Nadiad is a city in the state of Gujarat, India and the administrative centre of the Kheda district. It is known for the Santram Mandir, the Mai Mandir, It is the birthplace of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, the first Deputy Prime Minister of India.

Adalaj is a census town in Gandhinagar district located in the western Indian state of Gujarat. With a population of roughly 12,000 residents within the town limits as of 2011, Adalaj is known for its semi-arid climate and its historic and religious establishments. The town sits in a generally flat area covering about 18 sq. km.
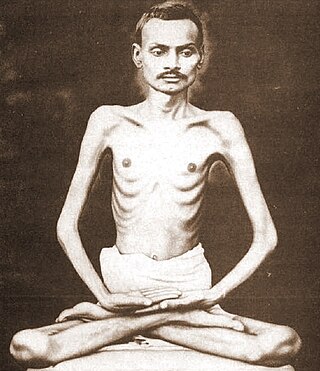
Shrimad Rajchandra, also known as Param Krupalu Dev, was a Jain poet, mystic, philosopher, scholar, and reformer from India. Born in Vavaniya, a village near Morbi, he claimed to have attained recollection of his past lives at the age of seven. He performed Avadhāna, a memory retention and recollection test that gained him popularity, but he later discouraged it in favour of his spiritual pursuits. He wrote much philosophical poetry including Atma Siddhi Shastra. He also wrote many letters and commentaries and translated some religious texts. He is known for his teachings on Jainism and his spiritual guidance to Mahatma Gandhi.
Dharampur is a town and a municipality in Valsad district in the state of Gujarat, India. There are more than 100 villages associated with Dharampur (Revenue) office. Ramsingh of the Sesodia clan, the second son of Ram Raja of Udaipur, defeated the local tribal chief in the 13th century and became the ruler of Dharampur State in South Gujarat.
Sakri is a census town and a taluka in the Dhule District of the Nashik division, Maharashtra state, India. The town of Sakri is the administrative headquarters for Sakri Taluka. Another Sakri is in Bihar, which is now a railway junction.

Dada Bhagwan, also known as Dadashri, born Ambalal Muljibhai Patel, was an Indian spiritual leader from Gujarat who founded the Akram Vignan Movement. He was spiritually inclined from an early age. He worked as a contractor for a company maintaining dry docks in Bombay before attaining "self-realization" in 1958. He left business and focused on his spiritual goals. The movement around his teaching grew into the Akram Vignan movement gaining followers in western India and abroad. Ahimsa (non-violence) and vegetarianism are an important part of Dada's teachings.

The credit for introducing Jainism to the West goes to a German scholar, Hermann Jacobi, who translated some Jain literature and published it in the series 'Sacred Books of East' in 1884. In Europe, the largest Jain populations are in Britain, with a population of about 25,000.

Kumarpal Balabhai Desai is an author, critic, editor, journalist, columnist and translator from Gujarat, India. He studied and later taught at the Gujarat University. He is associated with several social and Gujarati literary organisations such as Gujarati Sahitya Parishad. He has written and edited more than hundred books including biographies and several works on Jainism. He was awarded the Padma Shri in 2004.

Kanji Swami (1890–1980) was a teacher of Jainism. He was deeply influenced by the Samayasāra of Kundakunda in 1932. He lectured on these teachings for 45 years to comprehensively elaborate on the philosophy described by Kundakunda and others. He was given the title of "Koh-i-Noor of Kathiawar" by the people who were influenced by his religious teachings and philosophy.

Rakesh Jhaveri, also known as Pujya Gurudevshri Rakeshji, is a spiritual leader, mystic, scholar of Jainism, author and orator from India. Spiritually inclined from a young age, he is a follower of Shrimad Rajchandra, a Jain spiritual teacher. He completed doctoral studies on Shrimad's work Atmasiddhi. He founded Shrimad Rajchandra Mission, Dharampur which supports spiritual and social activities.
Atma Siddhi Shastra is a spiritual treatise in verse, composed in Gujarati by the nineteenth century Jain saint, philosopher poet Shrimad Rajchandra (1867–1901). Atma according to Jainism means "soul" or the "self" and "siddhi" means "attainment". Hence, Atma Siddhi is translated as self attainment or self realization. It is a composition of 142 verses in Gujarati, explaining the fundamental philosophical truths about the soul and its liberation. It propounds six fundamental truths on soul which are also known as satapada.

Pandit Niraj Jain was a scholar of Jainism, archaeologist, poet and speaker. His contributions to Jain studies span nearly 60 years. He was also an expert on Urdu poetry, which is unusual for a Jain scholar. He was associated with several organisations. He also lectured on the Ramayana He was a proponent of preserving historical nature of ancient temples. He had travelled and lectured widely in India and overseas .

The Gandhi Global Family medals and awards are awards offered by the Gandhi Global Family for contributions to society.

Niruben Amin, addressed as Pujya Niruma by her followers, was an Indian spiritual leader and an exponent of the Akram Vignan philosophy. A gynecologist by profession, she became a disciple of Dada Bhagwan during her study years. She nursed Dada Bhagwan during his illness and later succeeded him when he died. She headed the Dada Bhagwan Foundation.

Yugpurush: Mahatma Na Mahatma is a 2016 Gujarati play based on the relationship between Jain philosopher Shrimad Rajchandra and Indian independence leader Mahatma Gandhi. The play depicts the spiritual journey of Gandhi. It is written by Uttam Gada and directed by Rajesh Joshi. The original song for the play is composed by Sachin–Jigar. It is produced by Shrimad Rajchandra Mission, Dharampur and inspired by its founder Pujya Gurudevshri Rakeshbhai. The play is adapted into seven total languages including English, Bengali, Hindi, Marathi, Tamil and Kannada. It won the Best Drama award at the 16th Annual Transmedia Gujarati Screen and Stage Awards 2016. The play has completed 1004 shows as of November 2017.

Digish Nanubhai Mehta was a Gujarati language essayist, novelist and critic from Gujarat, India.
The Akram Vignan movement, also spelled Akram Vijnan, is a new religious movement originated in 1960s in Gujarat, India. It was founded by Dada Bhagwan and later spread to Maharashtra and Gujarati diaspora communities around the world. After death of Dada Bhagwan, the movement split in two factions: one led by Niruben Amin and the other led by Kanubhai Patel.
Shrimad Rajchandra Hospital is a charitable, multi-bed hospital located in the city of Dharampur in the Valsad district of Gujarat, India. The hospital currently operates under the administration of Shrimad Rajchandra Love and Care, a non-governmental organisation (NGO) which runs the hospital and other charitable activities. Established in 2003, it provides medical care at nominal rates or completely free of cost. Hospital records show that over 125,000 patients were treated in 2016, and over 1 million patients have been treated since the inception of the hospital in 2004.

Bhupendra Rajnikant Patel is an Indian politician and civil engineer who is serving as the 17th and current Chief Minister of Gujarat since 2021. He represents the Ghatlodia Assembly constituency in the Gujarat Legislative Assembly since 2017. He is a member of the BJP. He started his political career in municipal bodies of Ahmedabad.
Pujyashri Saubhagyabhai (1823–1896) born in Sayla, Saurashtra was one of the foremost devotees of Shrimad Rajchandra. Saubhagyabhai was 67 years old when he first met Shrimad. Though Shrimad was 44 years younger than him, he declared Shrimad as his Guru and is considered as Shrimad Rajchandra's divine soulmate. The great scripture, Atmasiddhi Shastra was composed by Shrimad Rajchandra upon the request of Saubhagyabhai in 1896.














