Related Research Articles
The Hauberg Mountains are a group of mountains of about 35 nautical miles extent, located 12 nautical miles north of Cape Zumberge and 30 nautical miles south of the Sweeney Mountains in eastern Ellsworth Land, Antarctica.
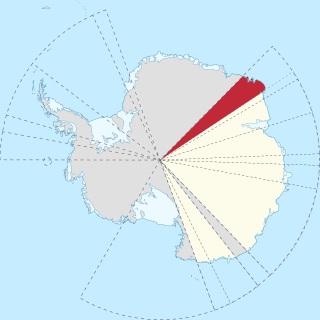
Enderby Land is a projecting landmass of Antarctica. Its shore extends from Shinnan Glacier at about 67°55′S44°38′E to William Scoresby Bay at 67°24′S59°34′E, approximately 1⁄24 of the earth's longitude. It was first documented in western and eastern literature in February 1831 by John Biscoe aboard the whaling brig Tula, and named after the Enderby Brothers of London, the ship's owners who encouraged their captains to combine exploration with sealing.
The McCuddin Mountains are a small cluster of mountains in Antarctica consisting mainly of two large mountains, Mount Flint and Mount Petras, along with several scattered peaks and nunataks. Located in Marie Byrd Land, 64 km (40 mi) east of the Ames Range, with Wallace Rock as its southeast extremity.
Mount Barre is a mountain with an ice-covered, pyramidal peak, 2,195 m, standing 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) northeast of Mount Gaudry in the south part of Adelaide Island. Discovered and surveyed in 1909 by the French Antarctic Expedition under Charcot. Resurveyed in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) and named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for Michel Barre, leader of the French Antarctic Expedition to the Adelie Coast, 1951–52.
Mount Bayonne is a mountain, 1,500 m, forming the north extremity of the Rouen Mountains in Alexander Island, Antarctica. The mountain lies immediately north of Les Dents and Mount Paris. First mapped by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10, under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, who named it for the French city. Resighted from the air by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) in 1936. Remapped from air photos taken by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947–48, by Searle of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1960.
Mount Bouvier is a massive, mainly ice-covered mountain, 2,070 metres (6,790 ft) high, immediately north of the head of Stonehouse Bay in the east part of Adelaide Island. It was discovered and roughly positioned by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1903–05, and named by Jean-Baptiste Charcot for Louis Bouvier, a prominent French naturalist. It was re-surveyed by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10, and by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1948–50.

Carey Glacier is a glacier on the east side of Miller and Fruzhin Peaks and west of Ruset and Malkoch Peaks in Petvar Heights at the southeast end of the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains, flowing southeast to Minnesota Glacier. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and from U.S. Navy air photos, 1957–59, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Lieutenant David W. Carey, pilot with U.S. Navy Squadron VX-6, who was killed in the crash of a P2V Neptune airplane at McMurdo Sound in October 1956.
Naess Glacier is a small glacier, which is separated from Chapman Glacier to the north by a rocky ridge, flowing from the west coast of Palmer Land into George VI Sound. First surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1954 for Erling D. Naess, Mgr. of the Vestfold Whaling Co., who was of great assistance to the BGLE, 1934–37.
Crosse Passage is a small passage leading southeast from Adelaide Anchorage between the Henkes Islands and the Skeen Rocks, off the south end of Adelaide Island. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1963 for Lieutenant Commander Anthony G. Crosse, Royal Navy, First Lieutenant of HMS Protector which was used by the Hydrographic Survey Unit in charting this area in 1961–63.

The Stokes Peaks is a group of peaks rising to about 800 m between McCallum Pass and Sighing Peak on the north side of Wright Peninsula, Adelaide Island, Antarctica. They were photographed from the air by the Falkland Islands and Dependencies Aerial Survey Expedition (FIDASE), 1956–57, and surveyed by the British Antarctic Survey (BAS), in 1961–62. They were named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1977 for Jeffrey C.A. Stokes, Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) assistant surveyor, Admiralty Bay, 1959–60, and Adelaide Island, 1960–61.
