The Dutch began their colonisation of the Guianas, the coastal region between the Orinoco and Amazon rivers in South America, in the late 16th century. The Dutch originally claimed all of Guiana but—following attempts to sell it first to Bavaria and then to Hanau and the loss of sections to Portugal, Britain, and France—the section actually settled and controlled by the Netherlands became known as Dutch Guiana.
Demerara is a historical region in the Guianas, on the north coast of South America, now part of the country of Guyana. It was a colony of the Dutch West India Company between 1745 and 1792 and a colony of the Dutch state from 1792 until 1815. It was merged with Essequibo in 1812 by the British who took control. It formally became a British colony in 1815 until Demerara-Essequibo was merged with Berbice to form the colony of British Guiana in 1831. In 1838, it became a county of British Guiana until 1958. In 1966, British Guiana gained independence as Guyana and in 1970 it became a republic as the Co-operative Republic of Guyana. It was located around the lower course of the Demerara River, and its main settlement was Georgetown.

Cuffy, also known as Kofi Badu, also spelled as Coffy, Cuffy, Kofi, or Koffi, was an Akan man who was captured in his native West Africa and stolen for slavery to work on the plantations of the Dutch colony of Berbice in present-day Guyana. In 1763, he led a major slave revolt of more than 3,800 slaves against the colonial regime. Today, he is a national hero in Guyana.

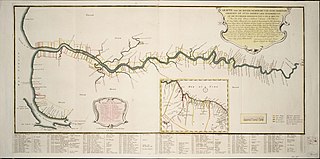
The Demerara River is a river in eastern Guyana that rises in the central rainforests of the country and flows to the north for 346 kilometres until it reaches the Atlantic Ocean. Georgetown, Guyana's largest seaport and capital, is situated on the east bank of the river's mouth. The river divides Essequibo Islands-West Demerara on the west bank from Demerara-Mahaica to the east.

The Guianas, also spelled Guyanas or Guayanas, is a geographical region in north-eastern South America. Strictly, the term refers to the three Guianas: Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana, formerly British, Dutch, and French Guiana. Broadly, it refers to the South American coast from the mouth of the Orinoco to the mouth of the Amazon.

Berbice is a region along the Berbice River in Guyana, which was between 1627 and 1792 a colony of the Dutch West India Company and between 1792 and 1815 a colony of the Dutch state. After having been ceded to the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in the latter year, it was merged with Demerara-Essequibo to form the colony of British Guiana in 1831. It became a county of British Guiana in 1838 till 1958. In 1966, British Guiana gained independence as Guyana and in 1970 it became a republic as the Co-operative Republic of Guyana.

Essequibo was a Dutch colony in the Guianas and later a county on the Essequibo River in the Guiana region on the north coast of South America. It was a colony of the Dutch West India Company between 1616 and 1792 and a colony of the Dutch state from 1792 until 1815. It was merged with Demerara in 1812 by the British who took control. It formally became a British colony in 1815 until Demerara-Essequibo was merged with Berbice to form the colony of British Guiana in 1831. In 1838, it became a county of British Guiana till 1958. In 1966, British Guiana gained independence as Guyana and in 1970 it became a republic as the Co-operative Republic of Guyana. It was located around the lower course of the Essequibo River.
Stabroek was the old name of Georgetown, Guyana, between 1784 and 1812, and was the capital of Demerara. Stabroek is currently a ward in the centre of Georgetown.

