Related Research Articles

The cosmic microwave background is microwave radiation that fills all space in the observable universe. It is a remnant that provides an important source of data on the primordial universe. With a standard optical telescope, the background space between stars and galaxies is almost completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope detects a faint background glow that is almost uniform and is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of the CMB in 1965 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s.
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey or SDSS is a major multi-spectral imaging and spectroscopic redshift survey using a dedicated 2.5-m wide-angle optical telescope at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico, United States. The project began in 2000 and was named after the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, which contributed significant funding.
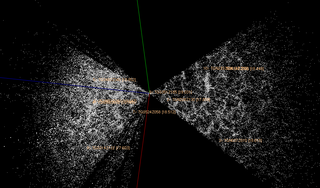
In astronomy, a redshift survey is a survey of a section of the sky to measure the redshift of astronomical objects: usually galaxies, but sometimes other objects such as galaxy clusters or quasars. Using Hubble's law, the redshift can be used to estimate the distance of an object from Earth. By combining redshift with angular position data, a redshift survey maps the 3D distribution of matter within a field of the sky. These observations are used to measure detailed statistical properties of the large-scale structure of the universe. In conjunction with observations of early structure in the cosmic microwave background, these results can place strong constraints on cosmological parameters such as the average matter density and the Hubble constant.

An astronomical survey is a general map or image of a region of the sky that lacks a specific observational target. Alternatively, an astronomical survey may comprise a set of images, spectra, or other observations of objects that share a common type or feature. Surveys are often restricted to one band of the electromagnetic spectrum due to instrumental limitations, although multiwavelength surveys can be made by using multiple detectors, each sensitive to a different bandwidth.

The Dark Energy Survey (DES) is an astronomical survey designed to constrain the properties of dark energy. It uses images taken in the near-ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared to measure the expansion of the universe using Type Ia supernovae, baryon acoustic oscillations, the number of galaxy clusters, and weak gravitational lensing. The collaboration is composed of research institutions and universities from the United States, Australia, Brazil, the United Kingdom, Germany, Spain, and Switzerland. The collaboration is divided into several scientific working groups. The director of DES is Josh Frieman.
In cosmology, baryon acoustic oscillations (BAO) are fluctuations in the density of the visible baryonic matter of the universe, caused by acoustic density waves in the primordial plasma of the early universe. In the same way that supernovae provide a "standard candle" for astronomical observations, BAO matter clustering provides a "standard ruler" for length scale in cosmology. The length of this standard ruler is given by the maximum distance the acoustic waves could travel in the primordial plasma before the plasma cooled to the point where it became neutral atoms, which stopped the expansion of the plasma density waves, "freezing" them into place. The length of this standard ruler can be measured by looking at the large scale structure of matter using astronomical surveys. BAO measurements help cosmologists understand more about the nature of dark energy by constraining cosmological parameters.
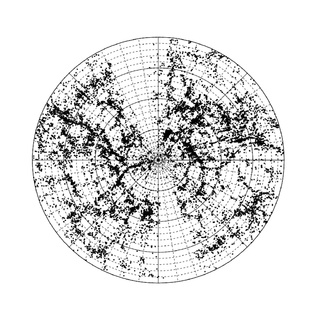
The 6dF Galaxy Survey, 6dF or 6dFGS is a redshift survey conducted by the Anglo-Australian Observatory (AAO) with the 1.2m UK Schmidt Telescope between 2001 and 2009. The data from this survey were made public on 31 March, 2009. The survey has mapped the nearby universe over nearly half the sky. Its 136,304 spectra have yielded 110,256 new extragalactic redshifts and a new catalog of 125,071 galaxies. For a subsample of 6dF a peculiar velocity survey is measuring mass distribution and bulk motions of the local Universe. As of July 2009, it is the third largest redshift survey next to the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) and the 2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey (2dFGRS).

Euclid is a wide-angle space telescope with a 600-megapixel camera to record visible light, a near-infrared spectrometer, and photometer, to determine the redshift of detected galaxies. It was developed by the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Euclid Consortium and was launched on 1 July 2023.

Michael Logan Lampton was an American astronaut, scientist, and founder of the optical ray tracing company Stellar Software. He was also known for his paper on electroacoustics with Susan M Lea, The theory of maximally flat loudspeaker systems.
Michael R. Blanton is an American physicist whose expertise is in the fields of galaxy evolution and cosmology. A professor in New York University's department of physics, Blanton has primarily focused on mapping the Universe.
Constance "Connie" Mary Rockosi is a professor and former department chair in the Astronomy and Astrophysics Department at the University of California, Santa Cruz. She earned her PhD in 2001 and helped design the camera for the telescope that was used as part of the initial Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS). She also was in charge of the SDSS-III domain for the Sloan Extension for Galactic Understanding and Exploration (SEGUE) project and is the primary investigator on SEGUE-2. Her focuses involve the study of the Milky Way galaxy, with a focus on the evolution that it took to reach its current state.
Idit Zehavi is an Israeli astrophysicist and researcher who discovered an anomaly in the mapping of the cosmos, which offered insight into how the universe is expanding. She is part of the team completing the Sloan Digital Sky Survey and is one of the world's most highly cited scientists according to the list published annually by Thomson Reuters.

