The transport sector comprises the physical infrastructure, docks and vehicle, terminals, fleets, ancillary equipment and service delivery of all the various modes of transport operating in Guyana. The transport services, transport agencies providing these services, the organizations and people who plan, build, maintain, and operate the system, and the policies that mold its development.

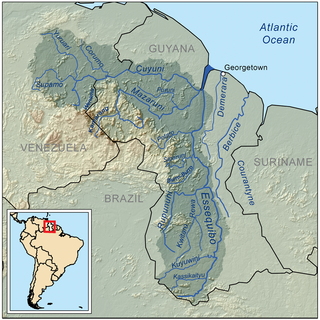
The Essequibo River is the largest river in Guyana, and the largest river between the Orinoco and Amazon. Rising in the Acarai Mountains near the Brazil–Guyana border, the Essequibo flows to the north for 1,014 km (630 mi) through forest and savanna into the Atlantic Ocean. It has a total drainage basin of 156,828 km2 (60,552 sq mi) and an average discharge of 5,650 m3/s (200,000 cu ft/s).

Bartica is a town located on the west bank of the Essequibo River in Cuyuni-Mazaruni, at the confluence of the Cuyuni and Mazaruni Rivers with the Essequibo River in Guyana. It is the regional capital of Cuyuni-Mazaruni.

Barima-Waini is a region of Guyana and is located in the northwest of the country. Barima-Waini has three sub-regions: Mabaruma, Matakai, and Moruca.

Cuyuni-Mazaruni is a region of Guyana. Its capital is Bartica, with villages including Issano, Kartabo, Kamarang, and Imbaimadai.

The Mazaruni River is a tributary of the Essequibo River in northern Guyana. Its source is in the remote western forests of the Pakaraima Mountains and its confluence with the Cuyuni River is near Bartica. As it descends from the Guiana Highlands the river runs south-east, past Issano, then northward to Bartica. The river is a source of alluvial gold.

Potaro-Siparuni is a region of Guyana. It borders the region of Cuyuni-Mazaruni to the north, the regions of Upper Demerara-Berbice and East Berbice-Corentyne to the east, the region of Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo to the south and Brazil to the west.

Fort Kyk-Over-Al was a Dutch fort in the colony of Essequibo, in what is now Guyana. It was constructed in 1616 at the intersection of the Essequibo, Cuyuni and Mazaruni rivers. It once served as the centre for the Dutch administration of the county, but now only ruins are left. The name Kyk-Over-Al derives from the Dutch for "See over all", a reference to the commanding view of the river from the fort.

Essequibo was a Dutch colony in the Guianas and later a county on the Essequibo River in the Guiana region on the north coast of South America. It was a colony of the Dutch West India Company between 1616 and 1792 and a colony of the Dutch state from 1792 until 1815. It was merged with Demerara in 1812 by the British who took control. It formally became a British colony in 1815 until Demerara-Essequibo was merged with Berbice to form the colony of British Guiana in 1831. In 1838, it became a county of British Guiana till 1958. In 1966, British Guiana gained independence as Guyana and in 1970 it became a republic as the Co-operative Republic of Guyana. It was located around the lower course of the Essequibo River.
Kurupung is a mining community in the Cuyuni-Mazaruni Region of Guyana, near the Pakaraima Mountains.

The Guyana–Venezuela territorial dispute is an ongoing territorial dispute between Guyana and Venezuela over the Essequibo region, also known as Esequibo or Guayana Esequiba in Spanish, a 159,500 km2 (61,600 sq mi) area west of the Essequibo River. The territory, excluding the Venezuelan-controlled Ankoko Island, is controlled by Guyana as part of six of its regions, based on the 1899 Paris Arbitral Award. It is also claimed by Venezuela as the Guayana Esequiba State. The boundary dispute was inherited from the colonial powers and has persisted following the independence of Venezuela and Guyana.
El Dorado is a small town in eastern Venezuela. It is situated in Bolívar State, on the Cuyuni River. It is the second-largest town in Sifontes Municipality; the capital of the municipality is Tumeremo.

Guyana–Venezuela relations include diplomatic, economic and other interactions between the neighboring countries of the Co-operative Republic of Guyana and the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela.
Wenamu River is a river in South America. It forms a portion of the international boundary between Venezuela and Guyana. It is part of the Essequibo River basin.
The Kako River is a river in the Cuyuni-Mazaruni region of Guyana and one of the largest tributaries of the Mazaruni River.
The Bartica Massacre refers to the murder of twelve residents of Bartica, Cuyuni-Mazaruni, Guyana, murdered by the criminal gang led by Rondell "Fineman" Rawlins. Rawlins and many of the other suspected gang members were later killed by Guyanese security forces. This massacre was part of a series of murders that appeared to have begun with the Mash Day Prison break.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Guyana was a part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached Guyana on 11 March 2020. The first case was a woman who travelled from New York, a 52-year-old woman with underlying health conditions, including diabetes and hypertension. The woman died at the Georgetown Public Hospital.
Issano is a village of Cuyuni-Mazaruni, Guyana. It's located along the Mazaruni River, and is a hub for mining.
Isseneru is an Amerindian settlement in the Cuyuni-Mazaruni region of Guyana, approximately 15–20 miles west of Kurupung.
Agatash is a village in the Cuyuni-Mazaruni Region of Guyana. It is located about 3 miles (4.8 km) south of Bartica along the Essequibo River opposite Sloth Island.












