The Essequibo River is the largest river in Guyana, and the largest river between the Orinoco and Amazon. Rising in the Acarai Mountains near the Brazil–Guyana border, the Essequibo flows to the north for 1,014 km (630 mi) through forest and savanna into the Atlantic Ocean. It has a total drainage basin of 156,828 km2 (60,552 sq mi) and an average discharge of 5,650 m3/s (200,000 cu ft/s).

Guyana is divided into 10 regions:

Bartica is a town located on the left bank of the Essequibo River in Cuyuni-Mazaruni, at the confluence of the Cuyuni and Mazaruni Rivers with the Essequibo River in Guyana. It is the regional capital of Cuyuni-Mazaruni.

The Guianas, also spelled Guyanas or Guayanas, is a region in north-eastern South America. Strictly, the term refers to the three Guyanas: Guyana, Suriname and French Guiana, formerly British, Dutch and French Guyana. Broadly it refers to the South American coast from the mouth of the Oronoco to the mouth of the Amazon.
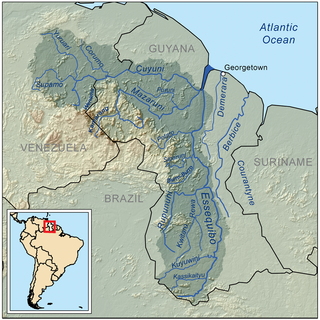
The Cuyuni River is a South American river and a tributary of the Essequibo River. It rises in the Guiana Highlands of Venezuela, where it descends northward to El Dorado, and turns eastward to meander through the tropical rain forests of the Cuyuni-Mazaruni Region of Guyana. It finally turns southeastward, flowing to its confluence with the Mazaruni River.

Cuyuni-Mazaruni is a region of Guyana. Its capital is Bartica, with villages including Issano, Kartabo, Kamarang, and Imbaimadai.

The Mazaruni River is a tributary of the Essequibo River in northern Guyana. Its source is in the remote western forests of the Pakaraima Mountains and its confluence with the Cuyuni River is near Bartica. As it descends from the Guiana Highlands the river runs south-east, past Issano, then northward to Bartica. The river is a source of alluvial gold.

Pomeroon-Supenaam is a region of Guyana. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the north, the region of Essequibo Islands-West Demerara to the east, the region of Cuyuni-Mazaruni to the south and the region of Barima-Waini to the west. Pomeroon-Supenaam contains the town of Anna Regina and the villages of Charity, Pickersgill, Spring Garden and Suddie. In 2012, an Official Census by the Government of Guyana listed the population of the Pomeroon-Supenaam Region at 46,810.

Potaro-Siparuni is a region of Guyana. It borders the region of Cuyuni-Mazaruni to the north, the regions of Upper Demerara-Berbice and East Berbice-Corentyne to the east, the region of Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo to the south and Brazil to the west.
Kartabo is a village in the Cuyuni-Mazaruni Region of Guyana.
The Imataka Mountains are located in the north-west of Guyana and north-east of Venezuela.

The Guyana–Venezuela territorial dispute is an ongoing territorial dispute between Guyana and Venezuela over the Essequibo region, also known as Esequibo or Guayana Esequiba in Spanish, a 159,500 km2 (61,600 sq mi) area west of the Essequibo River. The territory, excluding the Venezuelan-controlled Ankoko Island, is controlled by Guyana as part of six of its regions, based on the 1899 Paris Arbitral Award. It is also claimed by Venezuela as the Guayana Esequiba State. The boundary dispute was inherited from the colonial powers and has persisted following the independence of Venezuela and Guyana.
The Kako River is a river in the Cuyuni-Mazaruni region of Guyana and one of the largest tributaries of the Mazaruni River.
The Ekareku River is a river of Guyana, a tributary of the Wenamu River.
Koatse River is a stream in the Cuyuni-Mazaruni area in Guyana, South America.
Parmotrema aptrootii is a species of corticolous lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. Found in South America, it was described as new to science in 1992. The holotype specimen was collected in the Cuyuni-Mazaruni region of Guyana, where it was found growing on a Mahogany tree on the bank of the Kamarang River. It has a pale yellowish to greenish-grey thallus measuring up to about 10 cm (4 in). The specific epithet honours Dutch lichenologist André Aptroot. The lichen has also been recorded from Acre, Brazil, where it is commonly found on dead branches in dense shrubby campinas.
Isseneru is an Amerindian settlement in the Cuyuni-Mazaruni region of Guyana, approximately 15–20 miles west of Kurupung.
Paruima is an indigenous village of Pemon Amerindians in the Cuyuni-Mazaruni Region of Guyana. The village was founded as a mission of the Seventh-day Adventist Church. It is the only Pemon speaking community in Guyana.
Alleluia is a syncretic religion combining Christianity and traditions practiced by Carib-speaking Indigenous peoples in Guyana.