The transport sector comprises the physical infrastructure, docks and vehicle, terminals, fleets, ancillary equipment and service delivery of all the various modes of transport operating in Guyana. The transport services, transport agencies providing these services, the organizations and people who plan, build, maintain, and operate the system, and the policies that mold its development.

Georgetown is the capital and largest city of Guyana. It is situated in Demerara-Mahaica, region 4, on the Atlantic Ocean coast, at the mouth of the Demerara River. It is nicknamed the "Garden City of the Caribbean." It is the retail, administrative, and financial services centre of the country, and the city accounts for a large portion of Guyana's GDP. The city recorded a population of 118,363 in the 2012 census.

British Guiana was a British colony, part of the mainland British West Indies, which resides on the northern coast of South America. Since 1966 it has been known as the independent nation of Guyana.
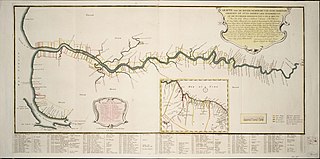
Demerara is a historical region in the Guianas, on the north coast of South America, now part of the country of Guyana. It was a colony of the Dutch West India Company between 1745 and 1792 and a colony of the Dutch state from 1792 until 1815. It was merged with Essequibo in 1812 by the British who took control. It formally became a British colony in 1815 until Demerara-Essequibo was merged with Berbice to form the colony of British Guiana in 1831. In 1838, it became a county of British Guiana until 1958. In 1966, British Guiana gained independence as Guyana and in 1970 it became a republic as the Co-operative Republic of Guyana. It was located around the lower course of the Demerara River, and its main settlement was Georgetown.

New Amsterdam is the regional capital of East Berbice-Corentyne, Guyana and one of the country's largest towns. It is 100 kilometres (62 mi) from the capital, Georgetown and located on the eastern bank of the Berbice River, 6 km (4 mi) upriver from its mouth at the Atlantic Ocean, and immediately south of the Canje River. New Amsterdam's population is 17,329 inhabitants as of 2012.

The Berbice River, located in eastern Guyana, is one of the country's major rivers. It rises in the highlands of the Rupununi region and flows northward for 595 kilometres (370 mi) through dense forests to the coastal plain. The river's tidal limit is between 160 and 320 km (99–199 mi) from the sea.

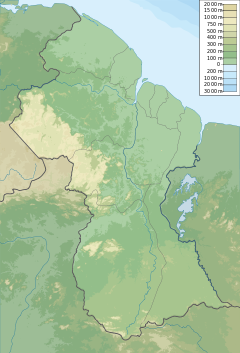
The Guianas, also spelled Guyanas or Guayanas, is a region in north-eastern South America. Strictly, the term refers to the three Guyanas: Guyana, Suriname and French Guiana, formerly British, Dutch and French Guyana. Broadly it refers to the South American coast from the mouth of the Oronoco to the mouth of the Amazon.

The Pomeroon River is located in Guyana, South America, situated between the Orinoco and the Essequibo rivers. The area has long been inhabited by Lokono people. The Pomeroon River is also one of the deepest rivers in Guyana.

Essequibo was a Dutch colony in the Guianas and later a county on the Essequibo River in the Guiana region on the north coast of South America. It was a colony of the Dutch West India Company between 1616 and 1792 and a colony of the Dutch state from 1792 until 1815. It was merged with Demerara in 1812 by the British who took control. It formally became a British colony in 1815 until Demerara-Essequibo was merged with Berbice to form the colony of British Guiana in 1831. In 1838, it became a county of British Guiana till 1958. In 1966, British Guiana gained independence as Guyana and in 1970 it became a republic as the Co-operative Republic of Guyana. It was located around the lower course of the Essequibo River.

The Demerara Harbour Bridge is a 6,074-foot (1,851 m) long floating toll bridge. It was commissioned on 2 July 1978. The bridge crosses the Demerara River 4 miles (6.4 km) south of the Guyanese capital Georgetown, from Peter's Hall, Demerara-Mahaica, East Bank Demerara to Schoon Ord, Essequibo Islands-West Demerara, West Bank Demerara. There is a pedestrian footwalk. A raised section lets small vessels pass under. A retractor span lets large vessels pass.
The Railways of Guyana comprised two public railways, the Demerara-Berbice Railway and the Demerara-Essequibo Railway. There are also several industrial railways mainly for the bauxite industry. The Demerara-Berbice Railway is the oldest in South America. None of the railways are in operation in the 21st century.
Guyana Power and Light (GPL) is a publicly owned utility company in Guyana, providing electric power in the country. Domestic voltage can be 110 or 220 depending on the area, both 50 and 60 cycle power. Services are provided from Charity to Moleson Creek, including the islands of Leguan and Wakenaam in the Essequibo River.
The Initiative for the Integration of the Regional Infrastructure of South America (IIRSA) is a development plan to link South America's economies through new transportation, energy, and telecommunications projects.

Guyana, officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern coast of South America, part of the historic mainland British West Indies. Guyana is an indigenous word which means "Land of Many Waters". Georgetown is the capital of Guyana and is also the country's largest city. Guyana is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, Brazil to the south and southwest, Venezuela to the west, and Suriname to the east. With a land area of 214,969 km2 (83,000 sq mi), Guyana is the third-smallest sovereign state by area in mainland South America after Uruguay and Suriname, and is the second-least populous sovereign state in South America after Suriname; it is also one of the least densely populated countries on Earth. It has a wide variety of natural habitats and very high biodiversity. The country also hosts a part of the Amazon rainforest, the largest tropical rainforest in the world.
The Guyana Cricket Board is the ruling body for cricket in Guyana.
The (northern) East-West Link is a road in Suriname between Albina in the eastern part of the country to Nieuw Nickerie in the western part, via the capital city of Paramaribo. The southern East-West Link connects Paramaribo with Apoera via Bitagron. Construction of the road link started in the 1960s.
Soesdyke is a village in the Demerara-Mahaica Region, Guyana, located between the Demerara River and the East Bank Public Road. Soesdyke is located just after the village called Den Heuvel (Coverden) if you are coming from Georgetown, which is the capital of Guyana. On the other end of Soesdyke is the village Timehri about 3 miles northeast of the Cheddi Jagan International Airport.

Plantation Peter's Hall was a plantation on the east bank of the River Demerara in Dutch Guiana and British Guiana. It was probably laid out in the mid-eighteenth century and by the early nineteenth century had over 200 slaves before that institution was abolished in the British Empire.
Borsselen is an island in the Demerara River of Guyana, and was the capital of Demerara between 1755 and 1782.

Kingston is a former village in Demerara. In 1837, it became a ward of Georgetown. The ward is located along the Atlantic Ocean coast. Kingston is home to many landmarks and historic buildings.