The transport sector comprises the physical infrastructure, docks and vehicle, terminals, fleets, ancillary equipment and service delivery of all the various modes of transport operating in Guyana. The transport services, transport agencies providing these services, the organizations and people who plan, build, maintain, and operate the system, and the policies that mold its development.
The history of Guyana begins about 35,000 years ago with the arrival of humans coming from Eurasia. These migrants became the Carib and Arawak tribes, who met Alonso de Ojeda's first expedition from Spain in 1499 at the Essequibo River. In the ensuing colonial era, Guyana's government was defined by the successive policies of Spanish, French, Dutch, and British settlers.

British Guiana was a British colony, part of the mainland British West Indies, which resides on the northern coast of South America. Since 1966 it has been known as the independent nation of Guyana.

Dutch colonisation of the Guianas—the coastal region between the Orinoco and Amazon rivers in South America—began in the late 16th century. The Dutch originally claimed all of Guiana but—following attempts to sell it first to Bavaria and then to Hanau and the loss of sections to Portugal, Britain, and France—the section actually settled and controlled by the Netherlands became known as Dutch Guiana.
Essequibo is the largest traditional region of Guyana but not an administrative region of Guyana today. It may also refer to:

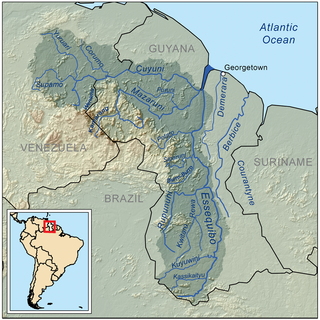
Demerara is a historical region in the Guianas on the north coast of South America which is now part of the country of Guyana. It was a Dutch colony until 1815 and a county of British Guiana from 1838 to 1966. It was located about the lower courses of the Demerara River, and its main town was Georgetown.

The Demerara River is a river in eastern Guyana that rises in the central rainforests of the country and flows to the north for 346 kilometres until it reaches the Atlantic Ocean. Georgetown, Guyana's largest seaport and capital, is situated on the east bank of the river's mouth. The river divides Essequibo Islands-West Demerara on the west bank from Demerara-Mahaica to the east.

The Guianas, sometimes called by the Spanish loan-word Guayanas, is a region in north-eastern South America which includes the following three territories:

Berbice is a region along the Berbice River in Guyana, which was between 1627 and 1815 a colony of the Dutch Republic. After having been ceded to the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in the latter year, it was merged with Essequibo and Demerara to form the colony of British Guiana in 1831. In 1966, British Guiana gained independence as Guyana.

Essequibo was a Dutch colony on the Essequibo River in the Guiana region on the north coast of South America from 1616 to 1814. The colony formed a part of the colonies that are known under the collective name of Dutch Guiana.
Hogg Island, is the largest of the hundreds of islands in the Essequibo River in Guyana, it is located just 5 km from the river's mouth in its estuary into the Atlantic Ocean.
The Railways of Guyana comprised two public railways, the Demerara-Berbice Railway and the Demerara-Essequibo railway. There are also several industrial railways mainly for the bauxite industry. The Demerara-Berbice Railway is the oldest in South America. None of the railways are in operation in the 21st century.

The Colony of Demerara-Essequibo was created on 28 April 1812, when the British combined the colonies of Demerara and Essequibo into the colony of Demerara-Essequibo. They were officially ceded to Britain on 13 August 1814. On 20 November 1815 the agreement was ratified by the Netherlands. On 21 July 1831 Demerara-Esequibo united with Berbice as British Guiana.

The Rev. Joseph Ketley (1802-1875) was a mid-nineteenth century Congregational missionary and abolitionist in Guyana, the former British colony of British Guiana which was known as Demerara and Essequibo at the time when his mission was established. The Dutch colonies of Berbice‚ Demerara and Essequibo were ceded to the British in 1814‚ and incorporated into a single colony in 1831. Guyana became independent in 1966.

Guyana, officially the Co‑operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America and the capital city is Georgetown. Guyana is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, Brazil to the south and southwest, Venezuela to the west, and Suriname to the east. With 215,000 square kilometres (83,000 sq mi), Guyana is the third-smallest sovereign state by area in mainland South America after Uruguay and Suriname; it is also the second-least populous sovereign state in South America after Suriname.

Fort Zeelandia is located on Fort Island, a fluvial island of the Essequibo River delta in the Essequibo Islands-West Demerara region of Guyana. Not to be confused with Fort Zeelandia in Paramaribo, Suriname, the current brick fort was built in 1743 for the Essequibo colony, replacing an earlier wooden fort built in 1726, and is among the oldest structures in Guyana. The fort replaced Fort Kyk-Over-Al as the capital of Essequibo in 1739.

The capture of Demerara and Essequibo was a French military expedition carried out in January 1782 as part of the American Revolutionary War. In 1781 Admiral Lord Rodney sent two sloops from his fleet at Sint Eustatius to take possession of the Dutch colonies of Essequibo and Demerara. In 1782 the French successfully took possession of these settlements, compelling British Governor Robert Kingston to surrender. The Treaty of Paris in 1783 restored these territories to the Dutch.

Pomeroon is the name of a former Dutch plantation colony on the Pomeroon River in the Guiana region on the north coast of South America. After early colonization attempts in the late 16th century were attacked by Spaniards and local Indians, the original inhabitants fled the interior of Guiana, founding the colony of Essequibo around Fort Kyk-Over-Al shortly after. A second, and more serious attempt at colonization started in 1650, but was ultimately unsuccessful, as French privateers destroyed the colony in 1689. In the late 18th century, a third attempt of colonization was started, this time under the jurisdiction of the Essequibo colony.

Laurens Storm van 's Gravesande was a Dutch governor of the colonies of Essequibo and Demerara from 1743 to 1772. He turned Demerara in a successful plantation colony, and the borders of Guyana are mainly based on his expeditions into the interior. He is also noted for his treatment of the Amerindians.












