
A sign is an object, quality, event, or entity whose presence or occurrence indicates the probable presence or occurrence of something else. A natural sign bears a causal relation to its object—for instance, thunder is a sign of storm, or medical symptoms a sign of disease. A conventional sign signifies by agreement, as a full stop signifies the end of a sentence; similarly the words and expressions of a language, as well as bodily gestures, can be regarded as signs, expressing particular meanings. The physical objects most commonly referred to as signs generally inform or instruct using written text, symbols, pictures or a combination of these.
Semiotics is the systematic study of sign processes and the communication of meaning. In semiotics, a sign is defined as anything that communicates intentional and unintentional meaning or feelings to the sign's interpreter.
A connotation is a commonly understood cultural or emotional association that any given word or phrase carries, in addition to its explicit or literal meaning, which is its denotation.

Roland Gérard Barthes was a French literary theorist, essayist, philosopher, critic, and semiotician. His work engaged in the analysis of a variety of sign systems, mainly derived from Western popular culture. His ideas explored a diverse range of fields and influenced the development of many schools of theory, including structuralism, anthropology, literary theory, and post-structuralism.
In linguistics and philosophy, the denotation of a word or expression is its strictly literal meaning. For instance, the English word "warm" denotes the property of having high temperature. Denotation is contrasted with other aspects of meaning including connotation. For instance, the word "warm" may evoke calmness, coziness, or kindness but these associations are not part of the word's denotation. Similarly, an expression's denotation is separate from pragmatic inferences it may trigger. For instance, describing something as "warm" often implicates that it is not hot, but this is once again not part of the word's denotation.
In semiotics, a sign is anything that communicates a meaning that is not the sign itself to the interpreter of the sign. The meaning can be intentional, as when a word is uttered with a specific meaning, or unintentional, as when a symptom is taken as a sign of a particular medical condition. Signs can communicate through any of the senses, visual, auditory, tactile, olfactory, or taste.
A sememe is a semantic language unit of meaning, analogous to a morpheme. The concept is relevant in structural semiotics.
Music semiology (semiotics) is the study of signs as they pertain to music on a variety of levels.
In semiotics, the value of a sign depends on its position and relations in the system of signification and upon the particular codes being used.
In semiotics, a modality is a particular way in which information is to be encoded for presentation to humans, i.e. to the type of sign and to the status of reality ascribed to or claimed by a sign, text, or genre. It is more closely associated with the semiotics of Charles Peirce (1839–1914) than Ferdinand de Saussure (1857–1913) because meaning is conceived as an effect of a set of signs. In the Peircean model, a reference is made to an object when the sign is interpreted recursively by another sign, a conception of meaning that does in fact imply a classification of sign types.
In the broadest sense, a code is a correspondence or rule between patterns. It can be an arrangement of physical matter, including the electromagnetic spectrum, that stores the potential to convey meaning. For instance, the pattern of vibration we call 'sound' when activated within the mind, triggers an image; say the word "cat". Also, seeing the shapes we call 'letters' forming the word makes one think of or visualize a cat. The words upon the screen were conceived in the human mind, and then translated into computer code.
In semiotics, the commutation test is used to analyze a signifying system. The test identifies signifiers as well as their signifieds, value and significance.
In semiotics, connotation arises when the denotative relationship between a signifier and its signified is inadequate to serve the needs of the community. A second level of meanings is termed connotative. These meanings are not objective representations of the thing, but new usages produced by the language group.
Encoding, in semiotics, is the process of creating a message for transmission by an addresser to an addressee. The complementary process – interpreting a message received from an addresser – is called decoding.
In semiotics, the study of sign processes (semiosis), the meaning of a sign is its place in a sign relation, in other words, the set of roles that the sign occupies within a given sign relation.
Semiotics of music videos is the observation of symbolism used within music videos.
Semiotics is the study of meaning-making on the basis of signs. Semiotics of photography is the observation of symbolism used within photography or "reading" the picture. This article refers to realistic, unedited photographs not those that have been manipulated in any way. Roland Barthes was one of the first people to study the semiotics of images. He developed a way to understand the meaning of images. Most of Barthes' studies related to advertising, but his concepts can apply to photography as well.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to semiotics:
Film semiotics is the study of sign process (semiosis), or any form of activity, conduct, or any process that involves signs, including the production of meaning, as these signs pertain to moving pictures. Film semiotics is used for the interpretation of many art forms, often including abstract art.
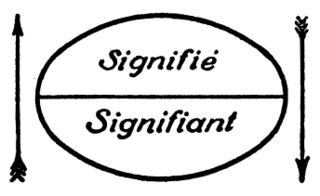
In semiotics, signified and signifier are the two main components of a sign, where signified is what the sign represents or refers to, known as the "plane of content", and signifier which is the "plane of expression" or the observable aspects of the sign itself. The idea was first proposed in the work of Swiss linguist Ferdinand de Saussure, one of the two founders of semiotics.


