Eritrea is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered on the northeast and east by the Red Sea, on the west and northwest by Sudan, on the south by Ethiopia, and on the southeast by Djibouti. The country has a high central plateau that varies from 1,800 to 3,000 meters (5,906–9,843 ft) above sea level. A coastal plain, western lowlands, and some 350 islands comprise the remainder of Eritrea's land mass.

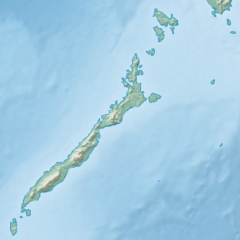
The Philippines is an archipelago that comprises 7,641 islands, and with a total land area of 300,000 square kilometers (115,831 sq mi), it is the world's fifth largest island country. The eleven largest islands contain 95% of the total land area. The largest of these islands is Luzon at about 105,000 square kilometers (40,541 sq mi). The next largest island is Mindanao at about 95,000 square kilometers (36,680 sq mi). The archipelago is around 800 kilometers (500 mi) from the Asian mainland and is located between Taiwan and Borneo.
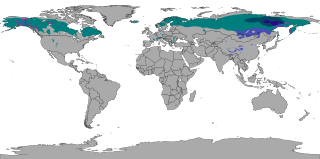
The subarctic climate is a continental climate with long, cold winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50°N to 70°N, poleward of the humid continental climates. Subarctic or boreal climates are the source regions for the cold air that affects temperate latitudes to the south in winter. These climates represent Köppen climate classification Dfc, Dwc, Dsc, Dfd, Dwd and Dsd.

Malta is an island in Southern Europe. It is the largest and most populous of the three major islands that constitute the Maltese Archipelago. The island is situated in the Mediterranean Sea, directly south of Italy and north of Libya. Lying to the south-east of the smaller islands of Gozo and Comino, it is sometimes referred to as Valletta for statistical purposes to distinguish the main island from the entire country. The island is 27 kilometres (17 mi) long and 14.5 kilometres (9 mi) wide, with a total area of 246 square kilometres (95 sq mi). The capital is Valletta, while the largest locality is Rabat. The island is made up of many small towns, which together form one larger urban zone with a population of 409,259. The landscape is characterised by low hills with terraced fields.
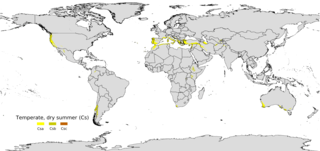
A Mediterranean climate, also called a dry summer climate, described by Köppen as Cs, is a temperate climate type that occurs in the lower mid-latitudes. Such climates typically have dry summers and wet winters, with summer conditions ranging from warm to hot and winter conditions typically being mild to cool. These weather conditions are typically experienced in the majority of Mediterranean-climate regions and countries, but remain highly dependent on proximity to the ocean, altitude and geographical location.

Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the Köppen climate classification identified with the letter A. Tropical climates are defined by a monthly average temperature of 18 °C (64.4 °F) or higher in the coolest month, and feature hot temperatures all year-round. Annual precipitation is often abundant in tropical climates, and shows a seasonal rhythm but may have seasonal dryness to varying degrees. There are normally only two seasons in tropical climates, a wet (rainy/monsoon) season and a dry season. The annual temperature range in tropical climates is normally very small. Sunlight is intense in these climates.

The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, German climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system in 1954 and 1961, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification.
The climate of Mumbai is an extreme version of a tropical wet and dry climate with a lengthy, practically rainless dry season and a relatively short, but extremely rainy wet season due to the Southwest Monsoon and orographic influences from the nearby Western Ghats. Some suburbs are sufficiently wet to qualify as a tropical monsoon climate. Mumbai's climate can be best described as moderately hot with a high level of humidity. Its coastal nature and tropical location ensure temperatures do not fluctuate much throughout the year.

Rapu-Rapu, officially the Municipality of Rapu-Rapu, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Albay in the Bicol Region of the Philippines. The population was 36,151 at the 2020 census.
Vico Equense is a coastal town and comune in the Metropolitan City of Naples, in southern Italy.

