The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it began operation on December 2, 1970, after Nixon signed an executive order. The order establishing the EPA was ratified by committee hearings in the House and Senate. The agency is led by its administrator, who is appointed by the president and approved by the Senate. The current administrator is Michael S. Regan. The EPA is not a Cabinet department, but the administrator is normally given cabinet rank.

Water quality refers to the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water based on the standards of its usage. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which compliance, generally achieved through treatment of the water, can be assessed. The most common standards used to monitor and assess water quality convey the health of ecosystems, safety of human contact, extend of water pollution and condition of drinking water. Water quality has a significant impact on water supply and oftentimes determines supply options.

The United States federal Superfund law, officially the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980 (CERCLA), established the federal Superfund program, administered by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The program is designed to investigate and clean up sites contaminated with hazardous substances. Sites managed under this program are referred to as "Superfund" sites. There are 40,000 federal Superfund sites across the country, and approximately 1,600 of those sites have been listed on the National Priorities List (NPL). Sites on the NPL are considered the most highly contaminated and undergo longer-term remedial investigation and remedial action (cleanups).

Environmental protection is the practice of protecting the natural environment by individuals, organizations and governments. Its objectives are to conserve natural resources and the existing natural environment and, where possible, to repair damage and reverse trends.

The Maumee River is a river running in the United States Midwest from northeastern Indiana into northwestern Ohio and Lake Erie. It is formed at the confluence of the St. Joseph and St. Marys rivers, where Fort Wayne, Indiana, has developed, and meanders northeastwardly for 137 miles (220 km) through an agricultural region of glacial moraines before flowing into the Maumee Bay of Lake Erie. The city of Toledo is located at the mouth of the Maumee. The Maumee was designated an Ohio State Scenic River on July 18, 1974. The Maumee watershed is Ohio’s breadbasket; it is two-thirds farmland, mostly corn and soybeans. It is the largest watershed of any of the rivers feeding the Great Lakes, and supplies five percent of Lake Erie’s water.

The St. Clair River is a 40.5-mile-long (65.2 km) river in central North America which flows from Lake Huron into Lake St. Clair, forming part of the international boundary between the Canadian province of Ontario and the United States at Michigan. The river is a significant component in the Great Lakes Waterway, whose shipping channels permit cargo vessels to travel between the upper and lower Great Lakes.

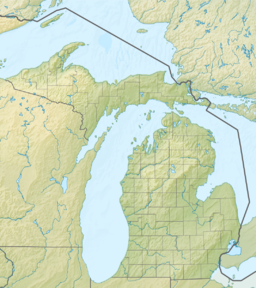
The Kalamazoo River is a river in the U.S. state of Michigan. The river is 130 miles (210 km) long from the junction of its North and South branches to its mouth at Lake Michigan, with a total length extending to 178 miles (286 km) when one includes the South Branch. The river's watershed drains an area of approximately 2,020 square miles (5,200 km2) and drains portions of eight counties in southwest Michigan: Allegan, Barry, Eaton, Van Buren, Kalamazoo, Calhoun, Jackson, Hillsdale, Kent and Ottawa. The river has a median flow of 1,863 cubic feet per second (52.8 m3/s) at New Richmond, upstream from its mouth at Saugatuck.

The Saint Louis River is a river in the U.S. states of Minnesota and Wisconsin that flows into Lake Superior. The largest U.S. river to flow into the lake, it is 192 miles (309 km) in length and starts 13 miles (21 km) east of Hoyt Lakes, Minnesota. The river's watershed covers 3,634 square miles (9,410 km2). Near the Twin Ports of Duluth, Minnesota and Superior, Wisconsin, the river becomes a freshwater estuary. The lower St. Louis is the only river in the state with whitewater rafting opportunities.

The River Rouge is a 127-mile river in the Metro Detroit area of southeastern Michigan. It flows into the Detroit River at Zug Island, which is the boundary between the cities of River Rouge and Detroit.

