
Thebes, known to the ancient Egyptians as Waset, was an ancient Egyptian city located along the Nile about 800 kilometers (500 mi) south of the Mediterranean. Its ruins lie within the modern Egyptian city of Luxor. Thebes was the main city of the fourth Upper Egyptian nome and was the capital of Egypt for long periods during the Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom eras. It was close to Nubia and the Eastern Desert, with its valuable mineral resources and trade routes. It was a cult center and the most venerated city of ancient Egypt during its heyday. The site of Thebes includes areas on both the eastern bank of the Nile, where the temples of Karnak and Luxor stand and where the city proper was situated; and the western bank, where a necropolis of large private and royal cemeteries and funerary complexes can be found.

Kom Ombo or Ombos or Latin: Ambo and Ombi – is an agricultural town in Egypt famous for the Temple of Kom Ombo. It was originally an Egyptian city called Nubt, meaning City of Gold. Nubt is also known as Nubet or Nubyt (Nbyt). It became a Greek settlement during the Greco-Roman Period. The town's location on the Nile, 50 kilometres (31 mi) north of Aswan (Syene), gave it some control over trade routes from Nubia to the Nile Valley, but its main rise to prominence came with the erection of the Temple of Kom Ombo in the 2nd century BC.

Luxor is a city in Upper (southern) Egypt and the capital of Luxor Governorate. The population numbers 506,535, with an area of approximately 417 square kilometres (161 sq mi).

Amenhotep III, also known as Amenhotep the Magnificent, was the ninth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. According to different authors, he ruled Egypt from June 1386 to 1349 BC, or from June 1388 BC to December 1351 BC/1350 BC, after his father Thutmose IV died. Amenhotep III was Thutmose's son by a minor wife, Mutemwiya.

The Atbarah River in northeast Africa rises in northwest Ethiopia, approximately 50 km north of Lake Tana and 30 km west of Gondar. It flows about 805 km (500 mi) to the Nile in north-central Sudan, joining it at the city of Atbarah. The river's tributary, the Tekezé (Setit) River, is perhaps the true upper course of the Atbarah, as the Tekezé follows the longer course prior to the confluence of the two rivers in northeastern Sudan. The Atbarah is the last tributary of the Nile before it reaches the Mediterranean.
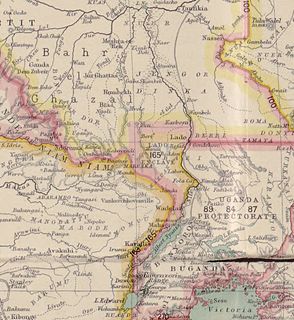
The Lado Enclave was an exclave of the Congo Free State and later of Belgian Congo that existed from 1894 until 1910, situated on the west bank of the Upper Nile in what is now South Sudan and northwest Uganda.

Akhmim is a city in the Sohag Governorate of Upper Egypt. Referred to by the ancient Greeks as Khemmis, Chemmis and Panopolis, it is located on the east bank of the Nile, 4 miles to the northeast of Sohag.

Juba is the capital and largest city of South Sudan. The city is situated on the White Nile and also serves as the capital of Central Equatoria State.
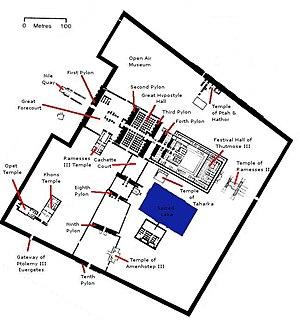
The Precinct of Amun-Re, located near Luxor, Egypt, is one of the four main temple enclosures that make up the immense Karnak Temple Complex. The precinct is by far the largest of these and the only one that is open to the general public. The temple complex is dedicated to the principal god of the Theban Triad, Amun, in the form of Amun-Re.