The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) is a scientific research instrument for conducting spectrographic astronomical surveys of distant galaxies. Its main components are a focal plane containing 5,000 fiber-positioning robots, and a bank of spectrographs which are fed by the fibers. The new instrument will enable an experiment to probe the expansion history of the universe and the mysterious physics of dark energy.
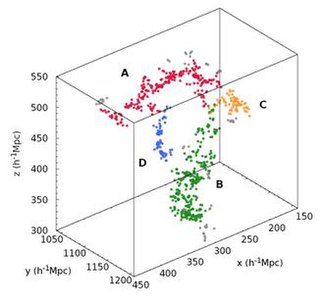
The BOSS Great Wall is a supercluster complex that was identified, using the Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey (BOSS) of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), in early 2016. It was discovered by a research team from several institutions, consisting of: Heidi Lietzen, Elmo Tempel, Lauri Juhan Liivamägi, Antonio Montero-Dorta, Maret Einasto, Alina Streblyanska, Claudia Maraston, Jose Alberto Rubiño-Martín and Enn Saar. The BOSS Great Wall is one of the largest superstructures in the observable universe, though there are even larger structures known.

The WiggleZ Dark Energy Survey is a large-scale astronomical redshift survey that was carried out on the 3.9 metre Anglo-Australian Telescope (AAT) at the Siding Spring Observatory, New South Wales between August 2006 and January 2011. The name stems from the measurement of baryon acoustic oscillations in the distribution of galaxies.
The Saraswati Supercluster is a massive galaxy supercluster about 1.2 gigaparsecs (4 billion light years) away within the Stripe 82 region of SDSS, in the direction of the constellation Pisces. It is one of the largest structures found in the universe, with a major axis in diameter of about 200 Mpc (652 million light years). It consists of at least 43 galaxy clusters, and has the mass of 2 × 1016 M☉, forming a galaxy filament.
Claudia Maraston is a Professor of Astrophysics at the University of Portsmouth. She designs models for the calculation of spectro-photometric evolution of stellar populations. She is the winner of the 2018 Royal Astronomical Society Eddington Medal.
Natalie Ann Roe is an experimental particle physicist and observational cosmologist, and the Associate Laboratory Director for the Physical Sciences Area at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) since 2020. Previously, she was the Physics Division Director for eight years. She has been awarded as the Fellow of American Physical Society (APS) and American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) for her exceptional scientific career and contributions.
Shirley Ho is an American astrophysicist and machine learning expert, currently at the Center for Computational Astrophysics at Flatiron Institute in NYC and at the New York University and the Carnegie Mellon University. Ho also has visiting appointment at Princeton University.
Mustapha Ishak-Boushaki is a theoretical physicist, cosmologist and professor at the University of Texas at Dallas. He is known for his contributions to the studies of cosmic acceleration and dark energy, gravitational lensing, and testing alternatives to general relativity; as well as his authorship of Testing General Relativity in Cosmology, a review article published in Living Reviews in Relativity. He was elected as a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) in 2021 and as a fellow of the American Physical Society (APS) with the quote: "For distinguished contributions to the field of theoretical cosmology, particularly for testing modifications to general relativity at cosmological scales, and for sustained excellence in teaching and mentoring of students."
References
- ↑ "David Schlegel". Berkeley Institute for Data Science. Retrieved 2020-04-14.
- ↑ "Schlegel, David J – Cosmology" . Retrieved 2020-04-14.
- ↑ Schlegel, David J.; Finkbeiner, Douglas P.; Davis, Marc (1998). "Maps of Dust Infrared Emission for Use in Estimation of Reddening and Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Foregrounds". The Astrophysical Journal. 500 (2): 525–553. arXiv: astro-ph/9710327 . Bibcode:1998ApJ...500..525S. doi:10.1086/305772.
- ↑ Biello, David. "Largest Map of Universe Yet Bolsters Theories about Dark Energy". Scientific American. Retrieved 2020-04-14.
- ↑ "APO Home Page". www.apo.nmsu.edu. Retrieved 2020-04-14.
- ↑ "The Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey (BOSS)". Archived from the original on 2014-08-28.
- ↑ Survey, Legacy (2019-07-05). "The Dark Energy Camera Legacy Survey (DECaLS)". Legacy Survey. Retrieved 2020-04-14.
- ↑ "Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument", Wikipedia, 2020-04-10, retrieved 2020-04-14
- ↑ Dey, Arjun; Schlegel, David J.; Lang, Dustin; Blum, Robert; Burleigh, Kaylan; Fan, Xiaohui; Findlay, Joseph R.; Finkbeiner, Doug; Herrera, David; Juneau, Stéphanie; Landriau, Martin; Levi, Michael; McGreer, Ian; Meisner, Aaron; Myers, Adam D.; Moustakas, John; Nugent, Peter; Patej, Anna; Schlafly, Edward F.; Walker, Alistair R.; Valdes, Francisco; Weaver, Benjamin A.; Yèche, Christophe; Zou, Hu; Zhou, Xu; Abareshi, Behzad; Abbott, T. M. C.; Abolfathi, Bela; Aguilera, C.; et al. (2019). "Overview of the DESI Legacy Imaging Surveys". The Astronomical Journal. 157 (5): 168. arXiv: 1804.08657 . Bibcode:2019AJ....157..168D. doi: 10.3847/1538-3881/ab089d . S2CID 56335994.
- ↑ "LAWRENCE David J. Schlegel, 2014 | U.S. DOE Office of Science (SC)". science.osti.gov. 2010-12-28. Retrieved 2020-04-14.