History
The extruder evolved from a mechanical pasta press first built in 1914. The mechanical version was replaced by a hydraulic version shortly thereafter.
Containing an auger screw and mixer, the extruder combined the functions of mixing, kneading and extruding in one machine, operations that formerly required three machines.
In the 1960s, the extruder underwent a series of changes that made it easy to sanitize and suitable for USDA food plants. These included a streamlined design with quick disassembly, and stainless steel construction with completely sealed welds. [2] Demaco engineers also designed a premixer for the extruder, which received a U.S. patent in 1975. [3] In the 1980s, the Demaco extruder became automated with PLC controls.
The DEMACO extruder is used to make a wide range of products, including pasta and cereal. [4] Additionally, DEMACO extruders are used to make some snacks, such as crisps and pizza rolls.

Pasta is a type of food typically made from an unleavened dough of wheat flour mixed with water or eggs, and formed into sheets or other shapes, then cooked by boiling or baking. Pasta was originally only made with durum, although the definition has been expanded to include alternatives for a gluten-free diet, such as rice flour, or legumes such as beans or lentils. Pasta is believed to have developed independently in Italy and is a staple food of Italian cuisine, with evidence of Etruscans making pasta as early as 400 BCE in Italy.

Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of edible plants. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are mixtures of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed oils, or fats from seeds. Olive oil, palm oil, and rice bran oil are examples of fats from other parts of plants. In common usage, vegetable oil may refer exclusively to vegetable fats which are liquid at room temperature. Vegetable oils are usually edible.
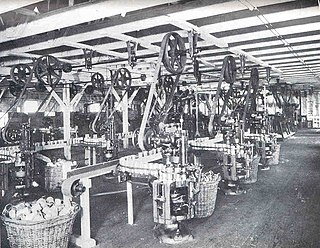
Canning is a method of food preservation in which food is processed and sealed in an airtight container. Canning provides a shelf life that typically ranges from one to five years, although under specific circumstances, it can be much longer. A freeze-dried canned product, such as canned dried lentils, could last as long as 30 years in an edible state.

Ravioli are a type of stuffed pasta comprising a filling enveloped in thin pasta dough. Usually served in broth or with a sauce, they originated as a traditional food in Italian cuisine. Ravioli are commonly square, though other forms are also used, including circular and semi-circular (mezzelune).

Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile by pushing material through a die of the desired cross-section. Its two main advantages over other manufacturing processes are its ability to create very complex cross-sections; and to work materials that are brittle, because the material encounters only compressive and shear stresses. It also creates excellent surface finish and gives considerable freedom of form in the design process.

Franco-American is a brand name of the Campbell Soup Company. Founded by Alphonse Biardot as Franco-American Food Company, it sells gravy and condensed soups; it was formerly used for SpaghettiOs and other pasta products until 2004 when it was replaced with the main Campbell's brand.
Continuous production is a flow production method used to manufacture, produce, or process materials without interruption. Continuous production is called a continuous process or a continuous flow process because the materials, either dry bulk or fluids that are being processed are continuously in motion, undergoing chemical reactions or subject to mechanical or heat treatment. Continuous processing is contrasted with batch production.

A mixer is a kitchen device that uses a gear-driven mechanism to rotate a set of "beaters" in a bowl containing the food or liquids to be prepared by mixing them.
KitchenAid is an American home appliance brand owned by Whirlpool Corporation. The company was started in 1919 by The Hobart Manufacturing Company to produce stand mixers; the H-5 is the first model that was introduced. The company faced competition as rivals moved into this emerging market, and introduced its trademarked silhouette in the 1930s with the model "K", the work of designer Egmont Arens. The brand's stand mixers have changed little in design since, and attachments from the model "K" onwards are compatible with the modern machines.

Pneumatic tires are manufactured according to relatively standardized processes and machinery, in around 455 tire factories in the world. With over 1 billion tires manufactured worldwide annually, the tire industry is a major consumer of natural rubber. Tire factories start with bulk raw materials such as synthetic rubber, carbon black, and chemicals and produce numerous specialized components that are assembled and cured.

Pizza rolls are a frozen food product consisting of bite-sized breaded pizza pockets with an interior of tomato sauce, imitation cheese, and various pizza toppings. They are sold in a variety of flavors including cheese, pepperoni, sausage, supreme, multiple imitation cheeses, and mixed meats. Other flavors included hamburger, cheeseburger, ham and cheese, and combination. Pizza snack rolls are designed to be quickly cooked in the oven or microwave. The name "pizza rolls" is a trademark of General Mills, current owner of the original product, currently sold under the Totino's brand.
The United States is the largest grower of commercial crops that have been genetically engineered in the world, but not without domestic and international opposition.

Manufactured feeds are an important part of modern commercial aquaculture. They provide the balanced nutrition needed by farmed fish. The feeds, in the form of granules or pellets, give nutrition in a stable and concentrated form, enabling the fish to feed efficiently and grow to their full potential.
The history of USDA nutrition guidelines includes over 100 years of nutrition advice promulgated by the USDA. The guidelines have been updated over time, to adopt new scientific findings and new public health marketing techniques. The current guidelines are the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2020–2025. The 2015–2020 guidelines were criticized as not accurately representing scientific information about optimal nutrition, and as being overly influenced by the agricultural industries the USDA promotes.

Lean finely textured beef (LFTB)—also called finely textured beef, boneless lean beef trimmings (BLBT), and colloquially known as pink slime—is a meat by-product used as a food additive to ground beef and beef-based processed meats, as a filler, or to reduce the overall fat content of ground beef. As part of the production process, heat and centrifuges remove the fat from the meat in beef trimmings. The resulting paste, without the fat, is exposed to ammonia gas or citric acid to kill bacteria. In 2001, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) approved the product for limited human consumption. The product, when prepared using ammonia gas, is banned for human consumption in Canada, and in the European Union, production of all mechanically separated beef is prohibited.

Demaco was founded in 1914 making it the oldest pasta equipment manufacturer in the United States and the only one that makes industrial capacity machines in America. In the 1960s, Demaco pioneered the sanitary extruder for washdown food plants.
The Bühler Holding AG is a Swiss multinational plant equipment manufacturer based in Uzwil, Switzerland. It is known for plant and equipment and related services for processing foods and manufacturing advanced materials. The organization holds leading market positions worldwide in the fields of technology as well as processes for transforming grain into flour and animal feeds, producing pasta and chocolate, and manufacturing die cast components. The core technologies of the Group are in the field of mechanical and thermal process engineering.

Extrusion in food processing consists of forcing soft mixed ingredients through an opening in a perforated plate or die designed to produce the required shape. The extruded food is then cut to a specific size by blades. The machine which forces the mix through the die is an extruder, and the mix is known as the extrudate. The extruder is typically a large, rotating screw tightly fitting within a stationary barrel, at the end of which is the die. In some cases, "extrusion" is taken as synonymous with extrusion cooking, which cooks the food with heat as it is squeezed through the die.

A double seam is a canning process for sealing a tin can by mechanically interlocking the can body and a can end.
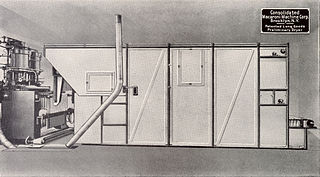
Pasta processing is the process in which wheat semolina or flour is mixed with water and the dough is extruded to a specific shape, dried and packaged.