Malkata, meaning the place where things are picked up in Arabic, is the site of an Ancient Egyptian palace complex built during the New Kingdom, by the 18th Dynasty pharaoh Amenhotep III. It is located on the West Bank of the Nile at Thebes, Upper Egypt, in the desert to the south of Medinet Habu. The site also included a temple dedicated to Amenhotep III's Great Royal Wife, Tiy, which honors Sobek, the crocodile deity.

Buhen was an ancient Egyptian settlement situated on the West bank of the Nile below the Second Cataract in what is now Northern State, Sudan. It is now submerged in Lake Nubia, Sudan. On the East bank, across the river, there was another ancient settlement, where the town of Wadi Halfa now stands.

The Theban Necropolis is a necropolis on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Thebes (Luxor) in Upper Egypt. It was used for ritual burials for much of the Pharaonic period, especially during the New Kingdom.
The Mahas are a sub-group of the Nubians ethnic group located in Sudan along the banks of the Nile. They are further split into the Mahas of the North and Mahas of the East. Some Mahas villages are intermixed with remaining remnants of the largely extinct Qamhat Bishari tribe. Just as Ababda people are Bejas that are bilingual in Arabic and Beja, and sometimes described as Bedouins the Qamhat Mahas are ethnic Beja speaking a Nubian language. Some Mahas of the Butana area have intermarried with the Rashaida people, therefore linking them with the Banu Abs tribe, from which the Rashaida people are descended.
Saï is a large island in the Nile River in Nubia between the second and third cataracts, in the country of Sudan. It is 12 km long and 5.5 km wide. Saï was intermittently occupied by the Egyptians during the New Kingdom. In the Makurian period it was the center of a bishopric, while in the second half of the 16th century the Ottomans founded a fortress on the island.

Kawa is a site in Sudan, located between the Third and Fourth Cataracts of the Nile on the east bank of the river, across from Dongola. In ancient times it was the site of several temples to the Egyptian god Amun, built by the Egyptian rulers Amenhotep III and Tutankhamun, and by Taharqa and other Kushite kings.
Bor-Duk District is a former administrative district located in what is now Jonglei State, South Sudan. The district headquarters was Bor. Until 1906, the Bor-Duk District was part of the Upper Nile Province under the colonial Anglo-Egyptian Condominium Government and encompassed all Dinka-speaking communities living on the east side of the Bahr al Jabal River. In 1906 the Bor-Duk District was shifted to Mongalla Province, which had been created from the southern districts of the Upper Nile Province. In 1909-1910, colonial officials began forcibly resettling people along the northern border of the Bor-Duk district, with the aim of separating Nuer and Dinka communities, who had formerly lived together. The Bor-Duk district was later redesignated "Bor County," divided into two in August 2001, and then divided into three counties in 2003: Duk County, Twic East County, and Bor County. The phrase "Greater Bor" refers to the entirety of the former Bor-Duk District, from Cuei-keer in Kolnyang, to the south, to Cuei-thon in the former Duk County, to the north.

The colossal red granite statue of Amenhotep III is a granite head of the 18th Dynasty Ancient Egyptian Pharaoh Amenhotep III. Dating from around 1370 BC, it was found in the temple enclosure of Mut at Karnak in Upper Egypt. Two parts of the broken colossal statue are known: the head and an arm. Both parts are now in the British Museum.

The colossal quartzite statue of Amenhotep III is an Ancient Egyptian sculpture dating from the 18th Dynasty. It was found in the massive mortuary temple of the pharaoh Amenhotep III on the West Bank of the River Nile at Thebes (Luxor) in Egypt. Only the head of the broken colossal statue survives. It is part of the British Museum's Department of Ancient Egypt and Sudan collection.

Soleb is an ancient town in Nubia, in present-day Sudan. The site is located north of the third cataract of the Nile, on the western side of the Nile. It was discovered and described by Karl Richard Lepsius in 1844.
Sesibi was a New Kingdom Egyptian town the west bank of the Nile, across from Delgo, Sudan. A temple was built there by Akhenaten who appointed a viceroy to maintain the structure, govern the local settlement, and secure traffic on the Nile.
















