Related Research Articles
Pop music is a genre of popular music that originated in its modern form during the mid-1950s in the United States and the United Kingdom. During the 1950s and 1960s, pop music encompassed rock and roll and the youth-oriented styles it influenced. Rock and pop music remained roughly synonymous until the late 1960s, after which pop became associated with music that was more commercial, ephemeral, and accessible.

Music theory is the study of the practices and possibilities of music. The Oxford Companion to Music describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory": The first is the "rudiments", that are needed to understand music notation ; the second is learning scholars' views on music from antiquity to the present; the third is a sub-topic of musicology that "seeks to define processes and general principles in music". The musicological approach to theory differs from music analysis "in that it takes as its starting-point not the individual work or performance but the fundamental materials from which it is built."

Arabic music is the music of the Arab world with all its diverse music styles and genres. Arabic countries have many rich and varied styles of music and also many linguistic dialects, with each country and region having their own traditional music.
Ad-Dawr is a small agricultural town in Saladin Governorate, Iraq, near Tikrit. It includes a great number of people from four tribes, al-Shuwaykhat, al-Mawashet, al-Bu Haydar and al-Bu Mdallal. Al-Mawashet tribe is famous for supporting Saddam Hussein.

The maqāma is an (originally) Arabic prosimetric literary genre which alternates the Arabic rhymed prose known as Saj‘ with intervals of poetry in which rhetorical extravagance is conspicuous.

Islamic music may refer to religious music, as performed in Islamic public services or private devotions, or more generally to musical traditions of the Muslim world. The heartland of Islam is the Middle East, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, West Africa, Iran, Central Asia, and South Asia. Due to Islam being a multi-ethnic religion, the musical expression of its adherents is vastly diverse. Indigenous traditions of various part have influenced the musical styles popular among Muslims today. The word "music" in Arabic, the language of Islam, is defined more narrowly than in English or some other languages, and "its concept" was at least originally "reserved for secular art music; separate names and concepts belonged to folk songs and to religious chants".
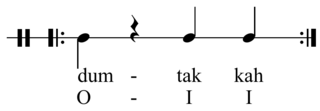
Rhythms in Arabic music are rich and very diverse, as they cover a huge region and peoples from Northern Africa to Western Asia. Rhymes are mainly analysed by means of rhythmic units called awzan and iqa'at.
Takht is the representative musical ensemble, the orchestra, of Middle Eastern music. In Egypt, Syria, Lebanon, Palestine, and Jordan, the ensemble consists of the oud, the qanun, the kamanjah, the ney, the riq, and the darabukkah. The word takht means "bed", "seat", or "podium" in Persian.

Iraqi Maqam is a genre of Arabic maqam music found in Iraq. The roots of modern Iraqi maqam can be traced as far back as the Abbasid Caliphate, when that large empire was controlled from Baghdad. The ensemble of instruments used in this genre, called Al Chalghi al Baghdadi, includes a qari' (singer), santur, goblet drum, joza, cello, and sometimes oud and naqqarat. The focus is on the poem sung in classical Arabic or an Iraqi dialect. A complete maqam concert is known as fasl and is named after the first maqam: Bayat, Hijaz, Rast, Nawa, or Husayni.
Muwashshah is the name for both an Arabic poetic form and a secular musical genre. The poetic form consists of a multi-lined strophic verse poem written in classical Arabic, usually consisting of five stanzas, alternating with a refrain with a running rhyme. It was customary to open with one or two lines which matched the second part of the poem in rhyme and meter; in North Africa poets ignore the strict rules of Arabic meter while the poets in the East follow them. The musical genre of the same name uses muwaššaḥ texts as lyrics, still in classical Arabic. This tradition can take two forms: the waṣla of the Mashriq and the Arab Andalusi nubah of the western part of the Arab world.
Pop rock is a rock fusion genre characterized by a strong commercial appeal, with more emphasis on professional songwriting and recording craft, and less emphasis on attitude than standard rock music. Originating in the late 1950s as an alternative to normal rock and roll, early pop rock was influenced by the beat, arrangements, and original style of rock and roll. It may be viewed as a distinct genre field rather than music that overlaps with pop and rock. The detractors of pop rock often deride it as a slick, commercial product and less authentic than rock music.
Chalga is a Bulgarian music genre. Chalga or pop-folk is essentially a folk-inspired dance music genre, with a blend of Bulgarian music and also primary influences from Greek, Turkish and Arabic.

Sufi music refers to the devotional music of the Sufis, inspired by the works of Sufi poets like Rumi, Hafiz, Bulleh Shah, Amir Khusrow, and Khwaja Ghulam Farid.
A wasla is a set of pieces in Arabic music. It comprises eight or more movements such as muwashshah, taqsim, layali, mawwal, qasida, dawr, sama'i, bashraf, dulab, and popular songs.

Comedy is a genre of fiction that consists of discourses or works intended to be humorous or amusing by inducing laughter, especially in theatre, film, stand-up comedy, television, radio, books, or any other entertainment medium. The term originated in ancient Greece: In Athenian democracy, the public opinion of voters was influenced by political satire performed by comic poets in theaters. The theatrical genre of Greek comedy can be described as a dramatic performance pitting two groups, ages, genders, or societies against each other in an amusing agon or conflict. Northrop Frye depicted these two opposing sides as a "Society of Youth" and a "Society of the Old". A revised view characterizes the essential agon of comedy as a struggle between a relatively powerless youth and the societal conventions posing obstacles to his hopes. In this struggle, the youth then becomes constrained by his lack of social authority, and is left with little choice but to resort to ruses which engender dramatic irony, which provokes laughter.
Dour can refer to:
Douri, Al-Douri or Ad-Douri is an Arabic-based surname, derived from the name of the Iraqi town Ad-Dawr. Douri may refer to:
Pop music is a genre of popular music that originated in its modern form during the mid-1950s in the United States and the United Kingdom. The terms popular music and pop music are often used interchangeably, although the former describes all music that is popular and includes many disparate styles. During the 1950s and 1960s, pop music encompassed rock and roll and the youth-oriented styles it influenced. Rock and pop music remained roughly synonymous until the late 1960s, after which pop became associated with music that was more commercial, ephemeral, and accessible.

Saad Sport Club is an Iraqi football team based in Ad-Dawr, Saladin, that plays in Iraq Division Three.
Shabab Al-Dawr Sport Club is an Iraqi football team based in Saladin, that plays in Iraq Division Two.
References
- ↑ Racy, Ali Jihad. Making Music in the Arab World: The Culture and Artistry of Tarab. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003.