Big Pocono State Park is a 1,305.6-acre (528.4 ha) Pennsylvania state park in Jackson and Pocono townships in Monroe County, Pennsylvania in Northeastern Pennsylvania. The park is located on Camelback Mountain and is maintained jointly by the Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources and Camelback Ski Corporation.
The climate of Houston is classified as a humid subtropical climate, with tropical influences. August normally ranks as the warmest month at an average temperature of 84.6 °F (29.2 °C) and January the coldest month at an average temperature of 53.1 °F (11.7 °C).

The tundra climate is a polar climate sub-type located in high latitudes and high mountains. It is classified as ET according to Köppen climate classification. It is a climate which at least one month has an average temperature high enough to melt snow, but no month with an average temperature in excess of 10 °C (50 °F). If the climate occurs at high elevations, it is known as alpine climate.
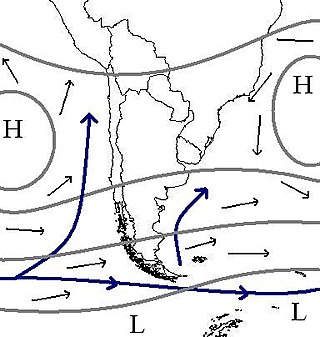
The climate of Chile comprises a wide range of weather conditions across a large geographic scale, extending across 38 degrees in latitude, making generalizations difficult. According to the Köppen system, Chile within its borders hosts at least seven major climatic subtypes, ranging from low desert in the north, to alpine tundra and glaciers in the east and southeast, tropical rainforest in Easter Island, Oceanic in the south and Mediterranean climate in central Chile. There are four seasons in most of the country: summer, autumn, winter, and spring.
Malta has a Subtropical-Mediterranean climate according to the Köppen climate classification (Csa), with very mild winters and warm to hot summers. Rain occurs mainly in winter, with summer being generally dry. According to the Troll-Paffen climate classification and the Siegmund/Frankenberg climate classification, Malta lies within the subtropical zone, being at 35ºN latitude.

The Philippines has five types of climates: tropical rainforest, tropical monsoon, tropical savanna, humid subtropical and oceanic characterized by relatively high temperature, oppressive humidity and plenty of rainfall. There are two seasons in the country, the wet season and the dry season, based upon the amount of rainfall. This is also dependent on location in the country as some areas experience rain all throughout the year. Based on temperature, the warmest months of the year are March through October; the winter monsoon brings cooler air from November to February. May is the warmest month, and January, the coolest.
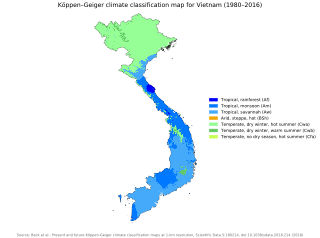
Vietnam has a monsoon-influenced climate typical of that of mainland Southeast Asia. The diverse topography, long latitude, and influences from the South China Sea lead to climatic conditions varying significantly between regions. The northern region experiences a monsoonal and temperate climate (Cfa) with four distinct seasons with winters typically dry and summers ranging from hot to mild. In more southern areas, the climate is tropical monsoon (Aw) with only two seasons. In addition, a temperate climate exists in mountainous areas, which are found in Sa Pa and Da Lat, while a more continental climate exists in Lai Châu Province and Sơn La Province.

The climate of the Nordic countries is that of a region in Northern Europe that consists of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden and their associated territories, which include the Faroe Islands, Greenland and Åland. Stockholm, Sweden has on average the warmest summer of the Nordic capitals, with an average maximum temperature of 23 °C (73 °F) in July; Copenhagen, Oslo and Helsinki have an average July maximum temperature of 22 °C (72 °F).

Cyprus has a subtropical climate - Mediterranean and semi-arid type - according to Köppen climate classification signes Csa and BSh, with very mild winters and warm to hot summers. Snow is possible only in the Troodos mountains in the central part of the island. Rain occurs mainly in winter, with summer being generally dry.
Ukuwela is a large suburb of Matale, Sri Lanka. lt lies south about 5.5 kilometres (3.4 mi) from the Matale Municipal Council, area, located on the Wattegama-Matale Road.