
Flanders is the Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, language, politics, and history, and sometimes involving neighbouring countries. The demonym associated with Flanders is Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is Flemish, which can also refer to the collective of Dutch dialects spoken in that area, or more generally the Belgian variant of Standard Dutch.

Belgium is a federal state comprising three communities and three regions that are based on four language areas. For each of these subdivision types, the subdivisions together make up the entire country; in other words, the types overlap.
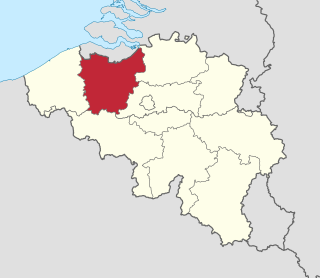
East Flanders is a province of Belgium. It borders the Dutch province of Zeeland and the Flemish province of Antwerp, Flemish Brabant, Hainaut and West Flanders. It has an area of 3,007 km2 (1,161 sq mi), divided into six administrative districts containing 60 municipalities, and a population of over 1.57 million as of January 2024. The capital is Ghent, home to the Ghent University and the Port of Ghent.

The minister of health is the minister of the Crown in the Canadian Cabinet who is responsible for overseeing health-focused government agencies including Health Canada and the Public Health Agency of Canada, as well as enforcing the Canada Health Act, the law governing Canada's universal health care system.

The Flemish Parliament constitutes the legislative power in Flanders for matters which fall within the competence of Flanders, both as a geographic region and as a cultural community of Belgium.

The Flemish Region, usually simply referred to as Flanders, is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and the Brussels-Capital Region. Covering the northern portion of the country, the Flemish Region is primarily Dutch-speaking. With an area of 13,626 km2 (5,261 sq mi), it accounts for only 45% of Belgium's territory, but 58% of its population. It is one of the most densely populated regions of Europe with around 500/km2 (1,300/sq mi).

Vlaamse Radio- en Televisieomroeporganisatie, commercially styled as VRT is one of the national public service broadcasters for the Flemish Community of Belgium.

The Flemish Community is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilities only within the precise geographical boundaries of the Dutch-language area and of the bilingual area of Brussels-Capital. Unlike in the French Community of Belgium, the competences of the Flemish Community have been unified with those of the Flemish Region and are exercised by one directly elected Flemish Parliament based in Brussels.

The Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport is the Dutch Ministry responsible for public health, health care, quality of life, social work and sport. The Ministry was created in 1951 as the "Ministry of Social Affairs and Health" and had several name changes before it became the "Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport" in 1994. The Ministry is headed by the Minister of Health, Welfare and Sport, currently Fleur Agema (PVV), assisted by two state secretaries, currently Vicky Maeijer (PVV) and Vincent Karremans (VVD).

The Flemish Government is the executive branch of the Flemish Community and the Flemish Region of Belgium. It consists of a government cabinet, headed by the Minister-President and accountable to the Flemish Parliament, and the public administration divided into 13 policy areas, each with an executive department and multiple agencies.

The Federal Public Service Foreign Affairs, Foreign Trade and Development Cooperation is the foreign affairs ministry of Belgium and is responsible for Belgian foreign policy, relations with the European Union, development cooperation policy and certain aspects of foreign trade policy. The central government in Brussels directs the network of diplomatic and consular representations abroad.

Belgium has a universal healthcare system, which is composed of three parts: first, there is a primarily publicly funded health care and social security service run by the federal government, which organises and regulates healthcare; independent private/public practitioners, university/semi-private hospitals and care institutions. There are a few private hospitals. Secondly is the insurance coverage provided for patients. Finally, industry coverage, which covers the production and distribution of healthcare products for research and development. The primary aspect of this research is done in universities and hospitals.

The Public Centre for Social Welfare is a public institution that exists in each of the 581 municipalities of Belgium. Every citizen of Belgium has the right to social assistance and social integration.
The state agencies that form Thailand's public sector consist of several types of functioning bodies. While some agencies established by mandate of the constitution are independent, others are directly or indirectly answerable to the executive of the Royal Thai Government. The majority of these are government agencies, which employ the civil service as well as the military. Others include public organizations and state enterprises.

Wivina Demeester-De Meyer is a Belgian politician who served as a Member of the Flemish Parliament and its predecessor bodies between 1974 and 1995 and 1999 and 2004; she also held various ministerial posts in the national and Flemish governments.
The Flemish Care Inspectorate is a part of the Department of Welfare, Public Health and Family of the Flemish Government. The Flemish Government is the executive branch of the Flemish Community of Belgium. In Belgium, the Communities are responsible for the inspection of health and welfare services and establishments. The Care Inspectorate consists of two complementary divisions of the department: one for the inspection of services for disabled people and child care services, and one for the inspection of welfare services, health services and financial matters. Together, they inspect all services and establishments in these domains that are recognised, licensed or subsidised by the department or any agency associated with it. The Care Inspectorate also inspects disabled people who receive a so-called personal assistance budget or financial compensation for assistive tools.
The Child and Family Agency is an agency of the Flemish Government. The Flemish Government is the executive branch of the Flemish Community of Belgium. In Belgium, the Communities are responsible for the provision of child and family services. The Child and Family Agency has three main tasks: the regulation and subsidising of child care services, the provision of preventive family support services and guidance to parents and children in cases of adoption. The agency also recognises and subsidises so-called confidential centres on child abuse, which offer voluntary assistance in cases of child abuse or child neglect. For the inspection of child care services, the agency relies on the Flemish Care Inspectorate.
The Agency for Care and Health is an agency of the Flemish Government. The Flemish Government is the executive branch of the Flemish Community of Belgium. In Belgium, the Communities are responsible for certain aspects of social care, health care and public health policy. The Agency for Care and Health is responsible for the recognition, licensing and subsidising of various providers and services for health care, elderly care, home care, residential care, and other forms of care, for facilitating the cooperation and data sharing between these services, for the organisation of preventive health services such as vaccinations and screening programs, for the control of infectious diseases, for environmental health monitoring, and for the organisation of the Flemish social protection programs. The Agency for Care and Health relies on the Flemish Care Inspectorate for the inspection of any of the services it is responsible for.
The Youth Welfare Agency is an agency of the Flemish Government responsible for child welfare.

The Diependaele Government (Regering-Diependaele) is the Flemish Government formed and sworn in on 30 September 2024, following the 2024 Belgian regional elections and replacing the Jambon Government.













