
A biological membrane, biomembrane or cell membrane is a selectively permeable membrane that separates the interior of a cell from the external environment or creates intracellular compartments by serving as a boundary between one part of the cell and another. Biological membranes, in the form of eukaryotic cell membranes, consist of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded, integral and peripheral proteins used in communication and transportation of chemicals and ions. The bulk of lipids in a cell membrane provides a fluid matrix for proteins to rotate and laterally diffuse for physiological functioning. Proteins are adapted to high membrane fluidity environment of the lipid bilayer with the presence of an annular lipid shell, consisting of lipid molecules bound tightly to the surface of integral membrane proteins. The cell membranes are different from the isolating tissues formed by layers of cells, such as mucous membranes, basement membranes, and serous membranes.

The lipid bilayer is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer, as are the nuclear membrane surrounding the cell nucleus, and membranes of the membrane-bound organelles in the cell. The lipid bilayer is the barrier that keeps ions, proteins and other molecules where they are needed and prevents them from diffusing into areas where they should not be. Lipid bilayers are ideally suited to this role, even though they are only a few nanometers in width, because they are impermeable to most water-soluble (hydrophilic) molecules. Bilayers are particularly impermeable to ions, which allows cells to regulate salt concentrations and pH by transporting ions across their membranes using proteins called ion pumps.

A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them (beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents.

Peripheral membrane proteins, or extrinsic membrane proteins, are membrane proteins that adhere only temporarily to the biological membrane with which they are associated. These proteins attach to integral membrane proteins, or penetrate the peripheral regions of the lipid bilayer. The regulatory protein subunits of many ion channels and transmembrane receptors, for example, may be defined as peripheral membrane proteins. In contrast to integral membrane proteins, peripheral membrane proteins tend to collect in the water-soluble component, or fraction, of all the proteins extracted during a protein purification procedure. Proteins with GPI anchors are an exception to this rule and can have purification properties similar to those of integral membrane proteins.

The plasma membranes of cells contain combinations of glycosphingolipids, cholesterol and protein receptors organised in glycolipoprotein lipid microdomains termed lipid rafts. Their existence in cellular membranes remains somewhat controversial. It has been proposed that they are specialized membrane microdomains which compartmentalize cellular processes by serving as organising centers for the assembly of signaling molecules, allowing a closer interaction of protein receptors and their effectors to promote kinetically favorable interactions necessary for the signal transduction. Lipid rafts influence membrane fluidity and membrane protein trafficking, thereby regulating neurotransmission and receptor trafficking. Lipid rafts are more ordered and tightly packed than the surrounding bilayer, but float freely within the membrane bilayer. Although more common in the cell membrane, lipid rafts have also been reported in other parts of the cell, such as the Golgi apparatus and lysosomes.

Cotransporters are a subcategory of membrane transport proteins (transporters) that couple the favorable movement of one molecule with its concentration gradient and unfavorable movement of another molecule against its concentration gradient. They enable coupled or cotransport and include antiporters and symporters. In general, cotransporters consist of two out of the three classes of integral membrane proteins known as transporters that move molecules and ions across biomembranes. Uniporters are also transporters but move only one type of molecule down its concentration gradient and are not classified as cotransporters.
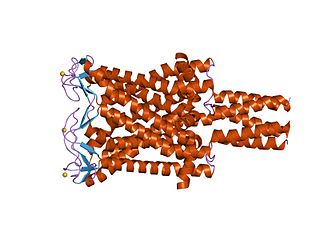
The ATP-binding cassette transporters are a transport system superfamily that is one of the largest and possibly one of the oldest gene families. It is represented in all extant phyla, from prokaryotes to humans. ABC transporters belong to translocases.
Phospholipase D (EC 3.1.4.4, lipophosphodiesterase II, lecithinase D, choline phosphatase, PLD; systematic name phosphatidylcholine phosphatidohydrolase) is an enzyme of the phospholipase superfamily that catalyses the following reaction

Molecular biophysics is a rapidly evolving interdisciplinary area of research that combines concepts in physics, chemistry, engineering, mathematics and biology. It seeks to understand biomolecular systems and explain biological function in terms of molecular structure, structural organization, and dynamic behaviour at various levels of complexity. This discipline covers topics such as the measurement of molecular forces, molecular associations, allosteric interactions, Brownian motion, and cable theory. Additional areas of study can be found on Outline of Biophysics. The discipline has required development of specialized equipment and procedures capable of imaging and manipulating minute living structures, as well as novel experimental approaches.

A colicin is a type of bacteriocin produced by and toxic to some strains of Escherichia coli. Colicins are released into the environment to reduce competition from other bacterial strains. Colicins bind to outer membrane receptors, using them to translocate to the cytoplasm or cytoplasmic membrane, where they exert their cytotoxic effect, including depolarisation of the cytoplasmic membrane, DNase activity, RNase activity, or inhibition of murein synthesis.
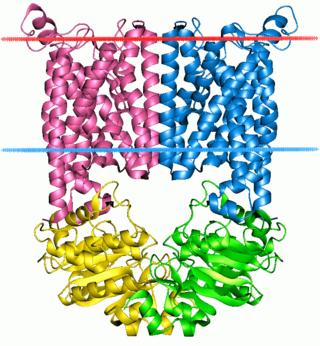
The Large Conductance Mechanosensitive Ion Channel (MscL) Family consists of pore-forming membrane proteins that are responsible for translating physical forces applied to cell membranes into electrophysiological activities. MscL has a relatively large conductance, 3 nS, making it permeable to ions, water, and small proteins when opened. MscL acts as stretch-activated osmotic release valve in response to osmotic shock.