Milorganite is a brand of biosolids fertilizer produced by treating sewage sludge by the Milwaukee Metropolitan Sewerage District. The term is a portmanteau of the term Milwaukee Organic Nitrogen. The sewer system of the District collects municipal wastewater from the Milwaukee metropolitan area. After settling, wastewater is treated with microbes to break down organic matter at the Jones Island sewage treatment plant in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. The byproduct sewage sludge is produced. This is heat-dried with hot air in the range of 900–1,200 °F (482–649 °C), which heats the sewage sludge to at least 176 °F (80 °C) to kill pathogens. The material is then pelletized and marketed throughout the United States under the name Milorganite. The result is recycling of the nitrogen and phosphorus from the waste-stream as fertilizer. The treated wastewater is discharged to Lake Michigan.

The Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) is the principal federal law in the United States intended to ensure safe drinking water for the public. Pursuant to the act, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is required to set standards for drinking water quality and oversee all states, localities, and water suppliers that implement the standards.

Great Lakes Areas of Concern are designated geographic areas within the Great Lakes Basin that show severe environmental degradation. There are a total of 43 areas of concern within the Great Lakes, 26 being in the United States, 17 in Canada, with five shared by the two countries.

The Clean Air Act (CAA) is the United States' primary federal air quality law, intended to reduce and control air pollution nationwide. Initially enacted in 1963 and amended many times since, it is one of the United States' first and most influential modern environmental laws.
Drinking water quality in the United States is generally safe. In 2016, over 90 percent of the nation's community water systems were in compliance with all published U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) standards. Over 286 million Americans get their tap water from a community water system. Eight percent of the community water systems—large municipal water systems—provide water to 82 percent of the US population.
The Killing Ground is a 1979 American documentary film written by Brit Hume. The film portrays environmental and human health effects of toxic waste dump-sites in Niagara Falls, New York and other locations. It was nominated for an Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature.

The Kalamazoo River oil spill occurred in July 2010 when a pipeline operated by Enbridge burst and flowed into Talmadge Creek, a tributary of the Kalamazoo River. A 6-foot (1.8 m) break in the pipeline resulted in one of the largest inland oil spills in U.S. history. The pipeline carries diluted bitumen (dilbit), a heavy crude oil from Canada's Athabasca oil sands to the United States. Cleanup took five years. Following the spill, the volatile hydrocarbon diluents evaporated, leaving the heavier bitumen to sink in the water column. Thirty-five miles (56 km) of the Kalamazoo River were closed for clean-up until June 2012, when portions of the river were re-opened. On March 14, 2013, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) ordered Enbridge to return to dredge portions of the river to remove submerged oil and oil-contaminated sediment.

Mercury regulation in the United States limit the maximum concentrations of mercury (Hg) that is permitted in air, water, soil, food and drugs. The regulations are promulgated by agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and Food and Drug Administration (FDA), as well as a variety of state and local authorities. EPA published the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS) regulation in 2012; the first federal standards requiring power plants to limit emissions of mercury and other toxic gases.

Pesticide regulation in the United States is primarily a responsibility of the Environmental Protection Agency. In America, it was not till the 1950s that pesticides were regulated in terms of their safety. The Pesticides Control Amendment (PCA) of 1954 was the first time Congress passed guidance regarding the establishment of safe limits for pesticide residues on food. It authorized the FDA to ban pesticides they determined to be unsafe if they were sprayed directly on food. The Food Additives Amendment, which included the Delaney Clause, prohibited the pesticide residues from any carcinogenic pesticides in processed food. In 1959, pesticides were required to be registered.

The Clean Water Rule is a 2015 regulation published by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) to clarify water resource management in the United States under a provision of the Clean Water Act of 1972. The regulation defined the scope of federal water protection in a more consistent manner, particularly over streams and wetlands which have a significant hydrological and ecological connection to traditional navigable waters, interstate waters, and territorial seas. It is also referred to as the Waters of the United States (WOTUS) rule, which defines all bodies of water that fall under U.S. federal jurisdiction. The rule was published in response to concerns about lack of clarity over the act's scope from legislators at multiple levels, industry members, researchers and other science professionals, activists, and citizens.
Michigan v. Environmental Protection Agency, 576 U.S. 743 (2015), is a landmark United States Supreme Court case in which the Court analyzed whether the Environmental Protection Agency must consider costs when deciding to regulate, rather than later in the process of issuing the regulation.