The Colony of Demerara-Essequibo was created on 28 April 1812, when the British combined the colonies of Demerara and Essequibo into the colony of Demerara-Essequibo. They were officially ceded to Britain on 13 August 1814. On 20 November 1815, the agreement was ratified by the Netherlands. On 21 July 1831, Demerara-Esequibo united with Berbice as British Guiana.
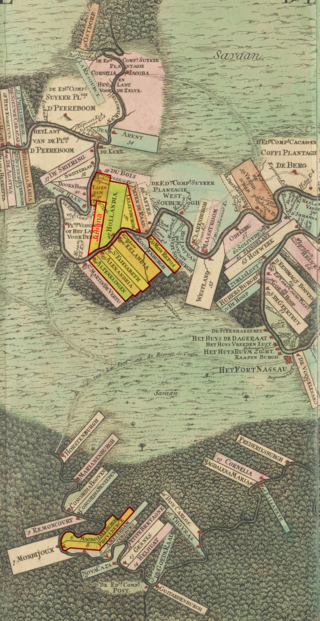
The Berbice Rebellion was a slave rebellion in Guyana that began on 23 February 1763 and lasted to December, with leaders including Coffij. The first major slave revolt in South America, it is seen as a major event in Guyana's anti-colonial struggles, and when Guyana became a republic in 1970 the state declared 23 February as a day to commemorate the start of the Berbice slave revolt.

Fort Zeelandia is located on Fort Island, a fluvial island of the Essequibo River delta in the Essequibo Islands-West Demerara region of Guyana. Not to be confused with Fort Zeelandia in Paramaribo, Suriname, the current brick fort was built in 1743 for the Essequibo colony, replacing an earlier wooden fort built in 1726, and is among the oldest structures in Guyana. The fort replaced Fort Kyk-Over-Al as the capital of Essequibo in 1739.
The Society of Berbice was founded on 24 October 1720 by the owners of the colony of Berbice currently in Guyana. These owners had acquired the colony from the French on 24 October 1714, who in turn had occupied the colony which was previously a hereditary fief in the possession of the Van Peere family.

Pomeroon is the name of a former Dutch plantation colony on the Pomeroon River in the Guyana region on the north coast of South America. After early colonization attempts in the late 16th century were attacked by Spaniards and local Indians, the original inhabitants fled the interior of Guyana, founding the colony of Essequibo around Fort Kyk-Over-Al shortly after. A second, and more serious attempt at colonization started in 1650, but was ultimately unsuccessful, as French privateers destroyed the colony in 1689. In the late 18th century, a third attempt of colonization was started, this time under the jurisdiction of the Essequibo colony.
Soesdyke is a village in the Demerara-Mahaica Region, Guyana, located between the Demerara River and the East Bank Public Road. Soesdyke is located just after the village called Den Heuvel (Coverden) if you are coming from Georgetown, which is the capital of Guyana. On the other end of Soesdyke is the village Timehri about 3 miles northeast of the Cheddi Jagan International Airport.

The College of Kiezers was an electoral college in the Dutch colonies of Essequibo and Demerara and their successor, British Guiana.

Baron Jan Cornelis van den Heuvel was a Dutch born plantation owner and politician who served as governor of the Dutch province of Demerara from 1765 to 1770 and later became a merchant in New York City with the Dutch West India Company.

Laurens Storm van 's Gravesande was a Dutch governor of the colonies of Essequibo and Demerara from 1743 to 1772. He turned Demerara in a successful plantation colony, and the borders of Guyana are mainly based on his expeditions into the interior. He is also noted for his treatment of the Amerindians.
Wolfert Simon van Hoogenheim was a Dutch States Army officer and colonial administrator who served as the governor of Berbice from 1760 to 1764. During his tenure as governor, the Berbice Rebellion took place.

Fort Island is an island in the Essequibo River located in the Essequibo Islands-West Demerara region of Guyana. It is about 16 kilometres (10 mi) from the mouth of the river, and to the east of Hogg Island. In 1687, a wooden fort was built on the island. In 1744, Fort Zeelandia was constructed and served as the capital of Essequibo, a Dutch colony which is nowadays part of Guyana. In 1752, the Court of Policy was built on the island as the legislative body for the colony.
Antony Beaujon also Anthony was a Dutch and British civil servant and politician in Guyana. He served as Governor of Demarara from May 1795 until 5 July 1802, and as Lieutenant governor of Demerara and Essequibo from 13 August 1804 until his death.