Outer membrane receptors, also known as TonB-dependent receptors, are a family of beta barrel proteins named for their localization in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. TonB complexes sense signals from the outside of bacterial cells and transmit them into the cytoplasm, leading to transcriptional activation of target genes. TonB-dependent receptors in gram-negative bacteria are associated with the uptake and transport of large substrates such as iron siderophore complexes and vitamin B12.

Myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MARCKS gene. It plays important roles in cell shape, cell motility, secretion, transmembrane transport, regulation of the cell cycle, and neural development. Recently, MARCKS has been implicated in the exocytosis of a number of vesicles and granules such as mucin and chromaffin. It is also the name of a protein family, of which MARCKS is the most studied member. They are intrinsically disordered proteins, with an acidic pH, with high proportions of alanine, glycine, proline, and glutamic acid. They are membrane-bound through a lipid anchor at the N-terminus, and a polybasic domain in the middle. They are regulated by Ca2+/calmodulin and protein kinase C. In their unphosphorylated form, they bind to actin filaments, causing them to crosslink, and sequester acidic membrane phospholipids such as PIP2.
Orientations of Proteins in Membranes (OPM) database provides spatial positions of membrane protein structures with respect to the lipid bilayer. Positions of the proteins are calculated using an implicit solvation model of the lipid bilayer. The results of calculations were verified against experimental studies of spatial arrangement of transmembrane and peripheral proteins in membranes.

In membrane biology, fusion is the process by which two initially distinct lipid bilayers merge their hydrophobic cores, resulting in one interconnected structure. If this fusion proceeds completely through both leaflets of both bilayers, an aqueous bridge is formed and the internal contents of the two structures can mix. Alternatively, if only one leaflet from each bilayer is involved in the fusion process, the bilayers are said to be hemifused. In hemifusion, the lipid constituents of the outer leaflet of the two bilayers can mix, but the inner leaflets remain distinct. The aqueous contents enclosed by each bilayer also remain separated.
A model lipid bilayer is any bilayer assembled in vitro, as opposed to the bilayer of natural cell membranes or covering various sub-cellular structures like the nucleus. They are used to study the fundamental properties of biological membranes in a simplified and well-controlled environment, and increasingly in bottom-up synthetic biology for the construction of artificial cells. A model bilayer can be made with either synthetic or natural lipids. The simplest model systems contain only a single pure synthetic lipid. More physiologically relevant model bilayers can be made with mixtures of several synthetic or natural lipids.
Membrane contact sites (MCS) are close appositions between two organelles. Ultrastructural studies typically reveal an intermembrane distance in the order of the size of a single protein, as small as 10 nm or wider, with no clear upper limit. These zones of apposition are highly conserved in evolution. These sites are thought to be important to facilitate signalling, and they promote the passage of small molecules, including ions, lipids and reactive oxygen species. MCS are important in the function of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), since this is the major site of lipid synthesis within cells. The ER makes close contact with many organelles, including mitochondria, Golgi, endosomes, lysosomes, peroxisomes, chloroplasts and the plasma membrane. Both mitochondria and sorting endosomes undergo major rearrangements leading to fission where they contact the ER. Sites of close apposition can also form between most of these organelles most pairwise combinations. First mentions of these contact sites can be found in papers published in the late 1950s mainly visualized using electron microscopy (EM) techniques. Copeland and Dalton described them as “highly specialized tubular form of endoplasmic reticulum in association with the mitochondria and apparently in turn, with the vascular border of the cell”.
Mechanosensitive channels (MSCs), mechanosensitive ion channels or stretch-gated ion channels are membrane proteins capable of responding to mechanical stress over a wide dynamic range of external mechanical stimuli. They are present in the membranes of organisms from the three domains of life: bacteria, archaea, and eukarya. They are the sensors for a number of systems including the senses of touch, hearing and balance, as well as participating in cardiovascular regulation and osmotic homeostasis (e.g. thirst). The channels vary in selectivity for the permeating ions from nonselective between anions and cations in bacteria, to cation selective allowing passage Ca2+, K+ and Na+ in eukaryotes, and highly selective K+ channels in bacteria and eukaryotes.
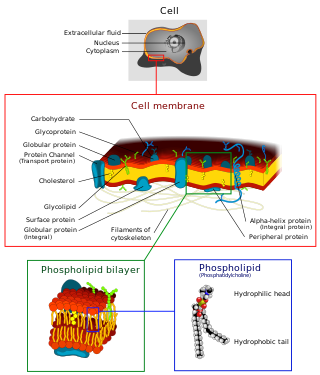
The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules. In addition, cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity, and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall and the carbohydrate layer called the glycocalyx, as well as the intracellular network of protein fibers called the cytoskeleton. In the field of synthetic biology, cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.

James J. Chou (周界文) is a Chinese American scientist and Professor of Biological Chemistry and Molecular Pharmacology at the Harvard Medical School. He is known for pioneering the use of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy to reveal the structural details of the membrane regions of cell surface proteins, particularly those of immune receptors and viral membrane proteins.














