
Deaf Sentence (2008) is a novel by British author David Lodge. [1]

Deaf Sentence (2008) is a novel by British author David Lodge. [1]

American Sign Language (ASL) is a natural language that serves as the predominant sign language of Deaf communities in the United States and most of Anglophone Canada. ASL is a complete and organized visual language that is expressed by employing both manual and nonmanual features. Besides North America, dialects of ASL and ASL-based creoles are used in many countries around the world, including much of West Africa and parts of Southeast Asia. ASL is also widely learned as a second language, serving as a lingua franca. ASL is most closely related to French Sign Language (LSF). It has been proposed that ASL is a creole language of LSF, although ASL shows features atypical of creole languages, such as agglutinative morphology.

Sign languages are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with non-manual markers. Sign languages are full-fledged natural languages with their own grammar and lexicon. Sign languages are not universal and are usually not mutually intelligible, although there are similarities among different sign languages.
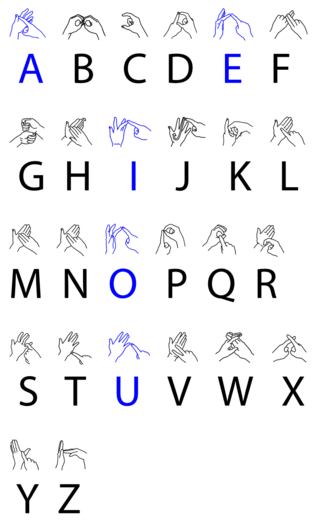
British Sign Language (BSL) is a sign language used in the United Kingdom and is the first or preferred language among the deaf community in the UK. While private correspondence from William Stokoe hinted at a formal name for the language in 1960, the first usage of the term "British Sign Language" in an academic publication was likely by Aaron Cicourel. Based on the percentage of people who reported 'using British Sign Language at home' on the 2011 Scottish Census, the British Deaf Association estimates there are 151,000 BSL users in the UK, of whom 87,000 are Deaf. By contrast, in the 2011 England and Wales Census 15,000 people living in England and Wales reported themselves using BSL as their main language. People who are not deaf may also use BSL, as hearing relatives of deaf people, sign language interpreters or as a result of other contact with the British Deaf community. The language makes use of space and involves movement of the hands, body, face and head.
David John Lodge CBE FRSL is an English author and critic. A literature professor at the University of Birmingham until 1987, some of his novels satirise academic life, notably the "Campus Trilogy" – Changing Places: A Tale of Two Campuses (1975), Small World: An Academic Romance (1984) and Nice Work (1988). The second two were shortlisted for the Booker Prize. Another theme is Roman Catholicism, beginning from his first published novel The Picturegoers (1960). Lodge has also written television screenplays and three stage plays. After retiring, he continued to publish literary criticism. His edition of Twentieth Century Literary Criticism (1972) includes essays on 20th-century writers such as T. S. Eliot. In 1992, he published The Art of Fiction, a collection of essays on literary techniques with illustrative examples from great authors, such as Point of View, The Stream of Consciousness and Interior Monologue, beginning with Beginning and ending with Ending.

The Deaflympics, also known as Deaflympiad are a periodic series of multi-sport events sanctioned by the International Olympic Committee (IOC) at which deaf athletes compete at an elite level. Unlike the athletes in other IOC-sanctioned events, athletes cannot be guided by sounds. The games have been organized by the Comité International des Sports des Sourds since the first event in 1924.
Manually Coded English (MCE) is an umbrella term referring to a number of invented manual codes intended to visually represent the exact grammar and morphology of spoken English. Different codes of MCE vary in the levels of adherence to spoken English grammar, morphology, and syntax. MCE is typically used in conjunction with direct spoken English.

German Sign Language is the sign language of the deaf community in Germany, Luxembourg and in the German-speaking community of Belgium. It is unclear how many use German Sign Language as their main language; Gallaudet University estimated 50,000 as of 1986. The language has evolved through use in deaf communities over hundreds of years.
Japanese Sign Language, also known by the acronym JSL, is the dominant sign language in Japan and is a complete natural language, distinct from but influenced by the spoken Japanese language.
Audism as described by deaf activists is a form of discrimination directed against deaf people, which may include those diagnosed as deaf from birth, or otherwise. Tom L. Humphries coined the term in an unpublished manuscript in 1975, which he later reiterated in his doctoral project in 1977, but it did not start to catch on until Harlan Lane used it in his writing. Humphries originally applied audism to individual attitudes and practices; whereas Lane broadened the term to include oppression of deaf people.
Harry Corbett OBE was an English magician, puppeteer and television presenter. He was best known as the creator of the glove puppet character Sooty in 1952.
Indo-Pakistani Sign Language (IPSL) is the predominant sign language in the subcontinent of South Asia, used by at least 15 million deaf signers. As with many sign languages, it is difficult to estimate numbers with any certainty, as the Census of India does not list sign languages and most studies have focused on the north and urban areas. As of 2024, it is the most used sign language in the world, and Ethnologue ranks it as the 149th most "spoken" language in the world.
A contact sign language, or contact sign, is a variety or style of language that arises from contact between deaf individuals using a sign language and hearing individuals using an oral language. Contact languages also arise between different sign languages, although the term pidgin rather than contact sign is used to describe such phenomena.
Oak Lodge School is a specialist day school with a residential provision for students with hearing, speech, language and communication needs aged 10–19. It is located in the London borough of Wandsworth in England.
Events from the year 1867 in the United States.

Linden Lodge School for the Blind is a specialist sensory and physical college located in Wimbledon, South London, England. It educates visually impaired children aged between two and nineteen, including those who are multi-disabled visually impaired.
Russian Sign Language (RSL) is the sign language used by the Deaf community in Russia, with what is possibly additional presence in Belarus and Tajikistan. It belongs to the French Sign Language family.
Hong Kong Sign Language (香港手語), alternatively romanized as Hong Kong Saujyu and popularly abbreviated in English as HKSL, is the deaf sign language of Hong Kong and Macau. It derived from the southern dialect of Chinese Sign Language, but is now an independent, mutually unintelligible language.
The Arab sign-language family is a family of sign languages spread across the Arab Middle East. Its extent is not yet known, because only some of the sign languages in the region have been compared.
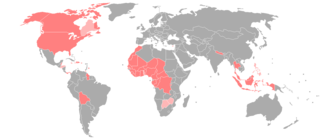
American Sign Language (ASL) developed in the United States, starting as a blend of local sign languages and French Sign Language (FSL). Local varieties have developed in many countries, but there is little research on which should be considered dialects of ASL and which have diverged to the point of being distinct languages.

David Lodge is a research fellow in the Department of Physiology and Pharmacology at the University of Bristol.