The Playfair Mountains are a group of mountains between Swann Glacier and Squires Glacier in southeast Palmer Land, Antarctica.
The Milky Way is a col situated between the southernmost extremity of the LeMay Range and the Planet Heights mountain range, in the eastern part of Alexander Island, Antarctica. It is the highest point on a possible sledging route between Jupiter Glacier and Uranus Glacier. The col was first mapped from air photos taken by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition in 1947–48, by D. Searle of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1960. It was named after the Milky Way by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee from association with the nearby Planet Heights and the glaciers which are named for the planets of the Solar System.
Mount Liotard is a mountain having a conspicuous ice-covered peak, 2,225 metres (7,300 ft) high, standing midway between Mount Gaudry and Mount Ditte in the south part of Adelaide Island, Antarctica. It was discovered and first surveyed by the Fourth French Antarctic Expedition in 1909. It was resurveyed in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Andre F. Liotard, a French observer with the FIDS in 1947–48 and the leader of the French Antarctic Expedition, 1949–51.
Hunt Peak is a triangular rock peak, 610 metres (2,000 ft) high, marking the north side of the entrance to Stonehouse Bay on the east coast of Adelaide Island, Antarctica. It was discovered and first roughly surveyed in 1909 by the French Antarctic Expedition under Jean-Baptiste Charcot. It was resurveyed in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), who named the point marked by this peak for Sergeant Kenneth D. Hunt, a mechanic for the expedition's Noorduyn Norseman airplane in 1950. Further survey in 1957–58 by the FIDS showed no definable point in the vicinity and the name was transferred to the peak.
McArthur Glacier is a glacier between the Christie Peaks and Swine Hill, flowing west from Palmer Land, Antarctica, into George VI Sound. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Alistair H. McArthur, a British Antarctic Survey geophysicist at Stonington Island, 1967–68.
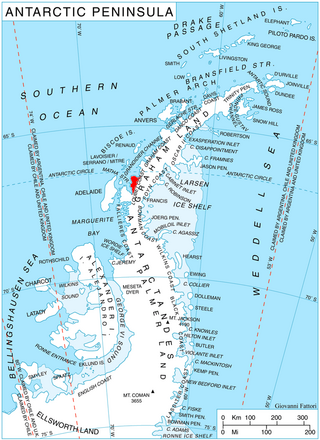
McCance Glacier is the 30-km long and 5 km wide glacier draining the Hutchison Hill area on the west slopes of Avery Plateau on Loubet Coast in Graham Land, Antarctica. It flows north-northwestwards along the west side of Osikovo Ridge, Kladnitsa Peak and Rubner Peak and enters Darbel Bay.
The Seue Peaks are peaks located on the Antarctic Peninsula, standing between Bentley Crag and Mount Rendu on Arrowsmith Peninsula in Graham Land. They were mapped by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey from surveys and air photos from 1956 to 1959, and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Christian Martini de Seue, a Norwegian surveyor and glaciologist who made pioneer measurements of glacial flow in Norway around 1870.
Relay Hills is a group of low, ice-covered hills, mainly conical in shape, between Mount Edgell and Kinnear Mountains in western Antarctic Peninsula. First roughly surveyed from the ground by British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE), 1936–37. Photographed from the air by Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), November 1947. Resurveyed by Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), November 1958. The name, applied by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC), arose because both the BGLE and the FIDS sledging parties had to relay their loads through this area to the head of Prospect Glacier.
Chapman Glacier is a glacier 11 miles (18 km) long and 10 miles (16 km) wide in its central part, narrowing to 3 miles (5 km) at its mouth, flowing west from the Dyer Plateau of Palmer Land to George VI Sound immediately south of Carse Point. It was first surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under John Rymill, and named by the UK Antarctic Place-names Committee in 1954 for Frederick S. Chapman, British mountaineer and Arctic explorer, who in 1934 brought 64 dogs from West Greenland to England for the use of the BGLE, 1934–37.
References
- ↑ "Deschanel Peak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior . Retrieved 2012-01-13.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Deschanel Peak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Deschanel Peak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.