
The officially stated goals of the foreign policy of the United States of America, including all the bureaus and offices in the United States Department of State, as mentioned in the Foreign Policy Agenda of the Department of State, are "to build and sustain a more democratic, secure, and prosperous world for the benefit of the American people and the international community". Liberalism has been a key component of US foreign policy since its independence from Britain. Since the end of World War II, the United States has had a grand strategy which has been characterized as being oriented around primacy, "deep engagement", and/or liberal hegemony. This strategy entails that the United States maintains military predominance; builds and maintains an extensive network of allies ; integrates other states into US-designed international institutions ; and limits the spread of nuclear weapons.

Freedom House is a non-profit organization based in Washington, D.C. It is best known for political advocacy surrounding issues of democracy, political freedom, and human rights. Freedom House was founded in October 1941, with Wendell Willkie and Eleanor Roosevelt serving as its first honorary chairpersons. Most of the organization's funding comes from the U.S. State Department and other government grants. It also receives funds from various semi-public and private foundations, as well as individual contributions.

The Bush Doctrine refers to multiple interrelated foreign policy principles of the 43rd President of the United States, George W. Bush. These principles include unilateralism, preemptive war, and regime change.
Neocolonialism is the control by a state over another nominally independent state through indirect means. The term neocolonialism was first used after World War II to refer to the continuing dependence of former colonies on foreign countries, but its meaning soon broadened to apply, more generally, to places where the power of developed countries was used to produce a colonial-like exploitation.

Walter Lippmann was an American writer, reporter, and political commentator. With a career spanning 60 years, he is famous for being among the first to introduce the concept of the Cold War, coining the term "stereotype" in the modern psychological meaning, as well as critiquing media and democracy in his newspaper column and several books, most notably his 1922 Public Opinion.
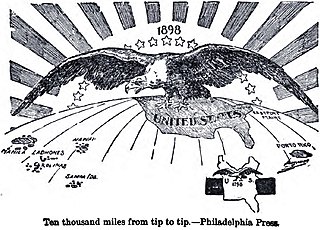
American imperialism is the expansion of American political, economic, cultural, media, and military influence beyond the boundaries of the United States of America. Depending on the commentator, it may include imperialism through outright military conquest; military protection; gunboat diplomacy; unequal treaties; subsidization of preferred factions; regime change; economic or diplomatic support; or economic penetration through private companies, potentially followed by diplomatic or forceful intervention when those interests are threatened.
The Kirkpatrick Doctrine was the doctrine expounded by United States Ambassador to the United Nations Jeane Kirkpatrick in the early 1980s based on her 1979 essay, "Dictatorships and Double Standards". The doctrine was used to justify the U.S. foreign policy of supporting Third World anti-communist dictatorships during the Cold War.

American exceptionalism is the belief that the United States is either distinctive, unique, or exemplary compared to other nations. Proponents argue that the values, political system, and historical development of the U.S. are unique in human history, often with the implication that it is both destined and entitled to play a distinct and positive role on the world stage.
United States Objectives and Programs for National Security, better known as NSC 68, was a 66-page top secret U.S. National Security Council (NSC) policy paper drafted by the Department of State and Department of Defense and presented to President Harry S. Truman on 7 April 1950. It was one of the most important American policy statements of the Cold War. In the words of scholar Ernest R. May, NSC 68 "provided the blueprint for the militarization of the Cold War from 1950 to the collapse of the Soviet Union at the beginning of the 1990s." NSC 68 and its subsequent amplifications advocated a large expansion in the military budget of the United States, the development of a hydrogen bomb, and increased military aid to allies of the United States. It made the rollback of global Communist expansion a high priority and rejected the alternative policies of détente and containment of the Soviet Union.

Hegemony or Survival: America's Quest for Global Dominance is a book about the United States and its foreign policy written by American political activist and linguist Noam Chomsky. It was first published in the United States in November 2003 by Metropolitan Books and then in the United Kingdom by Penguin Books. It was republished by Haymarket Books in January 2024.

Wolfowitz Doctrine is an unofficial name given to the initial version of the Defense Planning Guidance for the 1994–1999 fiscal years published by U.S. Under Secretary of Defense for Policy Paul Wolfowitz and his deputy Scooter Libby. Not intended for public release, it was leaked to the New York Times on March 7, 1992, and sparked a public controversy about U.S. foreign and defense policy. The document was widely criticized as imperialist, as the document outlined a policy of unilateralism and pre-emptive military action to suppress potential threats from other nations and prevent dictatorships from rising to superpower status.

Noam Chomsky is an intellectual, political activist, and critic of the foreign policy of the United States and other governments. Noam Chomsky describes himself as an anarcho-syndicalist and libertarian socialist, and is considered to be a key intellectual figure within the left wing of politics of the United States.

The Anti-Chomsky Reader is a 2004 anthology book about the linguist and social critic Noam Chomsky edited by Peter Collier and David Horowitz. Its contributors criticize Chomsky's political and linguistic writings, claiming that he cherry-picks facts to fit his theories.

Liberal democracy, western-style democracy, or substantive democracy is a form of government that combines the organization of a representative democracy with ideas of liberal political philosophy.
Several scholars have accused the United States of involvement in state terrorism. They have written about the US and other liberal democracies' use of state terrorism, particularly in relation to the Cold War. According to them, state terrorism is used to protect the interest of capitalist elites, and the U.S. organized a neo-colonial system of client states, co-operating with regional elites to rule through terror.
Inverted totalitarianism is a system where economic powers like corporations exert subtle but substantial power over a system that superficially seems democratic. Over time, this theory predicts a sense of powerlessness and political apathy, continuing a slide away from political egalitarianism.

Imperial Ambitions: Conversations with Noam Chomsky on the Post-9/11 World is a 2005 Metropolitan Books American Empire Project publication of interviews with American linguist and political activist Noam Chomsky conducted and edited by award-winning journalist David Barsamian of Alternative Radio.
The American Empire Project is a book series that deals with imperialist and exceptionalist tendencies in US foreign policy in the early 21st century. The series is published by Metropolitan Books and includes contributions by such notable American thinkers and authors as Noam Chomsky, Howard Zinn, Chalmers Johnson and Andrew Bacevich. The project's goal is to critique what the authors consider the imperial ambitions of the United States and to explore viable alternatives for foreign policy.

Democracy promotion by the United States aims to encourage governmental and non-governmental actors to pursue political reforms that will lead ultimately to democratic governance.

Occupy is a short study of the Occupy movement written by the American academic and political activist Noam Chomsky. Initially published in the United States by the Zuccotti Park Press as the first title in their Occupied Media Pamphlet Series in 2012, it was subsequently republished in the United Kingdom by Penguin Books later that year.














