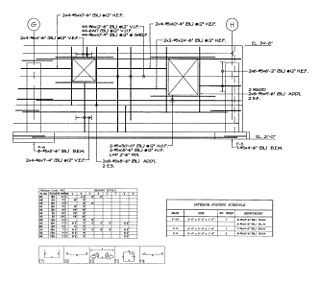
A shop drawing is a drawing or set of drawings produced by the contractor, supplier, manufacturer, subcontractor, consultants, or fabricator. Shop drawings are typically required for prefabricated components. Examples of these include: elevators, structural steel, trusses, pre-cast concrete, windows, appliances, cabinets, air handling units, and millwork. Also critical are the installation and coordination shop drawings of the MEP trades such as sheet metal ductwork, piping, plumbing, fire protection, and electrical. Shop drawings are produced by contractors and suppliers under their contract with the owner. The shop drawing is the manufacturer’s or the contractor’s drawn version of information shown in the construction documents. The shop drawing normally shows more detail than the construction documents. It is drawn to explain the fabrication and/or installation of the items to the manufacturer’s production crew or contractor's installation crews. The style of the shop drawing is usually very different from that of the architect’s drawing. The shop drawing’s primary emphasis is on the particular product or installation and excludes notation concerning other products and installations, unless integration with the subject product is necessary.
A test method is a method for a test in science or engineering, such as a physical test, chemical test, or statistical test. It is a definitive procedure that produces a test result. In order to ensure accurate and relevant test results, a test method should be "explicit, unambiguous, and experimentally feasible.", as well as effective and reproducible.
A specification often refers to a set of documented requirements to be satisfied by a material, design, product, or service. A specification is often a type of technical standard.
Technical documentation is a generic term for the classes of information created to describe the use, functionality or architecture of a product, system or service.

Decorative laminates are laminated products primarily used as furniture surface materials or wall paneling. It can be manufactured as either high- or low-pressure laminate, with the two processes not much different from each other except for the pressure applied in the pressing process. Also, laminate can be produced either in batches or in a continuous process; the latter is called continuous pressure laminate (CPL).
Tool management is needed in metalworking so that the information regarding the tools on hand can be uniformly organized and integrated. The information is stored in a database and is registered and applied using tool management. Tool data management consists of specific data fields, graphics and parameters that are essential in production, as opposed to managing general production equipment.
Chemical safety includes all those policies, procedures and practices designed to minimize the risk of exposure to potentially hazardous chemicals. This includes the risks of exposure to persons handling the chemicals, to the surrounding environment, and to the communities and ecosystems within that environment. Manufactured chemicals, either pure or in mixtures, solutions and emulsions, are ubiquitous in modern society, at industrial, occupational and private scale. However, there are chemicals that should not mix or get in contact with others, as they can produce byproducts that may be toxic, carcinogenic, explosive etc., or can be dangerous in themselves. To avoid disasters and mishaps, maintaining safety is paramount.








